Cognatic descent traces lineage through both maternal and paternal ancestors, offering a comprehensive view of your family heritage. This system contrasts with unilineal descent, which follows only one parent's line, providing richer genealogical insights. Explore the rest of the article to understand how cognatic descent shapes your identity and inheritance.
Table of Comparison
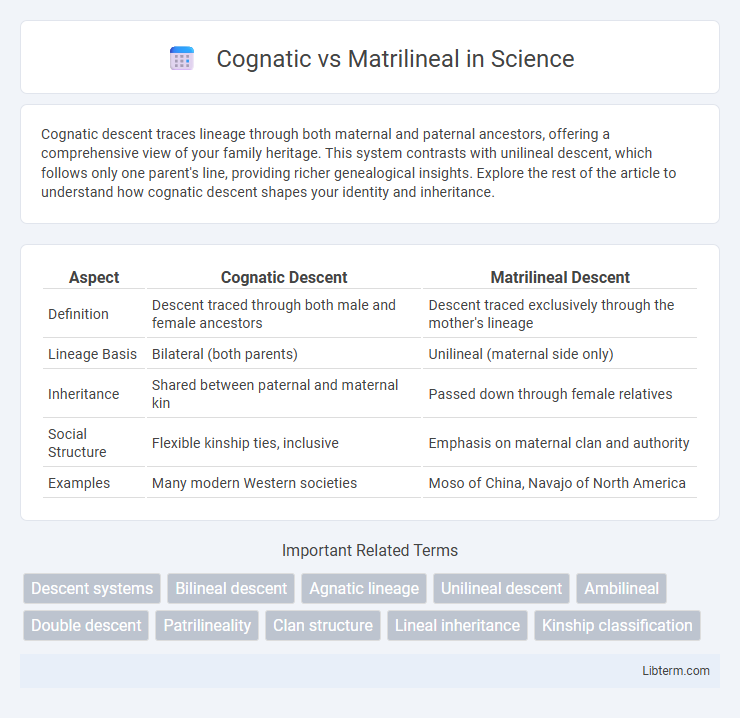
| Aspect | Cognatic Descent | Matrilineal Descent |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Descent traced through both male and female ancestors | Descent traced exclusively through the mother's lineage |
| Lineage Basis | Bilateral (both parents) | Unilineal (maternal side only) |
| Inheritance | Shared between paternal and maternal kin | Passed down through female relatives |
| Social Structure | Flexible kinship ties, inclusive | Emphasis on maternal clan and authority |
| Examples | Many modern Western societies | Moso of China, Navajo of North America |
Understanding Lineage Systems: Cognatic vs Matrilineal
Cognatic lineage systems trace descent through both male and female ancestors, allowing individuals to inherit status, property, or identity from either parent, which creates a more flexible and inclusive kinship structure. Matrilineal systems specifically emphasize descent through the mother's line, where inheritance, clan membership, and social identity are passed down from mothers to their children, reinforcing women's central role in lineage continuity. Understanding these systems reveals how societies organize family ties, inheritance rights, and social obligations based on gender-specific lineage tracking.
Defining Cognatic Descent: Key Features
Cognatic descent is a kinship system tracing ancestry through both male and female lines, allowing individuals to inherit family membership from either parent. This bilateral approach contrasts with matrilineal descent, which exclusively follows the maternal line. Key features of cognatic descent include flexible inheritance rights, equal importance of maternal and paternal relatives, and the formation of kin groups that recognize descent from multiple ancestors regardless of gender.
What is Matrilineal Descent? Core Concepts
Matrilineal descent refers to a system of lineage in which ancestry, inheritance, and kinship are traced exclusively through the mother's line, emphasizing maternal connections. Core concepts of matrilineal descent include the transmission of property, family name, and social status from mothers to their children, particularly daughters. This contrasts with cognatic descent, where lineage follows both paternal and maternal lines without strict preference.
Differences Between Cognatic and Matrilineal Lineage
Cognatic lineage traces descent through both male and female ancestors, allowing inheritance and family ties from either side, while matrilineal lineage traces descent exclusively through the female line, often emphasizing maternal inheritance and clan membership. In cognatic systems, individuals may belong to multiple lineages simultaneously due to bilateral descent, whereas matrilineal systems assign lineage membership strictly through the mother's line. Property rights, social status, and inheritance patterns in matrilineal societies typically follow maternal lines, contrasting with the more flexible and inclusive transmission found in cognatic societies.
Cultural Examples of Cognatic Society
Cognatic societies, such as the Yoruba of Nigeria and the Hawaiian Islanders, trace descent through both maternal and paternal lines, allowing flexible inheritance and kinship networks. This bilateral descent system contrasts with matrilineal cultures like the Minangkabau of Indonesia, where lineage and property pass strictly through the female line. Cognatic kinship structures promote inclusive social ties and diverse familial identities, enabling individuals to claim multiple ancestral connections for social, political, and economic advantages.
Matrilineal Societies: Global Case Studies
Matrilineal societies, such as the Minangkabau of Indonesia and the Khasi of India, trace lineage through the mother's line, emphasizing inheritance and social identity via female ancestors. These societies often assign property rights and familial responsibilities to women, highlighting the central role of maternal kin in social organization. Global case studies reveal that matrilineal systems influence gender roles, community cohesion, and governance structures in diverse cultural contexts.
Inheritance Patterns: Cognatic vs Matrilineal
Cognatic inheritance patterns allow property and titles to pass through both male and female lines, enabling descendants from either parent to inherit. In matrilineal systems, inheritance strictly follows the female lineage, with property and social status transferred from mothers to their children or through the maternal line. Cognatic patterns often promote bilateral kinship recognition, whereas matrilineal descent emphasizes the mother's line for succession and familial obligations.
Social Structure and Gender Roles
Cognatic descent systems trace lineage through both paternal and maternal lines, promoting flexible inheritance and social connections that accommodate diverse family structures. Matrilineal descent emphasizes inheritance and social identity through the mother's line, often positioning women as central figures in lineage continuity and property rights. This distinction shapes gender roles significantly, with matrilineal societies frequently granting women greater authority and influence in social organization compared to the more egalitarian or male-neutral roles seen in cognatic systems.
Impact on Family and Kinship Networks
Cognatic descent systems allow individuals to trace kinship through both maternal and paternal lines, promoting inclusive family networks that facilitate broader alliances and support structures. Matrilineal descent focuses exclusively on maternal ancestry, reinforcing strong maternal kin connections and often centralizing inheritance and social roles within the mother's lineage. These differing descent patterns significantly shape family organization, resource distribution, and social responsibilities within communities.
Contemporary Relevance and Changing Trends
Contemporary relevance of cognatic and matrilineal descent systems reflects shifting societal values emphasizing gender equality and individual identity. Cognatic descent, recognizing lineage through both parents, aligns with modern legal frameworks and diverse family structures, promoting inclusivity. Matrilineal systems, rooted in tracing ancestry through the mother, persist in indigenous and cultural communities, adapting to contemporary social dynamics while preserving heritage and property rights.
Cognatic Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com