Lateral movement refers to the technique cyber attackers use to move within a network after gaining initial access, aiming to reach critical systems or data unnoticed. Understanding lateral movement is essential for strengthening your cybersecurity defenses and preventing potential breaches. Explore the rest of the article to learn how to detect and mitigate lateral movement threats effectively.
Table of Comparison
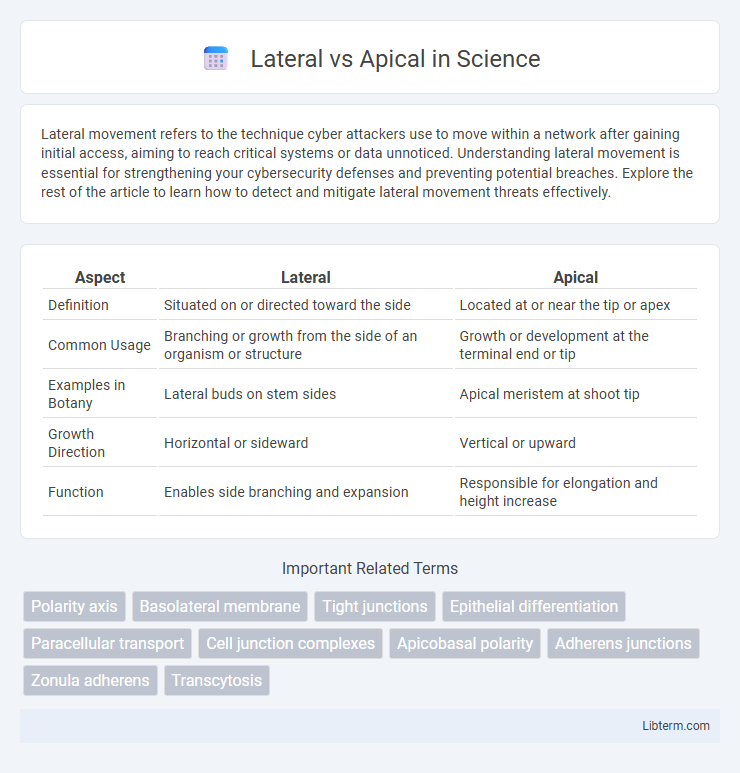
| Aspect | Lateral | Apical |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Situated on or directed toward the side | Located at or near the tip or apex |
| Common Usage | Branching or growth from the side of an organism or structure | Growth or development at the terminal end or tip |
| Examples in Botany | Lateral buds on stem sides | Apical meristem at shoot tip |
| Growth Direction | Horizontal or sideward | Vertical or upward |
| Function | Enables side branching and expansion | Responsible for elongation and height increase |
Introduction to Lateral vs Apical
Lateral and apical refer to distinct anatomical orientations commonly used in biology and medicine to describe positions relative to the body's midline or specific structures. Lateral denotes a position toward the sides or away from the midline, while apical indicates a location at the apex or tip of a structure, such as the heart's apex or a tooth's apex. Understanding these terms is crucial for accurate communication in clinical assessments and anatomical descriptions.
Definition of Lateral and Apical
Lateral refers to a position or direction situated at the side of the body or an organ, away from the midline, often used in anatomy to describe structures located on the outer edges. Apical pertains to the apex or tip of a structure, indicating the highest or most pointed part, commonly referenced in anatomy to specify the top end of an organ such as the heart or the lungs. Understanding the distinction between lateral and apical is crucial for accurately identifying locations and orientations in medical and biological contexts.
Anatomical Contexts: Lateral vs Apical
Lateral refers to structures situated away from the midline of the body, typically on the sides, such as the lateral epicondyle of the humerus or lateral ventricles of the brain. Apical denotes the apex or tip of a structure, often the highest or most distal point, exemplified by the apical lobe of the lung or the apical pulse in cardiology. In anatomical contexts, distinguishing lateral from apical helps in accurate localization and description of organs, tissues, or lesions within the body.
Differences in Cellular Orientation
Lateral cellular orientation refers to cells positioned side-by-side, facilitating intercellular adhesion and communication through structures like tight junctions and desmosomes. Apical orientation denotes the cell surface facing the lumen or external environment, specialized for absorption, secretion, and sensory functions, often featuring microvilli or cilia. These distinct orientations contribute to epithelial tissue polarity, enabling directional transport and selective barrier functions essential for organ physiology.
Functional Implications in Biology
Lateral and apical domains in cells exhibit distinct functional roles critical for tissue organization and signaling. The apical domain typically interfaces with external environments or lumen, facilitating selective absorption, secretion, and cellular communication. In contrast, the lateral domain mediates cell-to-cell adhesion and intercellular communication through specialized junctions like tight junctions and adherens junctions, ensuring cohesive tissue integrity and coordinated cellular responses.
Clinical Significance of Lateral and Apical Distinctions
Lateral and apical distinctions are crucial in clinical diagnosis and treatment planning, particularly in cardiology and dental care. Lateral refers to structures positioned away from the midline, influencing approaches in lateral wall myocardial infarction or lateral tooth root infections, while apical pertains to the tip or apex, affecting conditions like apical periodontitis or apical ballooning syndrome. Understanding these spatial differences guides targeted interventions, imaging techniques, and prognosis assessment, optimizing patient outcomes.
Examples in Histology and Anatomy
Lateral and apical terms describe spatial orientation in histology and anatomy, where apical refers to the tip or summit of a structure, such as the apical surface of epithelial cells facing the lumen in the intestine. Lateral denotes the sides, as seen in lateral cell membranes that interact with adjacent cells via tight junctions in epithelial tissues. For example, in kidney histology, the apical surface of proximal tubule cells contains microvilli for absorption, while lateral surfaces form junctions maintaining tissue integrity.
Relevance in Medical Imaging
Lateral and apical views in medical imaging provide distinct anatomical perspectives crucial for accurate diagnosis, especially in cardiac and pulmonary assessments. The lateral view offers a side angle, enhancing visualization of structures obscured in frontal images, while the apical view targets the apex of organs like the heart, revealing detailed morphology essential for detecting abnormalities. Understanding the relevance of these views ensures comprehensive evaluation and precise clinical decision-making in imaging studies.
Common Misconceptions
Lateral and apical are commonly confused terms describing root canal anatomy but refer to different canal positions; lateral canals extend horizontally from the main root canal, while apical canals are located at the root tip. A frequent misconception is that treatment of the apical canal alone resolves infection, overlooking the importance of cleaning lateral canals, which can harbor bacteria. Effective endodontic therapy requires recognizing both canal types to ensure comprehensive decontamination and prevent treatment failure.
Summary and Conclusion
Lateral roots emerge from the sides of existing roots and primarily enhance the root system's surface area for water and nutrient absorption, while apical roots grow from the root tip, facilitating depth penetration into the soil for accessing deeper resources. Understanding the distinction between lateral and apical roots is crucial for optimizing plant growth strategies and improving soil resource utilization. Efficient root development combines both lateral expansion and apical elongation to maximize overall plant stability and nutrient uptake.
Lateral Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com