Understanding structural engineering is essential for ensuring the safety and stability of buildings and infrastructure throughout their lifecycle. This discipline involves analyzing and designing frameworks that can withstand loads, environmental forces, and stress to prevent failure. Explore the rest of this article to discover how structural principles impact your everyday environment.
Table of Comparison
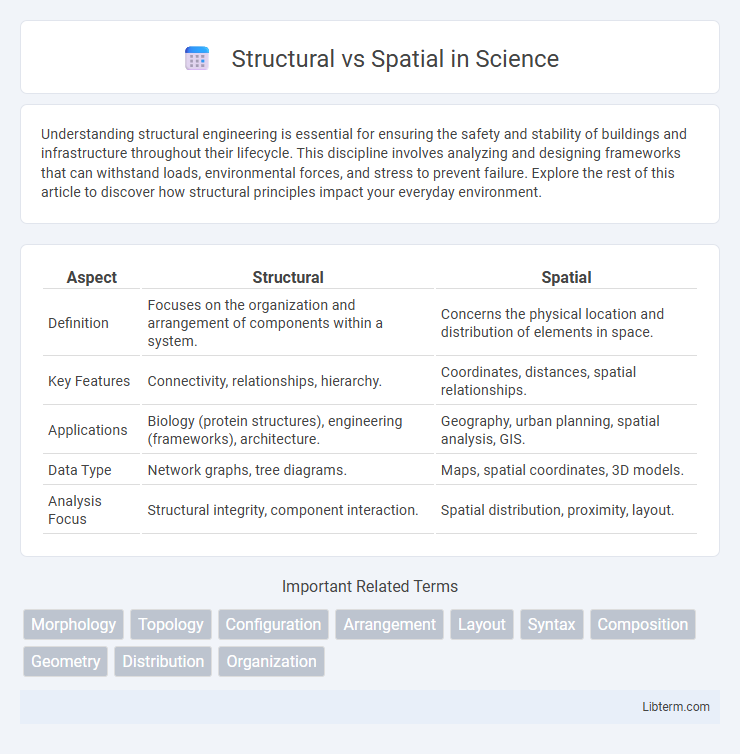
| Aspect | Structural | Spatial |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Focuses on the organization and arrangement of components within a system. | Concerns the physical location and distribution of elements in space. |
| Key Features | Connectivity, relationships, hierarchy. | Coordinates, distances, spatial relationships. |
| Applications | Biology (protein structures), engineering (frameworks), architecture. | Geography, urban planning, spatial analysis, GIS. |
| Data Type | Network graphs, tree diagrams. | Maps, spatial coordinates, 3D models. |
| Analysis Focus | Structural integrity, component interaction. | Spatial distribution, proximity, layout. |
Introduction to Structural and Spatial Concepts
Structural concepts refer to the organized framework or arrangement of elements within a system, emphasizing relationships and connections between components. Spatial concepts involve the understanding of physical space, location, and the geometric properties that describe how objects occupy and interact within an environment. Mastery of both structural and spatial concepts is essential for fields such as architecture, engineering, and geographic information systems, where design integrity and spatial accuracy are critical.
Defining Structural Analysis
Structural analysis involves examining the internal forces, stresses, and stability of physical structures such as buildings, bridges, and frameworks to ensure they can withstand applied loads. It focuses on understanding material properties, load distribution, and support conditions to predict the behavior of structural components. Key techniques include finite element analysis, stress-strain evaluation, and deflection calculations to optimize safety and performance.
Understanding Spatial Analysis
Spatial analysis involves examining the geographic patterns and relationships between spatial entities to uncover insights about their distribution and interaction. Unlike structural analysis, which focuses on the framework or organization of components within a system, spatial analysis leverages tools such as Geographic Information Systems (GIS) to analyze data based on location, proximity, and spatial correlation. Understanding spatial analysis enables better decision-making in urban planning, environmental management, and resource allocation by interpreting spatial dependencies and patterns.
Key Differences Between Structural and Spatial Approaches
Structural approaches emphasize the relationships and organization within a system, focusing on how components interact and form a coherent whole. Spatial approaches prioritize the physical location, distribution, and arrangement of elements in space, analyzing patterns and proximity effects. Key differences lie in the analytical focus: structural methods explore connectivity and function, while spatial methods investigate geographic or dimensional positioning.
Applications of Structural Analysis in Various Fields
Structural analysis plays a crucial role in civil engineering by ensuring the safety and stability of buildings, bridges, and other infrastructure through load assessment and stress evaluation. In aerospace engineering, it facilitates the design of aircraft and spacecraft by analyzing material behavior under aerodynamic forces. Additionally, structural analysis is vital in mechanical engineering for optimizing machinery components to withstand operational stresses and prevent failure.
Spatial Analysis in Practice
Spatial analysis in practice involves examining geographic patterns to identify relationships and trends within data sets, utilizing techniques such as spatial interpolation, point pattern analysis, and spatial autocorrelation. It leverages Geographic Information Systems (GIS) and remote sensing data to support decision-making in urban planning, environmental management, and public health. Effective spatial analysis enhances the accuracy of predictive models and facilitates targeted interventions by incorporating location-based insights.
Advantages of Structural Perspectives
Structural perspectives offer advantages by emphasizing the interrelationships and patterns within complex systems, enabling deeper understanding of underlying frameworks. This approach facilitates the identification of key components and their functions, leading to improved organization and efficient problem-solving in fields like architecture, linguistics, and sociology. Structural analysis also enhances predictive capabilities by revealing stable configurations that influence system behavior over time.
Benefits of Spatial Perspectives
Spatial perspectives enhance data analysis by revealing relationships and patterns across geographic locations, enabling more informed decision-making in urban planning, environmental management, and logistics. They facilitate the visualization of complex phenomena through Geographic Information Systems (GIS), improving resource allocation and risk assessment. Integrating spatial insights leads to better-targeted interventions that increase efficiency and sustainability in various sectors.
When to Use Structural vs Spatial Analysis
Structural analysis is ideal for examining relationships and patterns within interconnected networks, such as social or organizational systems, to understand influence, hierarchy, and connectivity. Spatial analysis excels in evaluating geographic data, helping to identify spatial distributions, clusters, and trends across physical locations for applications like urban planning or environmental monitoring. Use structural analysis when the focus is on node and link interactions, and opt for spatial analysis when geographic context and spatial relationships are critical.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Approach
Selecting the right approach between structural and spatial depends on the specific project requirements and desired outcomes. Structural methods excel in analyzing relationships and hierarchies within data, ideal for technical and engineering applications. Spatial approaches prioritize geographical context and location-based insights, making them essential for mapping, urban planning, and environmental studies.
Structural Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com