Ambilineal descent systems allow individuals to trace their ancestry through either the maternal or paternal line, offering flexibility in family affiliation. This system contrasts with strictly patrilineal or matrilineal societies by enabling you to choose which lineage to emphasize for inheritance or social identity. Explore the rest of the article to understand how ambilineal systems influence cultural practices and kinship structures worldwide.
Table of Comparison
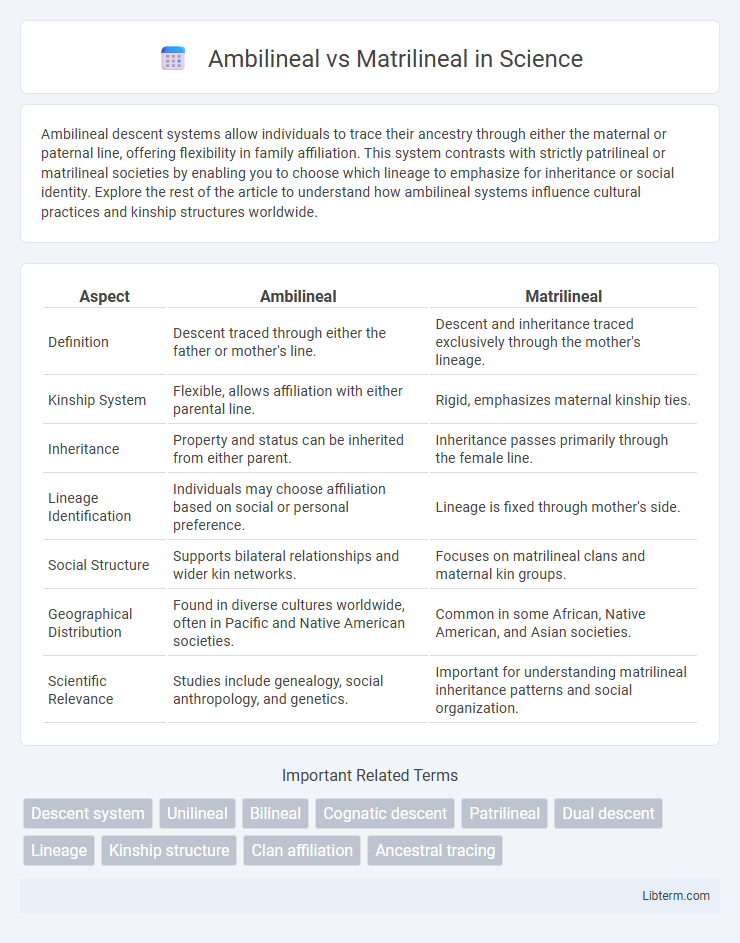
| Aspect | Ambilineal | Matrilineal |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Descent traced through either the father or mother's line. | Descent and inheritance traced exclusively through the mother's lineage. |
| Kinship System | Flexible, allows affiliation with either parental line. | Rigid, emphasizes maternal kinship ties. |
| Inheritance | Property and status can be inherited from either parent. | Inheritance passes primarily through the female line. |
| Lineage Identification | Individuals may choose affiliation based on social or personal preference. | Lineage is fixed through mother's side. |
| Social Structure | Supports bilateral relationships and wider kin networks. | Focuses on matrilineal clans and maternal kin groups. |
| Geographical Distribution | Found in diverse cultures worldwide, often in Pacific and Native American societies. | Common in some African, Native American, and Asian societies. |
| Scientific Relevance | Studies include genealogy, social anthropology, and genetics. | Important for understanding matrilineal inheritance patterns and social organization. |
Introduction to Lineal Descent Systems
Lineal descent systems categorize kinship based on the tracing of ancestry through specific parental lines, such as matrilineal descent, which follows the mother's lineage, or ambilineal descent, allowing individuals to affiliate with either the mother's or father's lineage. Matrilineal systems emphasize inheritance, social identity, and property rights through maternal ancestors, influencing social structures and group membership. Ambilineal descent offers flexibility by permitting affiliation with either lineage, adapting to social, economic, or environmental factors in diverse cultural contexts.
