Analytical skills enable you to break down complex information and identify patterns efficiently, improving decision-making and problem-solving abilities. Mastering these skills empowers you to approach challenges with a clear, logical framework that enhances productivity and accuracy. Dive into the rest of the article to discover techniques to sharpen your analytical thinking and boost your professional success.
Table of Comparison
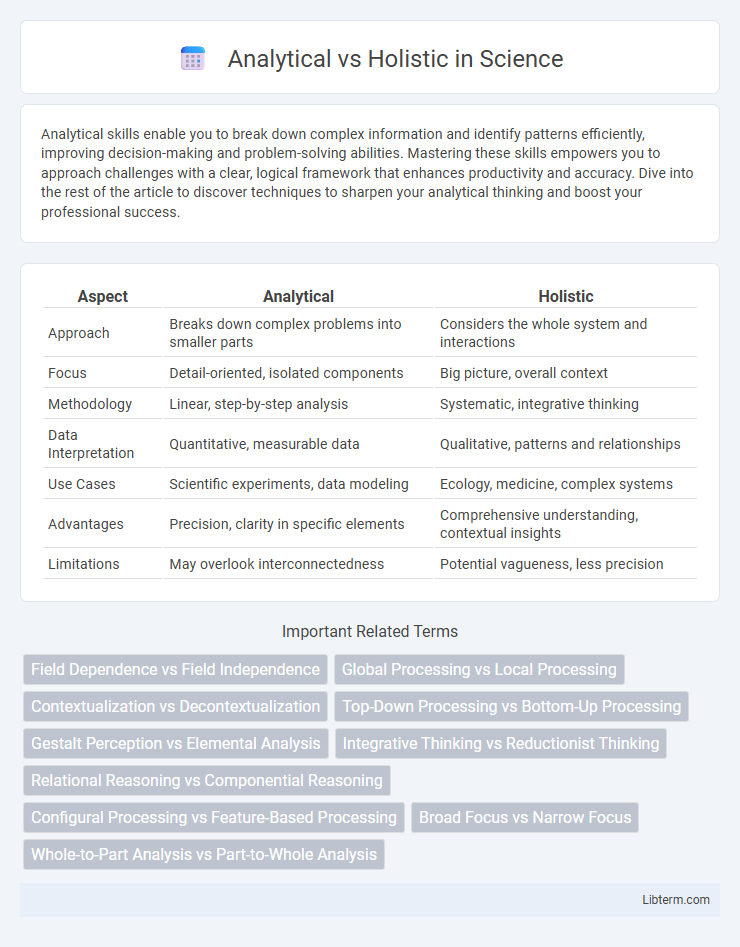
| Aspect | Analytical | Holistic |
|---|---|---|
| Approach | Breaks down complex problems into smaller parts | Considers the whole system and interactions |
| Focus | Detail-oriented, isolated components | Big picture, overall context |
| Methodology | Linear, step-by-step analysis | Systematic, integrative thinking |
| Data Interpretation | Quantitative, measurable data | Qualitative, patterns and relationships |
| Use Cases | Scientific experiments, data modeling | Ecology, medicine, complex systems |
| Advantages | Precision, clarity in specific elements | Comprehensive understanding, contextual insights |
| Limitations | May overlook interconnectedness | Potential vagueness, less precision |
Introduction to Analytical and Holistic Thinking
Analytical thinking involves breaking down complex information into smaller parts to understand relationships and causes, prioritizing logical reasoning and detailed examination. Holistic thinking considers the whole system, emphasizing context, patterns, and interconnectedness to capture a broader perspective. Both approaches are essential in decision-making, with analytical thinking excelling in problem-solving tasks and holistic thinking enhancing strategic planning.
Defining Analytical Thinking
Analytical thinking involves breaking down complex information into smaller, manageable parts to systematically evaluate and solve problems. It relies on data-driven reasoning, logical steps, and objective evaluation of evidence to reach conclusions. This cognitive process prioritizes detailed analysis and methodical approaches over intuition or broader context.
Defining Holistic Thinking
Holistic thinking involves understanding systems by examining the relationships and patterns among all components rather than isolating individual parts. It emphasizes context, interconnectedness, and the bigger picture to comprehend complex phenomena. This approach contrasts with analytical thinking, which breaks down information into smaller, manageable units for detailed examination.
Key Differences Between Analytical and Holistic Approaches
Analytical approaches break down complex problems into smaller, manageable components, emphasizing detailed examination and logical reasoning. Holistic approaches consider the entire system and its interconnections, prioritizing the integration of all elements to understand the bigger picture. Key differences lie in the focus on parts versus wholes, linear analysis versus systemic thinking, and detail-oriented scrutiny versus context-driven insight.
Advantages of Analytical Thinking
Analytical thinking enhances problem-solving by breaking complex issues into manageable parts, allowing for precise evaluation and data-driven decisions. This method supports systematic reasoning, which improves accuracy and consistency in identifying solutions. Utilizing structured frameworks, analytical thinking reduces cognitive biases and enhances clarity in both individual and team decision-making processes.
Advantages of Holistic Thinking
Holistic thinking offers the advantage of understanding complex systems by considering the interconnections and relationships among components, leading to more integrated and sustainable solutions. It promotes innovation by encouraging the synthesis of diverse perspectives and recognizing patterns that may be overlooked by analytical methods. This approach enhances adaptability in dynamic environments by fostering a comprehensive view of challenges and opportunities.
Real-World Applications of Analytical vs Holistic Approaches
Analytical approaches excel in data-driven fields like finance and engineering, where precise, step-by-step problem solving and decomposition of complex problems into simpler parts are critical. Holistic approaches dominate healthcare and environmental management, emphasizing interconnectedness and entire systems to address multifaceted challenges and foster sustainable solutions. Combining both methods enhances decision-making in business strategy by balancing detailed analysis with big-picture perspectives.
Challenges and Limitations of Each Approach
Analytical approaches often face challenges related to fragmentation, as breaking down complex problems into smaller parts can overlook interconnected factors and emergent properties. Holistic methods struggle with limitations in scalability and precision, making it difficult to quantify or isolate specific variables within complex systems. Both approaches require careful integration to balance depth of analysis with broader contextual understanding, ensuring comprehensive problem-solving without oversimplification or excessive generalization.
When to Use Analytical or Holistic Methods
Analytical methods excel in situations requiring detailed examination of complex problems, such as data analysis, financial forecasting, or scientific experiments, where breaking down components is crucial for accuracy. Holistic methods are best used in contexts involving human behavior, organizational development, or systems thinking, where understanding the interplay of factors and the bigger picture guides effective decision-making. Choosing between analytical and holistic approaches depends on the specific goals, complexity of the problem, and whether precision or integrative understanding is prioritized.
Integrating Analytical and Holistic Perspectives
Integrating analytical and holistic perspectives enhances decision-making by combining detailed data analysis with a comprehensive view of systems and contexts. Analytical approaches break down complex problems into smaller, manageable components, while holistic methods consider the interconnections and overall impact of these components within the broader environment. This integration fosters balanced solutions that leverage quantitative insights and qualitative understanding, driving more effective strategies in business, healthcare, and environmental management.
Analytical Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com