Changing your environment can significantly impact your mindset and productivity by fostering new perspectives and inspiring creativity. Small adjustments in your daily routine or workspace contribute to increased motivation and personal growth. Explore the rest of this article to discover practical strategies for effectively embracing change in your life.
Table of Comparison
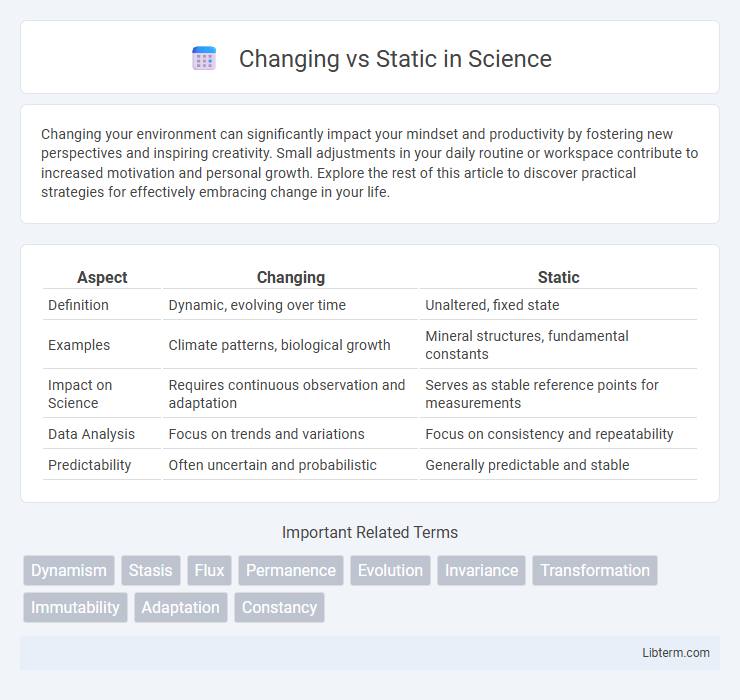
| Aspect | Changing | Static |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Dynamic, evolving over time | Unaltered, fixed state |
| Examples | Climate patterns, biological growth | Mineral structures, fundamental constants |
| Impact on Science | Requires continuous observation and adaptation | Serves as stable reference points for measurements |
| Data Analysis | Focus on trends and variations | Focus on consistency and repeatability |
| Predictability | Often uncertain and probabilistic | Generally predictable and stable |
Understanding Changing vs Static Concepts
Understanding changing versus static concepts involves recognizing the dynamic nature of elements that evolve over time compared to those that remain constant. Changing concepts, such as market trends or user behaviors, require continuous analysis and adaptation to maintain relevance and effectiveness. Static concepts, like foundational principles or fixed data points, provide stable reference frameworks essential for consistency and long-term planning.
Key Differences Between Changing and Static
Changing data refers to information that evolves over time, such as dynamic variables or real-time analytics, while static data remains constant, like archived records or fixed reference points. The key differences lie in data volatility, update frequency, and application use cases, with changing data requiring continuous monitoring and static data serving as stable benchmarks. Understanding these distinctions is crucial for effective database management and decision-making processes in dynamic environments.
The Importance of Change in Modern Systems
Modern systems thrive on adaptability, where dynamic change drives innovation and resilience against evolving challenges. Static systems often face obsolescence due to inflexible structures that cannot accommodate emerging technologies or shifting user demands. Embracing change enhances system performance, scalability, and long-term sustainability in competitive environments.
When Is Static the Best Choice?
Static content is the best choice when information remains consistent over time, such as product descriptions, company bios, or legal notices, ensuring fast load times and better SEO due to stable URLs and predictable structure. Websites with limited updates benefit from static pages because they require minimal server resources and reduce the risk of errors from frequent changes. For businesses prioritizing reliability and performance, static content delivers a seamless user experience without the complexity of dynamic content management.
Examples of Changing Systems in Everyday Life
Changing systems in everyday life include ecosystems, weather patterns, and human bodies, all exhibiting continuous adaptation and transformation. Traffic flow fluctuates based on time and conditions, while stock markets respond dynamically to economic news and investor behavior. These systems illustrate constant evolution driven by internal and external influences, contrasting sharply with static systems where variables remain constant.
Applications of Static Structures
Static structures are widely used in civil engineering for buildings, bridges, and dams due to their ability to efficiently support fixed loads without deformation. These structures provide stability and durability, ensuring safety under constant forces such as gravity and static pressure. Applications include residential constructions, commercial skyscrapers, and retaining walls where load conditions remain unchanged over time.
Pros and Cons of Changing Approaches
Changing approaches offer flexibility, enabling adaptation to new information and evolving environments, which can lead to innovative solutions and improved outcomes. However, frequent changes may cause inconsistency, decreased team alignment, and confusion, potentially hindering long-term progress. Static approaches provide stability and predictability, making processes easier to manage but risk becoming outdated and resistant to necessary improvements.
Pros and Cons of Static Approaches
Static approaches offer simplicity and predictability by relying on fixed rules or parameters, which reduce computational overhead and enhance system stability in controlled environments. However, their rigidity limits adaptability to dynamic conditions, often resulting in suboptimal performance when facing unforeseen scenarios or evolving data patterns. While static methods excel in efficiency and ease of implementation, their inability to respond to change hampers scalability and long-term effectiveness.
Choosing Between Changing or Static for Your Needs
Choosing between changing and static options depends on your specific needs and context, with changing solutions offering flexibility and adaptability while static options provide stability and consistency. Dynamic systems excel in environments requiring frequent updates or customization, ensuring responsiveness to evolving demands. In contrast, static configurations are ideal for scenarios prioritizing reliability and predictable performance without the need for constant adjustments.
Future Trends: The Shift from Static to Changing
The future trend in technology and data management emphasizes the transition from static models to dynamic, changing systems that adapt in real-time to evolving information. Emerging AI algorithms and adaptive frameworks enable continuous updates and predictive analytics, fostering more responsive and personalized user experiences. This shift from static datasets to changing, fluid structures is crucial for industries like finance, healthcare, and smart cities to enhance decision-making and operational efficiency.
Changing Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com