Isohel maps display lines of equal sunshine duration, providing valuable insights into solar exposure patterns across specific regions. These maps help planners, farmers, and environmentalists optimize land use, energy production, and agriculture by understanding sunlight distribution. Discover how Isohel maps can enhance Your decisions by reading the rest of the article.
Table of Comparison
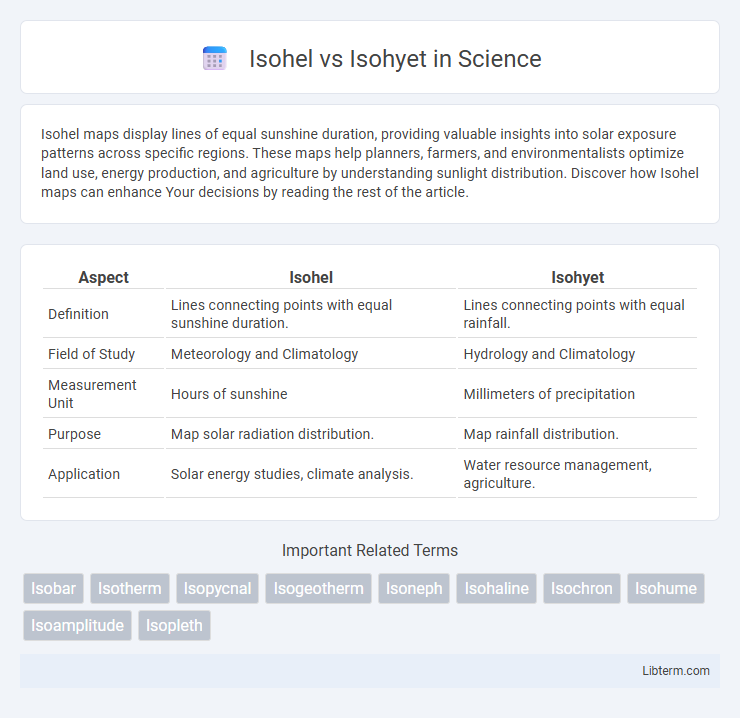
| Aspect | Isohel | Isohyet |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Lines connecting points with equal sunshine duration. | Lines connecting points with equal rainfall. |
| Field of Study | Meteorology and Climatology | Hydrology and Climatology |
| Measurement Unit | Hours of sunshine | Millimeters of precipitation |
| Purpose | Map solar radiation distribution. | Map rainfall distribution. |
| Application | Solar energy studies, climate analysis. | Water resource management, agriculture. |
Introduction to Isohels and Isohyets
Isohels are contour lines on a map connecting points with equal sunshine duration, providing crucial data for solar energy assessment and climate studies. Isohyets, by contrast, are lines that link points of equal precipitation, essential for hydrological analysis and agricultural planning. Both isohels and isohyets serve as fundamental tools in meteorology and environmental science for spatially visualizing weather patterns.
Definitions: What is an Isohel?
An Isohel is a line on a map connecting points that receive equal amounts of sunshine, used in climatology to analyze solar radiation distribution. It contrasts with an Isohyet, which links points of equal precipitation, serving meteorology by illustrating rainfall patterns. Understanding these lines aids in studying regional climate variations and planning in agriculture and urban development.
Definitions: What is an Isohyet?
An isohyet is a line on a map connecting points of equal precipitation, used in meteorology and hydrology to represent rainfall distribution over a geographic area. Unlike an isohel, which links locations with the same hours of sunshine, an isohyet specifically visualizes the spatial variation of precipitation intensity and accumulation. Isohyets are essential tools for analyzing rainfall patterns, managing water resources, and designing flood control systems.
Key Differences Between Isohels and Isohyets
Isohels represent lines connecting points of equal sunshine duration on a weather map, highlighting solar radiation variability, while Isohyets depict lines of equal precipitation, providing critical data on rainfall distribution. The key difference lies in their measured variables: Isohels quantify sunlight exposure in hours, essential for solar energy studies, whereas Isohyets measure precipitation depth in millimeters, crucial for hydrological assessments. These contours serve distinct purposes in meteorology, aiding in climate analysis and resource management by mapping solar radiation patterns versus rainfall intensity.
Scientific Importance of Isohels
Isohels, lines connecting points of equal sunshine duration, are crucial for climatology and solar energy studies as they help analyze spatial patterns of solar radiation affecting ecological and agricultural systems. Unlike isohyets, which map precipitation distribution, isohels provide insight into solar exposure influencing temperature regulation and weather variability. Mapping isohels supports optimizing solar panel placements and understanding microclimate variations essential for environmental planning and climate modeling.
Significance of Isohyets in Meteorology
Isohyets are critical in meteorology as they represent lines of equal precipitation, helping meteorologists analyze rainfall distribution and intensity across a region. This data is essential for understanding weather patterns, forecasting storms, and managing water resources effectively. Isohyets provide a spatial visualization of rainfall variability, enabling accurate assessment of droughts, floods, and climate trends.
How Isohels Are Mapped and Interpreted
Isohels are mapped by connecting points of equal sunshine duration, revealing spatial patterns of solar radiation over a given area. These lines help interpret the intensity and distribution of sunlight, essential for studies in climatology, agriculture, and solar energy planning. The contrast between isohels and isohyets lies in their focus--isohels measure sunlight hours, while isohyets represent precipitation levels.
Techniques for Plotting Isohyets
Techniques for plotting isohyets involve collecting rainfall data from multiple meteorological stations to map equal precipitation levels accurately. Methods such as the Thiessen polygon technique and the inverse distance weighting (IDW) interpolation are commonly used to spatially distribute rainfall measurements for precise isohyet construction. Digital tools and GIS software enhance this process by allowing automated contouring and integration of topographical factors, improving the reliability of isohyet maps compared to manual plotting.
Applications of Isohels and Isohyets in Weather Analysis
Isohels, which connect points of equal sunshine duration, are crucial in climate studies for analyzing solar radiation patterns and its effects on regional weather conditions and agricultural productivity. Isohyets, linking locations with equal rainfall, are essential in hydrological assessments, flood forecasting, and water resource management by mapping precipitation distribution over time. Both isohels and isohyets provide meteorologists with valuable data for predicting weather trends, optimizing crop planning, and managing natural hazards based on solar and precipitation variations.
Conclusion: Choosing Between Isohel and Isohyet
Isohel maps depict the distribution of sunlight or solar radiation, essential for solar energy planning and horticulture, while Isohyet maps represent precipitation patterns crucial for hydrological studies and agricultural management. Selecting between Isohel and Isohyet depends on the specific environmental variable of interest--solar irradiance for energy and climate analysis or rainfall distribution for water resource management and crop planning. Understanding the distinct applications and data requirements of each map ensures accurate decision-making in climate research and resource allocation.
Isohel Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com