Theoretical concepts form the foundation of understanding complex ideas and phenomena across various disciplines. They provide frameworks that guide research, analysis, and practical applications, enhancing the depth and clarity of knowledge. Explore the rest of the article to discover how these theories can enrich your perspective and inform your approach.
Table of Comparison
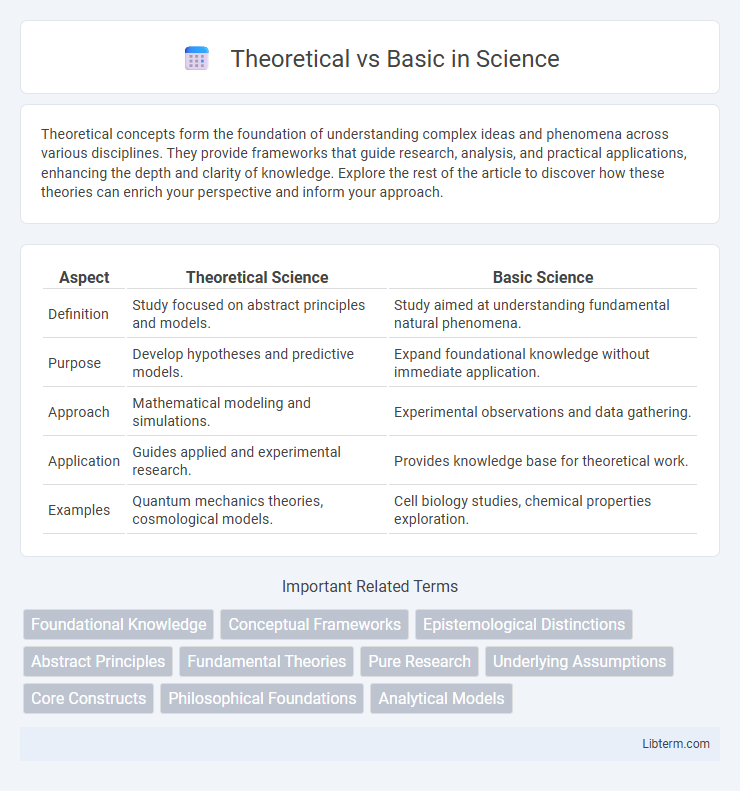
| Aspect | Theoretical Science | Basic Science |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Study focused on abstract principles and models. | Study aimed at understanding fundamental natural phenomena. |
| Purpose | Develop hypotheses and predictive models. | Expand foundational knowledge without immediate application. |
| Approach | Mathematical modeling and simulations. | Experimental observations and data gathering. |
| Application | Guides applied and experimental research. | Provides knowledge base for theoretical work. |
| Examples | Quantum mechanics theories, cosmological models. | Cell biology studies, chemical properties exploration. |
Introduction to Theoretical and Basic Concepts
Theoretical concepts provide a framework for understanding underlying principles and abstract ideas that drive knowledge in a specific field, emphasizing models, hypotheses, and systematic reasoning. Basic concepts introduce foundational information and essential terminologies necessary for grasping the subject's fundamentals, ensuring learners have a clear starting point. Exploring both theoretical and basic concepts enables a comprehensive understanding, bridging abstract theories with practical fundamentals for effective learning and application.
Defining Theoretical and Basic Approaches
Theoretical approaches involve abstract reasoning and conceptual frameworks to explain phenomena, often emphasizing models and hypotheses for deeper understanding. Basic approaches prioritize foundational principles and fundamental knowledge, serving as the groundwork for more complex theories. Understanding both approaches is essential for integrating empirical data with comprehensive theoretical insights.
Historical Evolution of Theoretical vs Basic
The historical evolution of theoretical versus basic research highlights key shifts in scientific inquiry since the early 20th century, with theoretical research focusing on abstract models and fundamental principles while basic research emphasizes experimental validation and foundational knowledge. Seminal figures like Albert Einstein contributed to theoretical frameworks, whereas pioneers such as Louis Pasteur advanced basic research through empirical studies. Over time, the interplay between these approaches has driven technological innovation and expanded understanding across disciplines including physics, biology, and chemistry.
Key Differences Between Theoretical and Basic
Theoretical concepts involve abstract principles and generalized frameworks used to explain phenomena, whereas basic concepts refer to fundamental, practical elements or simple facts. Key differences include the level of abstraction, with theoretical knowledge often requiring complex reasoning and basic knowledge focusing on concrete, foundational information. Theoretical understanding supports hypothesis generation and advanced analysis, while basic knowledge forms the essential building blocks necessary for daily tasks and initial learning.
Applications of Theoretical Methods
Theoretical methods in research provide predictive models and frameworks crucial for understanding complex systems, enabling precise simulation and optimization across fields such as physics, chemistry, and computer science. These methods support the development of advanced algorithms, enhance material design processes, and facilitate innovations in artificial intelligence by leveraging mathematical and computational theories. Basic methods, while foundational and essential for practical experimentation, often lack the depth required for high-level problem-solving that theoretical approaches deliver.
Real-World Impact of Basic Approaches
Basic approaches in various fields emphasize fundamental principles and straightforward methodologies that often yield practical solutions with immediate real-world impact. These approaches prioritize accessibility, scalability, and ease of implementation, enabling wide adoption across industries and communities. Unlike theoretical frameworks, basic methods frequently demonstrate measurable outcomes, driving innovation and improvements in everyday applications such as education, healthcare, and technology.
Advantages and Limitations of Theoretical Frameworks
Theoretical frameworks offer structured guidance for research, enabling clear hypothesis formulation and enhancing the interpretability of complex data through established concepts. Advantages include promoting consistency and enabling comprehensive analysis across diverse studies, while limitations involve potential rigidity and challenges in adapting to novel or interdisciplinary contexts. Dependence on pre-existing theories may restrict innovation and overlook emerging factors outside traditional paradigms.
Practical Benefits of Basic Principles
Basic principles provide foundational knowledge that directly enhances practical skills and problem-solving abilities in real-world scenarios. Theoretical concepts often offer abstract frameworks, while basic principles translate theory into actionable steps that improve efficiency and application. Emphasizing practical benefits, mastering basic principles fosters quicker learning curves and more reliable outcomes across various fields.
Choosing Between Theoretical and Basic Strategies
Choosing between theoretical and basic strategies involves evaluating the complexity and goals of your project. Theoretical strategies prioritize conceptual frameworks and abstract models to predict outcomes, ideal for research-driven environments requiring deep analysis. Basic strategies focus on practical, straightforward solutions emphasizing ease of implementation and immediate results, suitable for operational tasks with limited resources.
Conclusion: Integrating Theoretical and Basic Perspectives
Integrating theoretical and basic perspectives enhances comprehensive understanding by bridging abstract models with fundamental principles. This approach fosters innovation, as theoretical frameworks guide experimental design while basic research validates and refines these models. Combining both perspectives ensures practical applicability and advances knowledge across scientific disciplines.
Theoretical Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com