An allele represents one of the different versions of a gene found at a specific position on a chromosome, influencing traits such as eye color or blood type. Your genetic makeup depends on the combination of alleles inherited from both parents, which contributes to individual variation and inherited characteristics. Explore the full article to understand how alleles impact genetics and inheritance patterns.
Table of Comparison
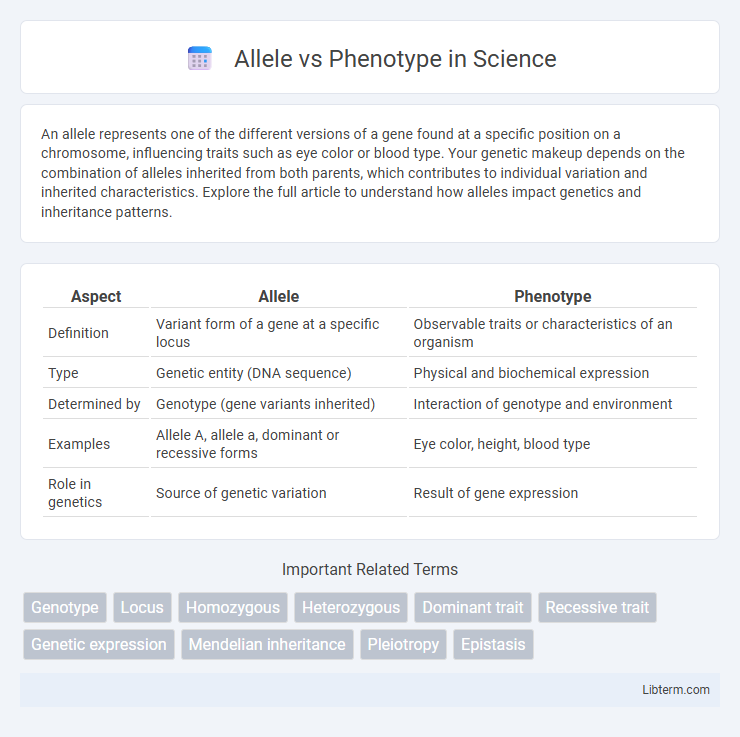
| Aspect | Allele | Phenotype |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Variant form of a gene at a specific locus | Observable traits or characteristics of an organism |
| Type | Genetic entity (DNA sequence) | Physical and biochemical expression |
| Determined by | Genotype (gene variants inherited) | Interaction of genotype and environment |
| Examples | Allele A, allele a, dominant or recessive forms | Eye color, height, blood type |
| Role in genetics | Source of genetic variation | Result of gene expression |
Introduction to Alleles and Phenotypes
Alleles are different versions of a gene located at the same position on homologous chromosomes that influence specific traits in an organism. Phenotypes refer to the observable physical characteristics or traits resulting from the interaction of alleles with the environment. Understanding the relationship between alleles and phenotypes is crucial for studying genetic inheritance and variation in populations.
Defining Alleles: The Genetic Blueprint
Alleles are specific variations of a gene found at the same locus on homologous chromosomes, serving as the fundamental units of genetic inheritance that determine distinct traits. These genetic blueprints encode variations in DNA sequences that influence the development of observable characteristics, known as phenotypes. Understanding the role of alleles is crucial for deciphering how genetic diversity manifests in traits such as eye color, blood type, and susceptibility to certain diseases.
What is a Phenotype? Expression of Traits
Phenotype refers to the observable physical or biochemical characteristics of an organism resulting from the interaction of its genotype and the environment. It encompasses traits such as height, eye color, and enzyme activity, which are expressed based on alleles inherited from parents. The phenotype represents how genetic information is manifested externally, providing a visible or measurable expression of underlying allelic variations.
Relationship Between Alleles and Phenotypes
Alleles are different versions of a gene that influence the expression of specific traits, while phenotypes represent the observable characteristics resulting from these genetic variations. The relationship between alleles and phenotypes is determined by dominant, recessive, codominant, or incomplete dominant inheritance patterns that dictate how traits manifest in an organism. The combination of alleles, or genotype, interacts with environmental factors to produce the final phenotype seen in organisms.
Types of Alleles: Dominant vs Recessive
Dominant alleles express their traits even when only one copy is present, masking the effect of recessive alleles, which require two copies to influence the phenotype. Types of alleles include complete dominance, where the dominant allele fully masks the recessive one, and incomplete dominance, where heterozygous traits blend. Codominance allows both alleles to be fully expressed, each contributing distinctly to the organism's phenotype.
Genotype vs Phenotype: Key Differences
Genotype refers to the genetic makeup of an organism, specifically the combination of alleles inherited from both parents, which determines potential traits. Phenotype represents the observable physical characteristics or traits expressed by the organism, influenced by both genotype and environmental factors. The key difference lies in genotype being the genetic code, while phenotype is the actual manifestation of those genes.
Examples Illustrating Allele-Phenotype Connections
The allele for the ABO blood group system includes A, B, and O variants, where the phenotype expresses as blood types A, B, AB, or O depending on the combination of alleles inherited. In pea plants, the allele for round seeds (R) is dominant over the allele for wrinkled seeds (r), producing corresponding seed shape phenotypes based on genotype combinations (RR or Rr yield round seeds, rr yields wrinkled seeds). Eye color in humans demonstrates multiple alleles influencing phenotypes, such as brown (dominant allele) and blue (recessive allele), where the specific phenotype emerges from the particular allelic combination present.
Environmental Influence on Phenotypes
Alleles provide the genetic blueprint for potential phenotypes, but environmental factors such as temperature, nutrition, and exposure to toxins significantly influence the expression of these traits. Phenotypic traits like skin color, height, and behavior often result from complex interactions between specific alleles and environmental conditions. This dynamic interplay explains why organisms with identical genotypes can exhibit variation in their observable characteristics.
Inheritance Patterns and Their Effects
Alleles are different forms of a gene that determine specific traits and influence inheritance patterns such as dominant, recessive, codominant, and incomplete dominance. Phenotypes result from the expression of alleles, reflecting observable characteristics shaped by genetic combinations and environmental interactions. Understanding allele interactions helps predict phenotypic ratios in offspring, crucial for studying Mendelian and non-Mendelian inheritance effects.
Importance of Understanding Alleles and Phenotypes
Understanding alleles and phenotypes is crucial for predicting genetic traits and inheritance patterns in organisms. Alleles represent variations of a gene that determine specific phenotypic characteristics, making their study vital in fields such as genetics, medicine, and agriculture. Accurate knowledge of allele distribution helps in diagnosing genetic disorders and developing targeted therapies by linking genotype to observable phenotypic traits.
Allele Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com