In ovo technology revolutionizes poultry incubation by injecting nutrients or vaccines into eggs, enhancing embryo development and hatchling health. This innovative approach reduces the need for antibiotics and improves overall flock performance, leading to increased productivity and sustainability in the poultry industry. Discover more about how in ovo techniques can transform your poultry operations in the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
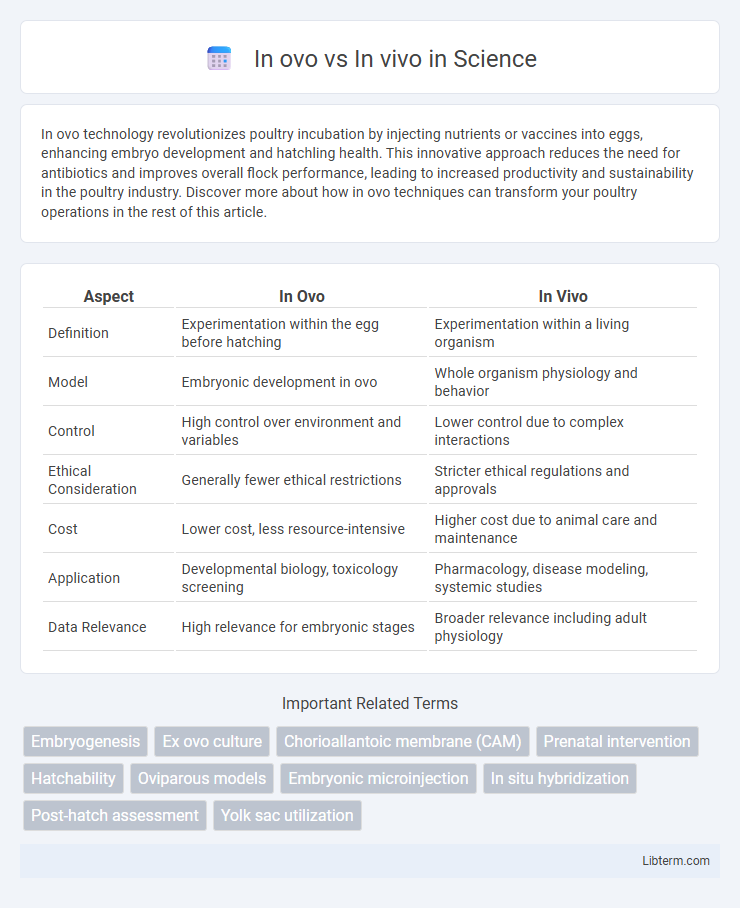
| Aspect | In Ovo | In Vivo |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Experimentation within the egg before hatching | Experimentation within a living organism |
| Model | Embryonic development in ovo | Whole organism physiology and behavior |
| Control | High control over environment and variables | Lower control due to complex interactions |
| Ethical Consideration | Generally fewer ethical restrictions | Stricter ethical regulations and approvals |
| Cost | Lower cost, less resource-intensive | Higher cost due to animal care and maintenance |
| Application | Developmental biology, toxicology screening | Pharmacology, disease modeling, systemic studies |
| Data Relevance | High relevance for embryonic stages | Broader relevance including adult physiology |
Introduction to In Ovo and In Vivo Methods
In ovo methods involve manipulating or studying embryos within the eggshell before hatching, providing a controlled environment for developmental biology and vaccine research. In vivo methods refer to experiments conducted on living organisms, allowing observation of physiological responses and systemic effects in real-time. Both approaches offer unique advantages for biomedical research, with in ovo serving as an intermediate model between in vitro and in vivo systems.
Defining In Ovo Techniques
In ovo techniques involve the manipulation and study of developing embryos within fertilized eggs, providing a controlled environment for biological and genetic research without the complexities of a living organism. These methods allow precise observation and intervention at early developmental stages, which is essential for vaccine development, gene editing, and embryotoxicity testing. Compared to in vivo studies, in ovo approaches reduce ethical concerns and enable high-throughput screening with lower resource requirements.
Understanding In Vivo Approaches
In vivo approaches involve studying biological processes within living organisms, offering a comprehensive understanding of systemic interactions, tissue-specific responses, and physiological relevance that in ovo models cannot fully replicate. These methods allow for real-time observation of complex mechanisms such as pharmacokinetics, immune responses, and disease progression in mammals. In vivo studies are essential for evaluating drug efficacy and safety, as well as understanding genetic and cellular functions in the context of an intact organism.
Key Differences Between In Ovo and In Vivo
In ovo refers to experiments or procedures conducted within the egg, typically involving the developing embryo, while in vivo pertains to studies performed inside a living organism. In ovo techniques offer a controlled environment for observing embryonic development and testing drug responses without systemic variability present in in vivo models. In vivo studies provide comprehensive insights into whole-organism physiological processes, immune responses, and complex interactions, essential for translational research and therapeutic evaluation.
Advantages of In Ovo Applications
In ovo applications provide precise control over embryonic development, leading to enhanced targeted delivery of vaccines, nutrients, and bioactive compounds, which reduces disease susceptibility and improves poultry performance. This method allows for early intervention without the stress associated with handling live animals, thereby improving animal welfare and hatchability rates. Furthermore, in ovo techniques enable high-throughput processing and scalability, optimizing production efficiency in commercial poultry operations.
Benefits of In Vivo Studies
In vivo studies offer precise insights into complex biological interactions within living organisms, enabling researchers to observe systemic responses that in ovo models may not replicate. These studies provide crucial data on pharmacokinetics, toxicity, and long-term effects essential for drug development and disease progression analysis. In vivo experiments ensure translational relevance, improving the predictability of human clinical outcomes compared to in ovo investigations.
Limitations of In Ovo Methods
In ovo methods face limitations such as a restricted ability to mimic complex biological interactions compared to in vivo models, resulting in less accurate representation of whole-organism physiology. The embryonic environment in in ovo assays often restricts long-term studies due to developmental stage constraints and ethical concerns regarding embryo viability. Moreover, variations in egg quality and incubation conditions can introduce inconsistencies, challenging reproducibility and scalability in experimental results.
Challenges in In Vivo Research
In vivo research faces challenges such as ethical concerns, high costs, and complex regulatory requirements, which limit the use of live animals in experiments. Variability in biological responses among individual animals complicates reproducibility and data interpretation. Furthermore, maintaining physiological conditions and ensuring animal welfare during prolonged studies present significant logistical difficulties.
Comparative Outcomes and Efficacy
In ovo and in vivo methods exhibit distinct comparative outcomes and efficacy profiles in biological research and agricultural applications. In ovo techniques enable earlier intervention with precise control over embryonic development, resulting in higher survival rates and consistent phenotypic traits compared to traditional in vivo experiments. However, in vivo approaches provide comprehensive systemic responses and long-term physiological effects, offering robust data for complex organismal studies.
Future Perspectives in In Ovo and In Vivo Research
Future perspectives in in ovo research emphasize advancements in embryonic gene editing and vaccine delivery, aiming to enhance poultry health and productivity with reduced environmental impact. In vivo studies are expected to leverage precision medicine techniques and real-time monitoring technologies to improve disease modeling and therapeutic interventions in humans and animals. Integrating omics data and artificial intelligence will drive innovative approaches in both in ovo and in vivo research, accelerating the development of personalized treatments and sustainable agricultural practices.
In ovo Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com