Positive thinking can significantly enhance your mental well-being and overall outlook on life by reducing stress and increasing resilience. Fostering optimism encourages healthier habits and improves relationships, paving the way for greater success and happiness. Explore the rest of the article to discover practical tips for cultivating a positive mindset every day.
Table of Comparison
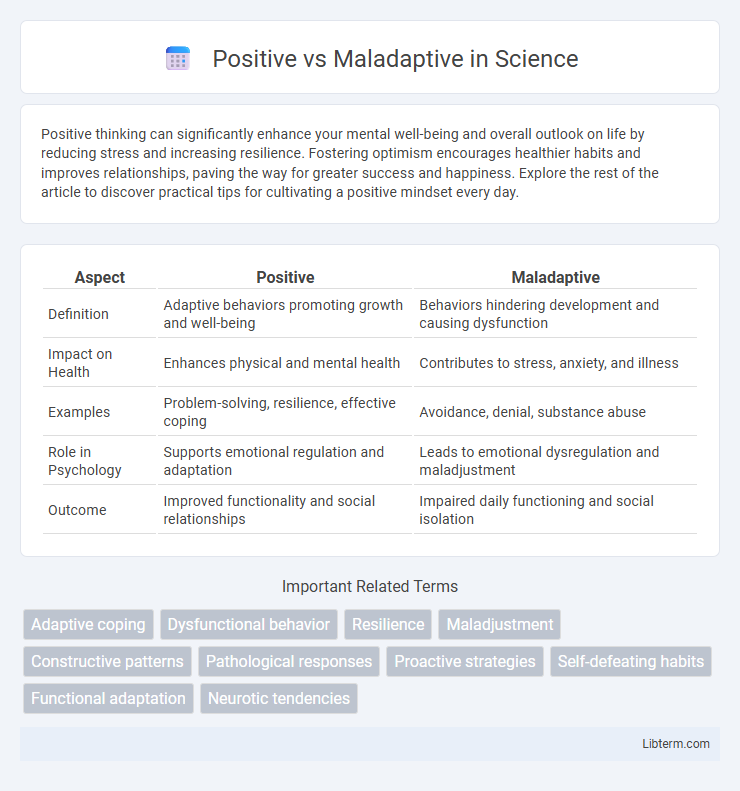
| Aspect | Positive | Maladaptive |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Adaptive behaviors promoting growth and well-being | Behaviors hindering development and causing dysfunction |
| Impact on Health | Enhances physical and mental health | Contributes to stress, anxiety, and illness |
| Examples | Problem-solving, resilience, effective coping | Avoidance, denial, substance abuse |
| Role in Psychology | Supports emotional regulation and adaptation | Leads to emotional dysregulation and maladjustment |
| Outcome | Improved functionality and social relationships | Impaired daily functioning and social isolation |
Understanding Positive vs Maladaptive Behaviors
Positive behaviors promote well-being, social adaptability, and personal growth by reinforcing healthy coping mechanisms and constructive actions. Maladaptive behaviors hinder functionality and emotional health through avoidance, harmful habits, or negative coping strategies that exacerbate stress or conflict. Recognizing the distinction between positive and maladaptive behaviors aids in developing effective interventions for mental health and social support systems.
Key Differences Between Positive and Maladaptive Patterns
Positive patterns promote adaptive behaviors that enhance well-being, resilience, and effective problem-solving in various contexts. Maladaptive patterns, by contrast, involve dysfunctional responses that hinder emotional regulation, increase stress, and perpetuate negative outcomes. Key differences lie in the impact on mental health, with positive patterns fostering growth and coping, while maladaptive ones contribute to stagnation and psychological distress.
Psychological Roots of Positive and Maladaptive Actions
Positive actions typically stem from psychological roots such as resilience, healthy coping mechanisms, and adaptive cognitive processes that promote well-being and constructive problem-solving. Maladaptive behaviors often originate from unresolved trauma, chronic stress, or dysfunctional thought patterns that impair emotional regulation and lead to harmful or counterproductive outcomes. Understanding these psychological foundations helps in developing effective interventions that foster positive change and reduce maladaptive tendencies.
Impact of Positive Behaviors on Mental Health
Positive behaviors such as regular exercise, social engagement, and mindful practices significantly enhance mental health by reducing symptoms of anxiety and depression and improving overall emotional resilience. These behaviors promote the release of neurotransmitters like serotonin and dopamine, which regulate mood and increase feelings of well-being. In contrast, maladaptive behaviors like avoidance or substance abuse can exacerbate mental health issues by reinforcing negative thought patterns and impairing coping mechanisms.
Consequences of Maladaptive Strategies
Maladaptive strategies often lead to negative consequences such as increased stress, anxiety, and impaired emotional regulation, which can exacerbate mental health disorders. These ineffective coping mechanisms may result in social withdrawal, poor decision-making, and deteriorating relationships, ultimately undermining overall well-being. Persistent use of maladaptive behaviors can hinder personal growth and reduce resilience, making it difficult to adapt to future challenges effectively.
Recognizing Signs of Maladaptive Responses
Recognizing signs of maladaptive responses involves identifying patterns such as persistent avoidance, excessive anxiety, and impaired functioning in daily life. Unlike positive coping mechanisms that promote resilience and problem-solving, maladaptive behaviors often exacerbate stress and hinder emotional regulation. Key indicators include withdrawal from social interactions, increased irritability, and difficulty adapting to change, signaling the need for early intervention and support.
Cultivating Positive Coping Mechanisms
Cultivating positive coping mechanisms such as mindfulness, problem-solving, and social support fosters resilience and emotional well-being. Positive strategies enhance adaptive functioning by reducing stress, improving mental health, and promoting constructive outcomes. Maladaptive coping, including avoidance or substance use, often exacerbates psychological distress and hinders recovery.
Transitioning from Maladaptive to Positive Patterns
Transitioning from maladaptive to positive patterns involves identifying harmful behaviors and gradually replacing them with constructive habits that enhance mental and emotional well-being. Cognitive-behavioral strategies, such as self-monitoring and mindfulness, facilitate awareness and control over negative thought cycles, promoting adaptive responses. Consistent practice and support from therapy or peer groups accelerate this shift, reinforcing resilience and improved coping mechanisms.
Role of Support Systems in Behavior Change
Support systems play a crucial role in distinguishing positive from maladaptive behaviors by providing emotional encouragement, accountability, and resources that reinforce healthy change. Positive behavior change is often sustained when individuals engage with supportive networks, such as family, friends, or professional counselors, which foster resilience and adaptive coping strategies. In contrast, the absence or dysfunction of support systems can contribute to the persistence of maladaptive behaviors by increasing isolation, stress, and vulnerability to negative influences.
Long-Term Benefits of Positive Over Maladaptive Approaches
Positive coping strategies such as problem-solving, emotional regulation, and seeking social support foster resilience and improve mental health over time by promoting adaptive brain plasticity and stress reduction. In contrast, maladaptive approaches like avoidance, substance abuse, and denial often provide temporary relief but exacerbate stress and impair cognitive functioning, leading to chronic psychological issues. Long-term benefits of positive coping include enhanced emotional intelligence, sustained well-being, and improved quality of life, while maladaptive patterns increase the risk of anxiety, depression, and diminished life satisfaction.
Positive Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com