Defining Ambilineal Descent
Ambilineal descent is a kinship system in which individuals trace their lineage through either the mother's or father's line, allowing flexibility in choosing affiliation based on social, economic, or cultural factors. This contrasts with matrilineal descent, where lineage and inheritance strictly follow the mother's side, emphasizing female ancestry and maternal kinship bonds. Ambilineal systems enable dynamic family connections and inheritance patterns, accommodating diverse social structures and genealogical identities.
Understanding Matrilineal Descent
Matrilineal descent traces lineage through the mother's ancestry, emphasizing inheritance, clan membership, and social identity based on maternal lines. This system contrasts with ambilineal descent, where individuals may choose affiliation with either the mother's or father's lineage, allowing more flexibility in kinship ties. Understanding matrilineal descent highlights the significance of maternal inheritance patterns and their impact on family structure and cultural traditions.
Key Differences Between Ambilineal and Matrilineal Systems
Ambilineal systems allow individuals to choose their lineage affiliation, tracing descent through either the mother's or the father's line, providing flexibility in inheritance and identity. In contrast, matrilineal systems strictly trace descent and inheritance through the mother's lineage, emphasizing maternal kinship bonds and property transfer. Key differences include lineage determination, inheritance rights, and social roles, where ambilineal societies adapt to social and economic conditions, while matrilineal societies prioritize female ancestry continuity.
Cultural Examples of Ambilineal Societies
Ambilineal descent systems allow individuals to affiliate with either their mother's or father's lineage, commonly found in indigenous Australian groups and many Polynesian societies such as the Maori of New Zealand. These cultures emphasize flexibility in kinship, enabling social and economic advantages through strategic lineage affiliations. Ambilineal societies often integrate inheritance, residence, and leadership roles across multiple family lines, contrasting with the fixed, mother-based lineage of matrilineal systems like those of the Minangkabau in Indonesia.
Societies Practicing Matrilineal Descent
Societies practicing matrilineal descent trace lineage, inheritance, and kinship through the mother's line, prominently seen in communities such as the Minangkabau of Indonesia and the Mosuo of China. These cultures emphasize female inheritance rights, with property, family name, and social status passed down through women, fostering strong maternal bonds and matriarchal household structures. Matrilineal systems often influence social organization, marriage patterns, and political alliances, differing significantly from ambilineal societies where lineage affiliation is flexible and can be traced through either parent.
Inheritance Patterns: Ambilineal vs Matrilineal
Ambilineal inheritance allows individuals to trace descent and inherit property through either the male or female line, providing flexibility in inheritance patterns based on family or social preferences. Matrilineal inheritance mandates descent and property transfer strictly through the female line, ensuring that inheritance rights and lineage are preserved within the maternal lineage. These contrasting patterns significantly influence social organization, kinship roles, and the transmission of wealth and status within communities.
Social Roles and Gender Dynamics
Ambilineal descent systems allow individuals to affiliate with either the mother's or father's lineage, creating flexible social roles and often promoting balanced gender dynamics in heritage and inheritance. In contrast, matrilineal systems prioritize the mother's line for lineage and property transmission, typically enhancing women's social status and influence within the community. These differing models shape gender roles distinctly, with matrilineality frequently empowering female authority while ambilineality fosters more adaptable gender-based social responsibilities.
Modern Impacts on Descent Systems
Modern impacts on descent systems reveal a growing preference for ambilineal structures due to increased social mobility and diverse family dynamics, allowing individuals to choose affiliation with either maternal or paternal lines. Matrilineal descent remains significant in contemporary societies emphasizing women's inheritance and leadership roles, particularly among Indigenous and tribal communities adapting to legal and economic changes. The blending of traditional matrilineal practices with modern legal frameworks often results in hybrid descent models accommodating gender equality while preserving cultural identity.
Conclusion: The Significance of Descent in Society
Descent systems like ambilineal and matrilineal shape social organization by determining lineage, inheritance, and identity, influencing kinship ties and resource distribution. Ambilineal descent allows individuals to affiliate with either parental line, promoting flexibility and broader social networks, while matrilineal descent emphasizes maternal lineage, often strengthening female roles in lineage continuity and property transmission. Understanding these descent patterns reveals their significance in maintaining cultural heritage, social cohesion, and the dynamics of power within societies.
Ambilineal Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com