Strict management enforces clear rules and consistent consequences to maintain order and achieve goals effectively. This approach emphasizes discipline, accountability, and precision in execution to minimize errors and maximize productivity. Discover how adopting a strict management style can transform your team's performance in the full article.
Table of Comparison
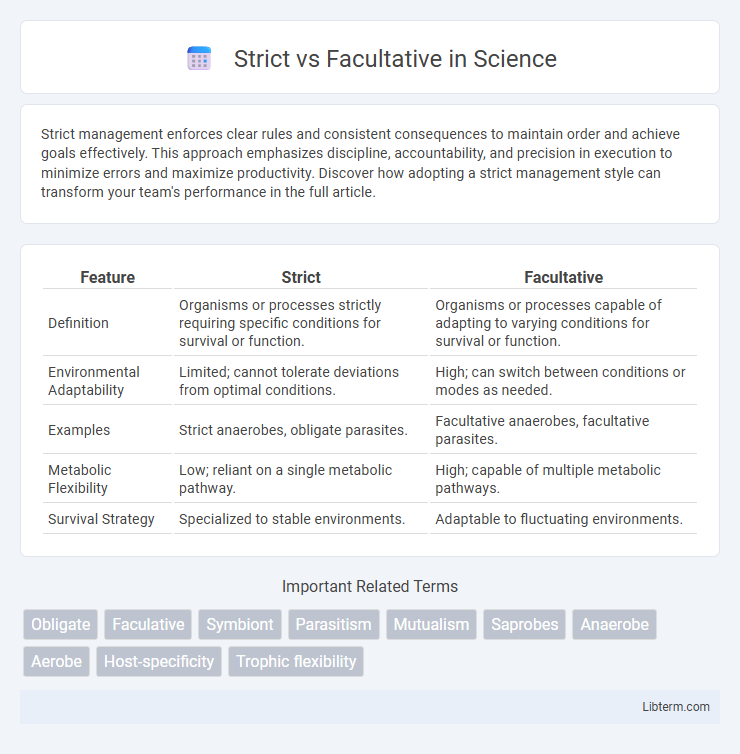
| Feature | Strict | Facultative |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Organisms or processes strictly requiring specific conditions for survival or function. | Organisms or processes capable of adapting to varying conditions for survival or function. |
| Environmental Adaptability | Limited; cannot tolerate deviations from optimal conditions. | High; can switch between conditions or modes as needed. |
| Examples | Strict anaerobes, obligate parasites. | Facultative anaerobes, facultative parasites. |
| Metabolic Flexibility | Low; reliant on a single metabolic pathway. | High; capable of multiple metabolic pathways. |
| Survival Strategy | Specialized to stable environments. | Adaptable to fluctuating environments. |
Introduction to Strict vs Facultative
Strict organisms require specific environmental conditions or substrates for survival and reproduction, exhibiting narrow tolerance ranges that limit their habitats. Facultative organisms display greater ecological flexibility by adapting to a variety of conditions or substrates, enabling survival in diverse environments. Understanding the distinctions between strict and facultative organisms is crucial in fields like microbiology, ecology, and evolutionary biology for predicting species distribution and behavior.
Understanding the Terminology
Strict definitions imply rigid adherence to specific rules or criteria, often excluding exceptions, while facultative indicates flexibility and allowance for optional actions or variations. Understanding these terms is essential in fields like biology, where strict organisms require specific conditions, and facultative organisms can adapt to varying environments. Clear comprehension of strict versus facultative distinctions aids accurate interpretation in scientific research and legal contexts.
Key Differences Between Strict and Facultative
Strict organisms require specific environmental conditions to survive, such as strict aerobes needing oxygen, while facultative organisms can adapt to varying conditions by switching between metabolic pathways. Strict anaerobes cannot tolerate oxygen, whereas facultative anaerobes thrive in both aerobic and anaerobic environments. This flexibility gives facultative organisms an adaptive advantage, enabling survival across diverse habitats compared to the specialized needs of strict organisms.
Examples in Biology and Ecology
Strict symbiosis refers to relationships where species are entirely dependent on each other for survival, such as the mutualism between coral polyps and zooxanthellae algae, where corals cannot thrive without the algae providing nutrients via photosynthesis. Facultative symbiosis occurs when species can live independently but benefit from association, exemplified by cleaner fish like wrasses that remove parasites from larger fish; both species survive alone but gain advantages from interaction. In ecology, strict parasitism is demonstrated by the cuckoo bird's reliance on host birds to rear its young, contrasting with facultative parasitism seen in certain fungi that can decompose organic matter independently or infect living hosts opportunistically.
Applications in Microbial Associations
Strict microbial associations require obligatory interactions between species for survival, commonly seen in endosymbiotic relationships such as Buchnera aphidicola in aphids. Facultative microbial associations allow flexibility, enabling organisms like Rhizobium bacteria to form nitrogen-fixing nodules on legumes under favorable conditions. These distinctions impact biotechnological applications, where strict symbioses offer stable mutualistic platforms, while facultative associations provide adaptability in microbial consortia engineering.
Importance in Environmental Adaptation
Strict organisms exhibit specialized adaptations that enable survival in narrow environmental conditions, ensuring high efficiency but limited flexibility. Facultative organisms possess genetic and physiological traits that allow them to adjust and thrive across diverse environments, enhancing resilience and ecological success. This adaptability difference is critical for understanding species distribution and response to environmental changes.
Implications for Host-Parasite Relationships
Strict parasites depend entirely on their host for survival, resulting in a high degree of host specificity and often complex coevolutionary adaptations. Facultative parasites can survive independently or parasitize hosts opportunistically, leading to more flexible host relationships and potentially broader host ranges. This distinction influences the dynamics of host-parasite interactions, disease transmission, and evolutionary pressures on both parasite and host populations.
Impact on Evolutionary Processes
Strict and facultative traits influence evolutionary processes differently by shaping adaptive flexibility in populations. Strict traits are genetically fixed, leading to consistent phenotypic expression and potentially constraining evolutionary change but ensuring stability in stable environments. Facultative traits enable phenotypic plasticity by responding to environmental cues, increasing evolutionary potential through variable selection pressures and promoting diversification.
Case Studies: Strict vs Facultative in Nature
Strict and facultative behaviors exemplify adaptive strategies observed in diverse species, with strict organisms relying on obligatory associations for survival, such as the coral-zooxanthellae symbiosis critical for reef ecosystems. Facultative interactions, evident in animals like African oxpeckers, display flexibility by engaging in mutualistic relationships only when beneficial, enhancing survival without exclusive dependence. Case studies highlight that strict symbioses often drive co-evolution and specialization, whereas facultative relationships promote ecological versatility and resilience in fluctuating environments.
Conclusion: Choosing Strict or Facultative Approaches
Choosing between strict and facultative approaches depends largely on the desired balance between control and flexibility in project management or policy enforcement. Strict approaches enforce rigid guidelines and predictable outcomes, ideal for high-risk environments demanding consistency, while facultative approaches offer adaptability and responsiveness to changing circumstances, enhancing innovation and stakeholder engagement. Evaluating project requirements, risk tolerance, and organizational culture is crucial for selecting the most effective approach to ensure success and sustainability.
Strict Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com