Induced effects occur when an external force or stimulus triggers a specific response, often seen in physics, biology, and psychology. Understanding how induced phenomena operate can significantly enhance your insights into cause-and-effect relationships across various disciplines. Explore the full article to discover detailed examples and applications of induced processes.
Table of Comparison
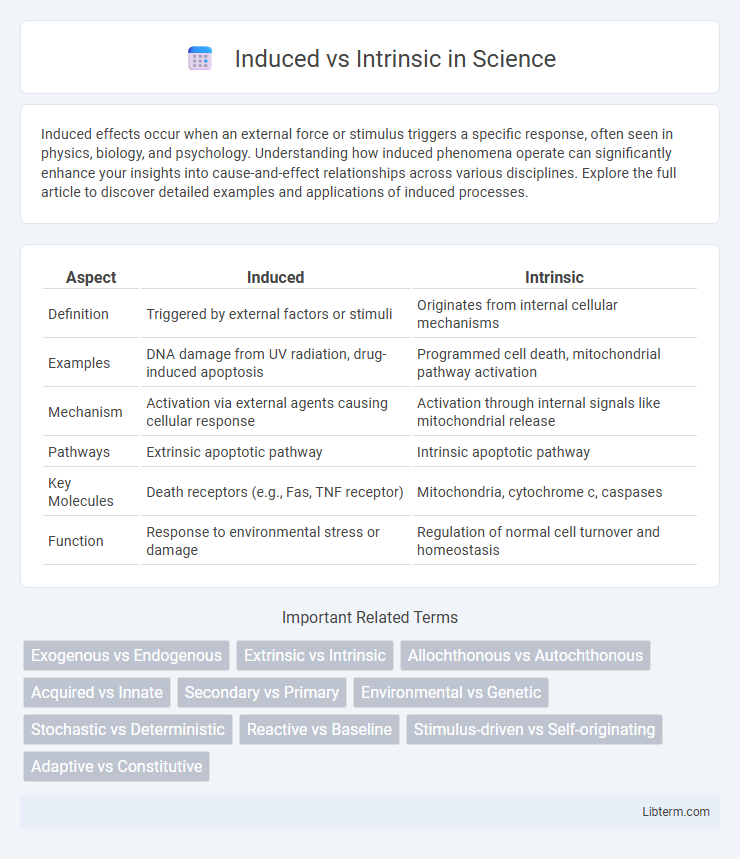
| Aspect | Induced | Intrinsic |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Triggered by external factors or stimuli | Originates from internal cellular mechanisms |
| Examples | DNA damage from UV radiation, drug-induced apoptosis | Programmed cell death, mitochondrial pathway activation |
| Mechanism | Activation via external agents causing cellular response | Activation through internal signals like mitochondrial release |
| Pathways | Extrinsic apoptotic pathway | Intrinsic apoptotic pathway |
| Key Molecules | Death receptors (e.g., Fas, TNF receptor) | Mitochondria, cytochrome c, caspases |
| Function | Response to environmental stress or damage | Regulation of normal cell turnover and homeostasis |
Understanding Induced and Intrinsic: Key Definitions
Induced properties arise from external factors or influences applied to a system, such as induced magnetism resulting from an external magnetic field. Intrinsic properties are inherent qualities of a material or system, independent of external conditions, like intrinsic electrical conductivity determined by atomic structure. Understanding the distinction between induced and intrinsic characteristics is crucial for accurately analyzing material behavior and designing applications based on fundamental versus environmentally influenced attributes.
Core Differences Between Induced and Intrinsic
Induced properties arise due to external influences or forces acting upon a system, while intrinsic properties are inherent and exist independently of external factors. Induced characteristics often depend on environmental conditions, such as temperature or pressure, whereas intrinsic traits are stable and fundamental to the material's nature. Understanding the core differences between induced and intrinsic enables accurate analysis in fields like physics, chemistry, and material science.
Causes of Induced Phenomena
Induced phenomena occur due to external influences or environmental factors that alter the state of a system, such as electromagnetic fields causing polarization in materials or mechanical stress leading to deformation. These causes include applied forces, temperature changes, or electromagnetic radiation, which trigger a response not intrinsic to the material or system itself. Understanding these external triggers is crucial for controlling induced effects in applications like sensors, actuators, and material engineering.
Origins of Intrinsic Properties
Intrinsic properties originate from the fundamental nature or constitution of an object, independent of external influences or interactions. These properties, such as mass, charge, or atomic structure, exist inherently within the substance and define its essential characteristics. Understanding the origins of intrinsic properties involves exploring quantum mechanics and atomic theory, which explain how internal configurations and energy states determine an object's inherent attributes.
Real-World Examples of Induced vs Intrinsic
Induced traits result from environmental factors, such as tanning caused by prolonged sun exposure or increased muscle mass due to consistent strength training. Intrinsic traits are genetically encoded characteristics, exemplified by eye color determined by DNA or natural blood type inheritance. Real-world cases highlight how intrinsic traits like inherited diseases remain constant, while induced traits like callouses adapt dynamically to external conditions.
Implications in Science and Engineering
Induced properties arise from external stimuli such as electromagnetic fields or mechanical stress, while intrinsic properties are inherent to the material's atomic or molecular structure. Understanding the distinction between induced and intrinsic characteristics allows engineers to tailor material performance for specific applications, such as enhancing magnetic properties through doping or strain engineering. This knowledge is critical for innovations in sensor technology, semiconductor design, and adaptive materials, where precise control over material behavior under operational conditions drives efficiency and functionality.
Advantages and Limitations of Induced Attributes
Induced attributes provide the advantage of being derived from existing data, enabling dynamic feature creation that can improve machine learning model accuracy without requiring additional data collection. These attributes can capture complex relationships and patterns in the dataset, offering enhanced predictive power. However, the limitation lies in the potential for overfitting and increased computational complexity, as induced attributes may introduce noise or redundant information if not carefully selected or validated.
The Role of Intrinsic Traits in Performance
Intrinsic traits such as natural talent, cognitive abilities, and personality characteristics significantly influence individual performance by shaping motivation, resilience, and problem-solving skills. Unlike induced factors, which are developed through external training and environmental stimuli, intrinsic traits offer a foundational framework that affects how effectively one can acquire and apply new skills. Research highlights that individuals with strong intrinsic motivation and inherent abilities consistently demonstrate higher productivity and adaptability across various performance domains.
How to Distinguish Induced from Intrinsic
Induced properties arise from external factors or environmental influences, whereas intrinsic properties are inherent to the material or entity itself, independent of outside conditions. To distinguish induced from intrinsic characteristics, analyze the origin of the property--observe whether it changes when external conditions vary, indicating induction, or remains constant, reflecting intrinsic nature. Testing under controlled environments and comparing responses to stimuli like temperature, pressure, or magnetic fields effectively reveal whether a property is induced or intrinsic.
Future Trends: Induced and Intrinsic Perspectives
Future trends in induced and intrinsic perspectives emphasize the integration of artificial intelligence and machine learning to enhance decision-making processes. Advances in neurotechnology will enable deeper understanding of intrinsic motivations, while induced behavior analysis will increasingly rely on real-time data analytics and adaptive systems. The convergence of these approaches promises personalized, predictive, and responsive models across healthcare, education, and marketing sectors.
Induced Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com