In silico refers to experiments or processes conducted via computer simulations rather than physical lab work. This method accelerates research by allowing researchers to model complex biological systems and predict outcomes efficiently. Discover how in silico techniques can revolutionize your scientific studies in the rest of this article.
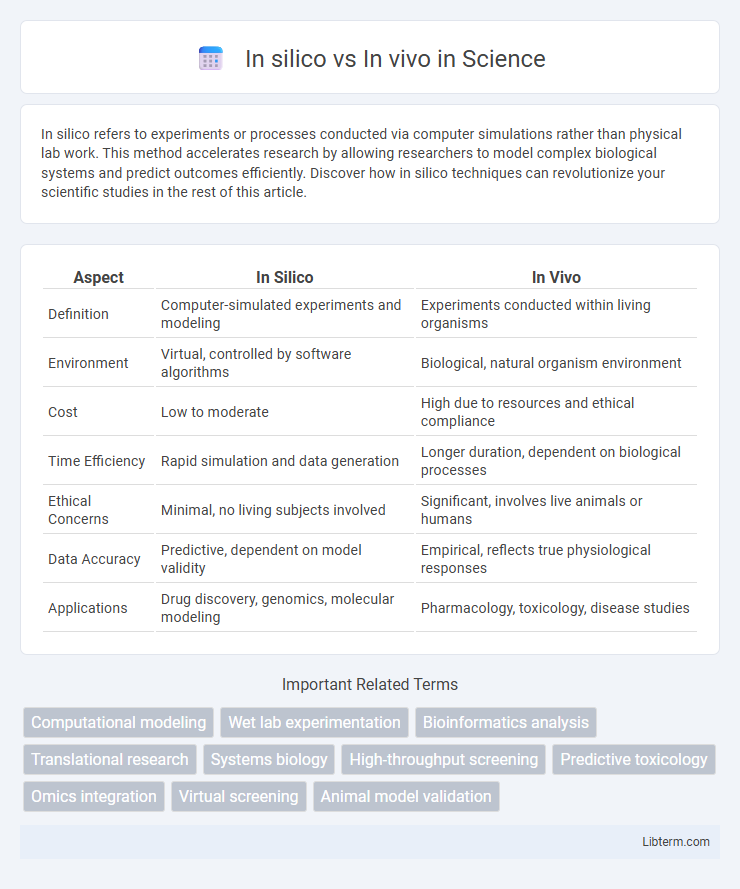
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | In Silico | In Vivo |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Computer-simulated experiments and modeling | Experiments conducted within living organisms |
| Environment | Virtual, controlled by software algorithms | Biological, natural organism environment |
| Cost | Low to moderate | High due to resources and ethical compliance |
| Time Efficiency | Rapid simulation and data generation | Longer duration, dependent on biological processes |
| Ethical Concerns | Minimal, no living subjects involved | Significant, involves live animals or humans |
| Data Accuracy | Predictive, dependent on model validity | Empirical, reflects true physiological responses |
| Applications | Drug discovery, genomics, molecular modeling | Pharmacology, toxicology, disease studies |
Introduction: Defining In Silico and In Vivo
In silico refers to computer-simulated experiments and modeling used to predict biological processes and drug interactions through advanced algorithms and data analysis. In vivo describes experimental studies conducted within living organisms, providing real-time insights into physiological and pathological responses. Both approaches are essential for comprehensive research, with in silico offering rapid hypothesis testing and in vivo delivering empirical validation.
Historical Evolution of Research Methods
In silico research methods emerged in the mid-20th century with the advent of computer technology, revolutionizing drug discovery and molecular biology by enabling complex simulations and data analysis. In contrast, in vivo studies trace back to ancient times with direct experimentation on living organisms, providing foundational insights into physiology and pathology through empirical observation. The historical evolution reflects a transition from exclusive reliance on in vivo experiments toward integration with computational models, enhancing research efficiency and predictive accuracy.
Key Differences Between In Silico and In Vivo
In silico studies utilize computer simulations and computational models to predict biological processes, offering high-throughput analysis and cost-effective experimentation. In vivo experiments involve testing within living organisms, providing comprehensive insight into physiological interactions and real-time biological responses. The key difference lies in the controlled, predictive environment of in silico approaches versus the complex, dynamic conditions found in vivo testing.
Advantages of In Silico Approaches
In silico approaches offer significant advantages such as enabling rapid, cost-effective simulations and data analysis without ethical concerns associated with animal testing. These computational models allow for high-throughput screening of drug candidates, accelerating the drug discovery process and reducing reliance on in vivo experiments. Advanced algorithms and machine learning enhance predictive accuracy, optimizing experimental design before validation in living organisms.
Strengths and Limitations of In Vivo Studies
In vivo studies offer critical insights into biological processes within the complexity of living organisms, enabling observation of systemic effects and interactions not replicable in vitro or in silico. They provide reliable data on pharmacodynamics and pharmacokinetics essential for drug development but are limited by ethical concerns, high costs, and variability due to genetic and environmental differences among test subjects. Despite these challenges, in vivo research remains indispensable for validating hypotheses generated from computational models and in vitro experiments.
Applications of In Silico Methods in Modern Science
In silico methods revolutionize modern science through applications such as drug discovery, genetic analysis, and protein structure prediction, enabling rapid and cost-effective simulations. These computational techniques facilitate the identification of novel drug candidates, optimization of molecular interactions, and modeling of complex biological systems without the ethical concerns of in vivo experiments. High-throughput screening, virtual docking, and bioinformatics harness in silico tools to accelerate biomedical research, significantly reducing the need for animal testing.
The Role of In Vivo Experiments in Drug Development
In vivo experiments play a crucial role in drug development by providing comprehensive insights into the physiological and toxicological effects of candidate compounds within living organisms, which cannot be fully replicated in silico models. These experiments enable the evaluation of pharmacokinetics, bioavailability, and systemic interactions, ensuring drug safety and efficacy before clinical trials. Regulatory agencies often require robust in vivo data to approve progression to human studies, underscoring their indispensable contribution alongside computational methods.
Integrative Approaches: Combining In Silico and In Vivo
Integrative approaches combining in silico and in vivo methods enhance predictive accuracy and experimental validation by leveraging computational models alongside biological experimentation. This synergistic strategy accelerates drug discovery, enabling simulation of complex biological systems in silico followed by targeted in vivo testing to confirm efficacy and safety. Advanced techniques such as molecular docking paired with animal models exemplify this integration, optimizing research efficiency and reducing resource consumption.
Ethical Considerations in Experimental Design
In silico methods offer significant ethical advantages by reducing the need for animal testing, minimizing harm and distress in experimental design. In vivo studies, while providing critical biological insights, raise ethical concerns regarding animal welfare and require strict adherence to guidelines like the 3Rs (Replacement, Reduction, Refinement). Implementing in silico simulations can enhance ethical standards in research by supplementing or replacing in vivo experiments, fostering responsible scientific practices.
Future Trends and Innovations in Biomedical Research
In silico methods harness artificial intelligence and machine learning to accelerate drug discovery, enabling predictive modeling of biological systems with increasing accuracy. Future trends emphasize integration of multi-omics data and digital twin technologies to personalize treatments and reduce reliance on in vivo animal testing. Innovations such as virtual clinical trials and advanced computational simulations are set to revolutionize biomedical research by enhancing efficiency and ethical standards.
In silico Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com