Radical ideas challenge established norms and inspire profound change by questioning traditional viewpoints and encouraging innovative thinking. Embracing radical perspectives can lead to breakthrough solutions in various fields, from technology to social reform. Discover how exploring radical concepts can transform your understanding by reading the rest of the article.
Table of Comparison
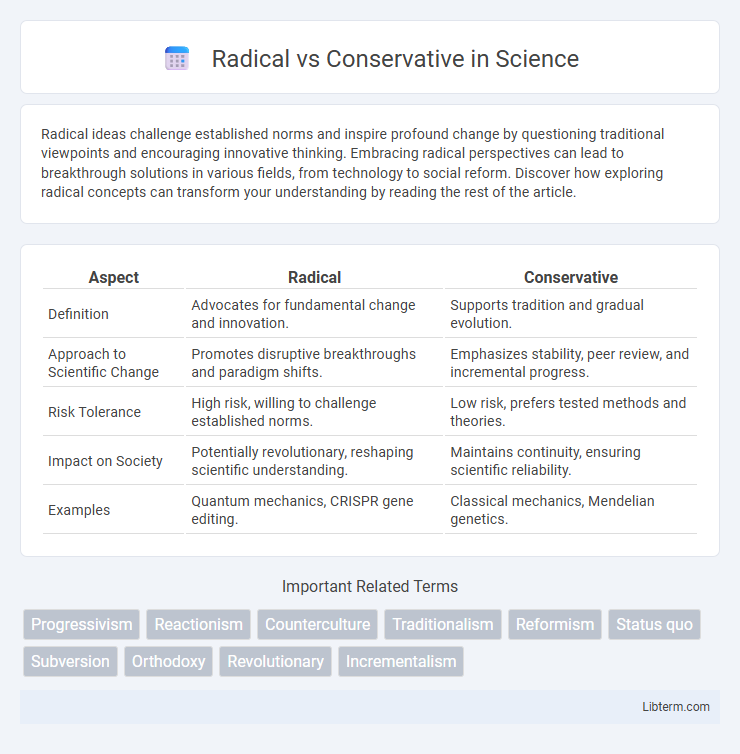
| Aspect | Radical | Conservative |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Advocates for fundamental change and innovation. | Supports tradition and gradual evolution. |
| Approach to Scientific Change | Promotes disruptive breakthroughs and paradigm shifts. | Emphasizes stability, peer review, and incremental progress. |
| Risk Tolerance | High risk, willing to challenge established norms. | Low risk, prefers tested methods and theories. |
| Impact on Society | Potentially revolutionary, reshaping scientific understanding. | Maintains continuity, ensuring scientific reliability. |
| Examples | Quantum mechanics, CRISPR gene editing. | Classical mechanics, Mendelian genetics. |
Introduction: Defining Radical and Conservative
Radical and conservative represent two distinct political ideologies characterized by their approaches to social change and tradition. Radicals advocate for fundamental, often revolutionary reforms to achieve systemic transformation, emphasizing progress and innovation. Conservatives prioritize preserving established institutions and values, favoring gradual evolution over drastic shifts to maintain social stability.
Historical Origins of Radicalism and Conservatism
Radicalism emerged in the late 18th and early 19th centuries, rooted in Enlightenment ideals advocating for extensive social, political, and economic reforms, challenging traditional hierarchies and established authority. Conservatism originated as a reaction to the French Revolution, championing the preservation of established institutions, social stability, and continuity, emphasizing tradition and gradual change over abrupt transformation. Key historical figures like Edmund Burke embodied conservatism's defense of inherited rights, while radicals often aligned with revolutionary leaders seeking to overhaul existing systems.
Core Principles: What Radicals Believe
Radicals fundamentally believe in profound societal transformation to address systemic inequality and injustice, advocating for revolutionary changes rather than incremental reforms. They prioritize dismantling existing power structures and institutions perceived as oppressive, seeking to create a more equitable and inclusive social order. Radical ideology often emphasizes grassroots activism, direct action, and the redistribution of wealth and resources to achieve fundamental social justice.
Core Principles: What Conservatives Believe
Conservatives prioritize tradition, limited government, and individual responsibility as core principles guiding political and social policies. They emphasize preserving established institutions, free-market capitalism, and personal liberties while advocating for gradual change rather than radical reform. The belief in strong national defense and traditional family values also shapes conservative ideology.
Key Differences Between Radical and Conservative Ideologies
Radical ideologies advocate for rapid, fundamental changes to social, political, or economic systems, often challenging existing institutions and norms, while conservative ideologies emphasize preserving traditional values, institutions, and gradual evolution over sudden shifts. Radicals support transformative reforms aimed at achieving equality and restructuring power dynamics, whereas conservatives prioritize stability, order, and continuity, resisting abrupt alterations that might disrupt societal cohesion. The core difference lies in radicals seeking systemic overhaul to address perceived injustices, contrasted with conservatives aiming to maintain established structures and cautious adaptation.
Radical vs Conservative in Politics and Governance
Radical politics advocates for profound and immediate transformations in social, economic, or political structures, often challenging existing norms and power dynamics to achieve systemic change. Conservative politics emphasizes preserving traditional institutions, values, and gradual reform, prioritizing stability, order, and continuity within governance. In governance, radicals push for revolutionary policies to address inequality and injustice, while conservatives promote incremental adjustments to maintain social cohesion and established hierarchies.
Social and Cultural Perspectives
Radical social perspectives advocate for profound transformation of cultural norms and institutions to achieve equality and justice, often challenging traditional values and mainstream ideologies. Conservative social views emphasize preserving established customs, cultural heritage, and social order, prioritizing continuity and gradual change over abrupt shifts. The cultural divide between radical and conservative positions frequently centers on issues like civil rights, gender roles, and multiculturalism, reflecting deep ideological differences about societal progression.
Economic Approaches: Radical vs Conservative Solutions
Radical economic approaches prioritize systemic change through wealth redistribution, government intervention, and dismantling established financial structures to achieve equity. Conservative economic solutions emphasize market-driven growth, limited government interference, and fiscal responsibility to maintain stability and encourage entrepreneurship. These contrasting strategies reflect differing views on addressing inequality, economic efficiency, and the role of state intervention in the economy.
Notable Figures: Radicals and Conservatives Through History
Radical figures such as Thomas Paine and Che Guevara championed profound social and political transformations, advocating for systemic change and revolution. Conservative icons like Edmund Burke and Ronald Reagan emphasized tradition, stability, and gradual reform to preserve established institutions and societal order. These notable individuals shaped ideological foundations that continue to influence political discourse and movements worldwide.
Conclusion: The Impact of Radical and Conservative Thought
Radical thought drives transformative social and political change by challenging existing norms and advocating for rapid reforms, often reshaping societal structures fundamentally. Conservative thought emphasizes preservation of tradition and gradual evolution, promoting stability and continuity within established institutions. The interplay between these ideologies shapes policy development, cultural dynamics, and governance models across diverse societies.
Radical Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com