A descriptive text vividly captures the sensory details and emotions of a scene, person, or object to create a clear mental image for the reader. Using rich adjectives and precise language, it helps Your imagination to fully experience the moment being described. Explore the rest of the article to master the art of writing compelling descriptive passages.
Table of Comparison
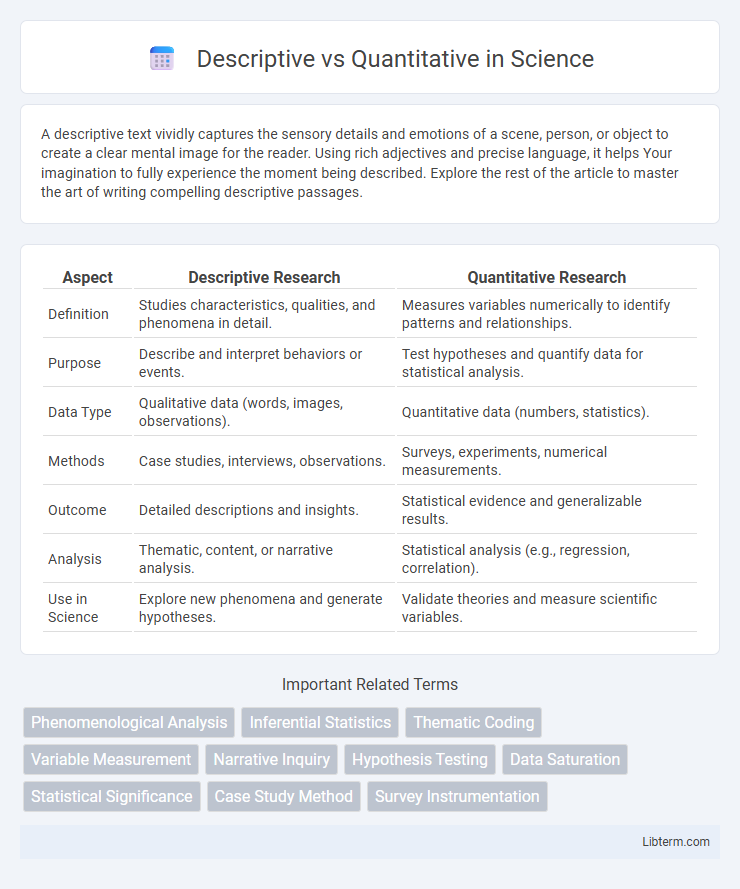
| Aspect | Descriptive Research | Quantitative Research |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Studies characteristics, qualities, and phenomena in detail. | Measures variables numerically to identify patterns and relationships. |
| Purpose | Describe and interpret behaviors or events. | Test hypotheses and quantify data for statistical analysis. |
| Data Type | Qualitative data (words, images, observations). | Quantitative data (numbers, statistics). |
| Methods | Case studies, interviews, observations. | Surveys, experiments, numerical measurements. |
| Outcome | Detailed descriptions and insights. | Statistical evidence and generalizable results. |
| Analysis | Thematic, content, or narrative analysis. | Statistical analysis (e.g., regression, correlation). |
| Use in Science | Explore new phenomena and generate hypotheses. | Validate theories and measure scientific variables. |
Understanding Descriptive Research
Descriptive research focuses on systematically collecting detailed information to accurately characterize phenomena, behaviors, or conditions without manipulating variables. It provides foundational insights by summarizing data through measures such as frequencies, means, and percentages, which help identify patterns and trends in qualitative or quantitative contexts. This type of research is essential for understanding the current status of a subject before conducting further experimental or correlational studies.
Defining Quantitative Research
Quantitative research involves the systematic collection and analysis of numerical data to identify patterns, test hypotheses, and make predictions. It emphasizes measurable variables and statistical techniques to ensure objectivity and replicability in results. This method contrasts with descriptive research, which primarily focuses on detailed, qualitative accounts without rigorous quantification.
Key Differences Between Descriptive and Quantitative Approaches
Descriptive research focuses on summarizing and interpreting data to identify patterns, trends, and characteristics without relying on numerical measurement. Quantitative research emphasizes numerical data collection and statistical analysis to test hypotheses and establish relationships between variables. The key difference lies in descriptive methods providing qualitative insights, whereas quantitative approaches deliver precise, measurable, and generalizable results.
Objectives of Descriptive Research
Descriptive research aims to systematically capture and illustrate characteristics, behaviors, or phenomena within a specific population or context without manipulating variables. It prioritizes objectives such as identifying patterns, measuring frequencies, and detailing the attributes of subjects to provide a comprehensive snapshot of the studied situation. Unlike quantitative research, which seeks to test hypotheses through numerical analysis, descriptive research focuses on observation and precise documentation to inform further inquiry.
Purpose of Quantitative Research
Quantitative research aims to quantify data and uncover patterns through statistical analysis, enabling researchers to test hypotheses and generalize findings to larger populations. It focuses on measuring variables numerically, often using surveys, experiments, or secondary data, to establish relationships and causality. This method provides objective evidence that supports data-driven decision-making in various fields like healthcare, marketing, and social sciences.
Data Collection Methods: Descriptive vs Quantitative
Descriptive data collection methods often involve observations, interviews, and surveys aimed at capturing detailed, qualitative insights about characteristics or behaviors. Quantitative data collection relies on structured instruments like questionnaires, experiments, and numerical measurements to gather quantifiable data for statistical analysis. Both approaches employ distinct tools tailored to their objectives: descriptive methods emphasize context and depth, while quantitative methods prioritize precision and numerical validation.
Data Analysis Techniques Compared
Descriptive data analysis techniques focus on summarizing and organizing data through measures such as mean, median, mode, and standard deviation to reveal patterns and trends. Quantitative data analysis employs statistical methods like hypothesis testing, regression analysis, and inferential statistics to draw conclusions from numerical data and make predictions. Both techniques serve distinct purposes; descriptive analysis provides a clear overview of data characteristics while quantitative analysis facilitates deeper insights through mathematical modeling and validation.
Examples of Descriptive Research Studies
Descriptive research studies often include case studies, observational research, and surveys that detail characteristics of a population or phenomenon without manipulating variables. Examples include surveys measuring consumer satisfaction, observational studies of classroom behavior, and case studies documenting patient experiences with a new treatment. These studies provide qualitative insights and detailed descriptions, focusing on "what" rather than "why" or "how much," distinguishing them from quantitative research that emphasizes numerical measurement and statistical analysis.
Examples of Quantitative Research Studies
Quantitative research studies employ numerical data and statistical methods to quantify variables and identify patterns, such as surveys measuring customer satisfaction with Likert scale responses or experiments analyzing the effects of different drug dosages on blood pressure. Epidemiological studies tracking disease incidence rates across populations and randomized controlled trials assessing treatment effectiveness represent common examples of quantitative research. These studies emphasize objectivity, replication, and generalizability by utilizing large sample sizes, standardized measurements, and statistical analysis software like SPSS or R.
Choosing the Right Approach for Your Study
Choosing the right approach for your study depends on the research goals and data type; descriptive research provides detailed insights by summarizing characteristics of a dataset, ideal for understanding patterns and trends. Quantitative research employs statistical methods to test hypotheses and measure variables numerically, suitable for establishing relationships and generalizing findings. Evaluating whether the focus is on in-depth exploration or precise measurement guides the decision between descriptive and quantitative methodologies.
Descriptive Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com