Functional design focuses on practicality and efficiency, ensuring objects or spaces serve their intended purpose effectively. Prioritizing usability and simplicity, this approach enhances user experience by eliminating unnecessary features. Discover how functional design can transform Your daily interactions in the rest of the article.
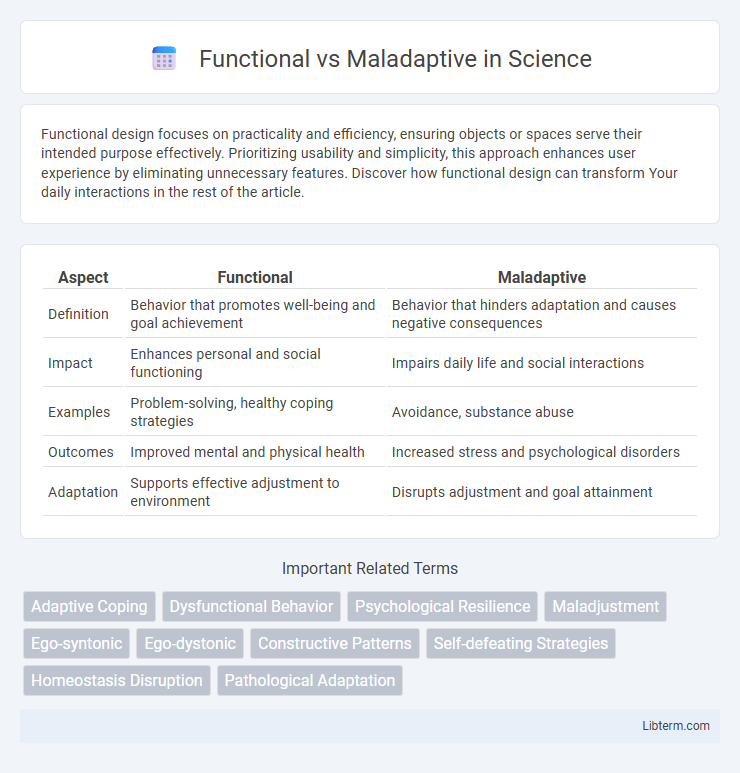
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Functional | Maladaptive |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Behavior that promotes well-being and goal achievement | Behavior that hinders adaptation and causes negative consequences |
| Impact | Enhances personal and social functioning | Impairs daily life and social interactions |
| Examples | Problem-solving, healthy coping strategies | Avoidance, substance abuse |
| Outcomes | Improved mental and physical health | Increased stress and psychological disorders |
| Adaptation | Supports effective adjustment to environment | Disrupts adjustment and goal attainment |
Understanding Functional vs. Maladaptive Behaviors
Functional behaviors effectively meet an individual's needs and adapt to environmental demands, promoting well-being and social integration. Maladaptive behaviors, in contrast, hinder daily functioning, often causing distress or impairing relationships by failing to appropriately address underlying issues. Understanding the distinction between functional and maladaptive behaviors is essential for developing targeted interventions that foster adaptive skills and reduce behavioral challenges.
Key Differences Between Functional and Maladaptive Patterns
Functional patterns promote adaptive behaviors that support personal growth, well-being, and effective coping with stress, enabling individuals to navigate challenges productively. In contrast, maladaptive patterns involve dysfunctional responses that hinder emotional regulation, exacerbate psychological distress, and impair social or occupational functioning. Key differences highlight that functional behaviors contribute to resilience and goal achievement, whereas maladaptive behaviors perpetuate negative cycles and obstruct recovery.
Psychological Foundations of Functional Behaviors
Functional behaviors are adaptive actions rooted in psychological foundations that promote effective coping, goal achievement, and social integration. These behaviors arise from cognitive processes such as problem-solving, emotional regulation, and reinforcement learning, enabling individuals to respond constructively to environmental demands. In contrast, maladaptive behaviors often stem from distorted cognitive schemas or emotional dysregulation, hindering psychological well-being and adaptive functioning.
Origins and Causes of Maladaptive Responses
Maladaptive responses often stem from early life experiences such as trauma, chronic stress, or inadequate emotional support, which disrupt healthy coping mechanisms and brain development. Genetic predispositions combined with environmental factors, including family dynamics and social influences, contribute significantly to the formation of maladaptive behaviors. These responses serve as ineffective attempts to manage psychological distress but can reinforce negative patterns when underlying causes remain unaddressed.
Impact on Mental and Emotional Well-Being
Functional behaviors promote positive mental and emotional well-being by enhancing coping skills, resilience, and adaptive responses to stress. Maladaptive behaviors, such as avoidance or self-destructive habits, undermine mental health by exacerbating anxiety, depression, and emotional dysregulation. Recognizing and shifting from maladaptive to functional patterns is crucial for improving psychological stability and overall emotional balance.
Assessing Functionality in Everyday Life
Assessing functionality in everyday life involves evaluating an individual's ability to perform daily tasks such as self-care, work responsibilities, and social interactions without impairment. Functional behaviors support adaptability and goal achievement, while maladaptive behaviors hinder productivity and may contribute to distress or dysfunction. Measurement tools like the Global Assessment of Functioning (GAF) scale and Activities of Daily Living (ADL) assessments provide objective insights into the degree of an individual's functional competence versus maladaptation.
The Role of Environment in Behavior Formation
Environmental factors significantly influence the development of functional and maladaptive behaviors by shaping an individual's responses to stimuli and stressors. Positive environments promoting safety, support, and learning tend to foster adaptive, functional behaviors, while adverse conditions such as trauma, neglect, or chronic stress can lead to maladaptive coping mechanisms and dysfunctional behavior patterns. Research in behavioral psychology highlights the critical role of early environmental experiences in neuroplasticity, affecting long-term emotional regulation and social functioning.
Strategies to Foster Functional Behaviors
Strategies to foster functional behaviors include consistent positive reinforcement, clear communication of expectations, and the use of structured routines to enhance predictability. Implementing individualized behavior intervention plans (BIPs) and teaching coping skills promote adaptive responses to challenging situations. Collaboration between educators, therapists, and families ensures a supportive environment that reduces maladaptive behaviors and strengthens functional outcomes.
Addressing and Reframing Maladaptive Patterns
Addressing and reframing maladaptive patterns involves recognizing dysfunctional thoughts and behaviors that hinder emotional well-being and replacing them with functional, adaptive alternatives to promote healthier coping mechanisms. Cognitive-behavioral strategies target negative automatic thoughts and maladaptive schemas, enabling individuals to reinterpret experiences and foster resilience. Integrating mindfulness and self-reflection enhances awareness, facilitating sustained behavioral change and improved mental health outcomes.
Moving Toward Positive Change and Resilience
Functional behaviors promote moving toward positive change by fostering resilience, adaptability, and proactive problem-solving skills. Maladaptive behaviors hinder progress by reinforcing negative patterns and limiting emotional growth, often exacerbating stress and vulnerability. Emphasizing functional strategies enhances coping mechanisms and supports sustained mental well-being in challenging situations.
Functional Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com