Composite materials combine two or more distinct substances to create a material with enhanced properties, such as improved strength, durability, and lightweight performance. These materials are widely used in industries like aerospace, automotive, and construction for their ability to offer customized solutions to specific engineering challenges. Explore the article to discover how composite technologies can benefit your projects and transform material applications.
Table of Comparison
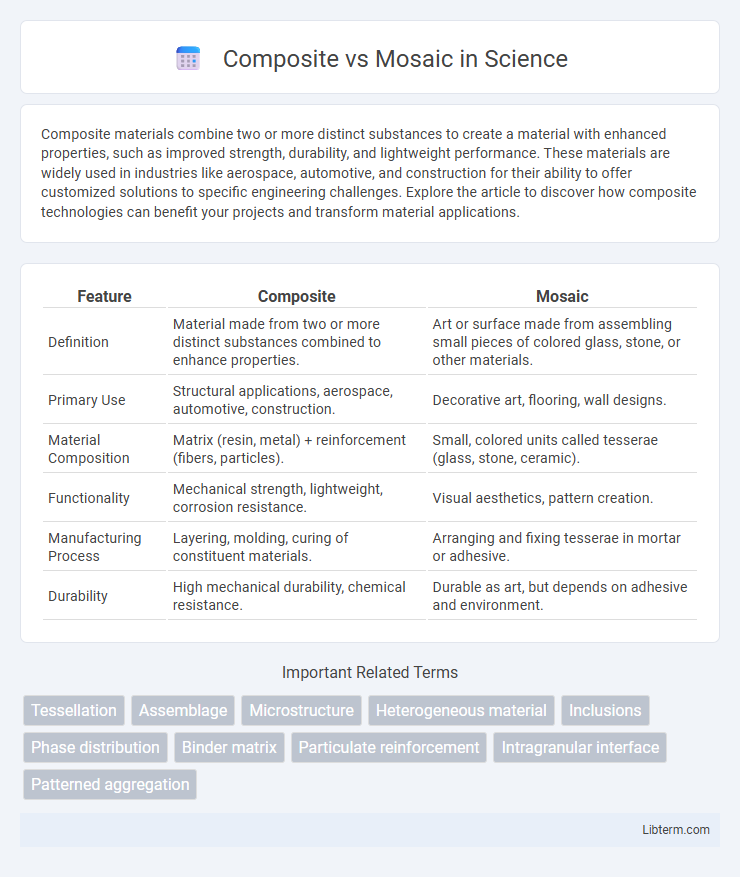
| Feature | Composite | Mosaic |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Material made from two or more distinct substances combined to enhance properties. | Art or surface made from assembling small pieces of colored glass, stone, or other materials. |
| Primary Use | Structural applications, aerospace, automotive, construction. | Decorative art, flooring, wall designs. |
| Material Composition | Matrix (resin, metal) + reinforcement (fibers, particles). | Small, colored units called tesserae (glass, stone, ceramic). |
| Functionality | Mechanical strength, lightweight, corrosion resistance. | Visual aesthetics, pattern creation. |
| Manufacturing Process | Layering, molding, curing of constituent materials. | Arranging and fixing tesserae in mortar or adhesive. |
| Durability | High mechanical durability, chemical resistance. | Durable as art, but depends on adhesive and environment. |
Introduction to Composite and Mosaic
Composite and Mosaic are design patterns used in software engineering to represent tree-like hierarchical structures. Composite allows individual objects and compositions of objects to be treated uniformly by defining a common interface for both simple and complex elements. Mosaic emphasizes partitioning a surface into distinct regions, enabling modular assembly of complex scenes from smaller, independently defined tiles.
Defining Composite Images
Composite images are created by merging multiple visual elements from different sources into a single, seamless picture, enhancing storytelling or artistic expression. These images often involve careful blending, masking, and layering techniques to maintain harmony and visual coherence across diverse components. The process allows for creative freedom in constructing scenes that either represent realistic environments or imaginative concepts beyond natural photography.
Understanding Mosaic Techniques
Mosaic techniques involve arranging small, colored pieces of materials such as glass, stone, or ceramic into intricate patterns or images, creating detailed visual effects and texture. These techniques emphasize precise placement and color variation to achieve depth and contrast, often used in artistic and architectural applications. Understanding mosaic methods requires knowledge of tesserae selection, grout application, and surface preparation to ensure durability and aesthetic appeal.
Key Differences Between Composite and Mosaic
Composite materials combine two or more distinct substances to create a new material with enhanced properties, such as increased strength and durability. Mosaic, often referring to art or biological patterns, involves assembling small, distinct pieces to form a cohesive image or pattern rather than altering material properties. The key difference lies in composites being engineered materials designed for performance enhancement, whereas mosaics emphasize aesthetic arrangement and pattern formation.
Common Applications in Art and Design
Composite images integrate multiple elements into a single, cohesive artwork widely used in digital art, advertising, and photo manipulation to create surreal or enhanced visuals. Mosaic art arranges small, colored pieces such as tiles or glass to form patterns or images, commonly found in architectural decoration, classical art, and contemporary installations. Both techniques apply distinct methods for visual storytelling, with composites emphasizing layered imagery and mosaics focusing on texture and pattern.
Tools and Software for Creating Composites
Photoshop and GIMP are industry-standard tools for creating composite images, offering advanced layering and masking capabilities to seamlessly blend multiple photos. Adobe After Effects excels in composite video creation, providing robust tracking, keying, and visual effects integration for complex motion graphics. For mosaics, specialized software such as AndreaMosaic and Mazaika automate tile selection and arrangement, enabling high-resolution image mosaics built from thousands of smaller images.
Tools and Software for Mosaic Creation
Mosaic creation tools such as Adobe Photoshop, Mazaika, and Mosaic Creator offer advanced image processing algorithms that assemble numerous small images into seamless large-scale mosaics. Composite image software like GIMP and Affinity Photo focus on layering and blending individual photos for artistic or realistic effects, differing from mosaic tools that emphasize pattern recognition and tile placement. Specialized mosaic software often includes features like color matching, tile shape customization, and high-resolution output options essential for detailed mosaic productions.
Advantages of Using Composite Images
Composite images offer enhanced creative flexibility by seamlessly blending multiple photos into a single cohesive artwork, which enables designers to convey complex concepts more effectively. They allow for precise control over lighting, color grading, and perspective, resulting in visually striking images that stand out in advertising and digital media. Composite techniques also streamline post-production workflows, reducing the need for extensive reshoots and saving time and costs.
Benefits of Mosaic Artworks
Mosaic artworks offer durability and timeless beauty, as individual tesserae made of glass, stone, or ceramic resist fading and wear over time. Their intricate design allows for high visual complexity and rich texture, providing a unique aesthetic that composite images often cannot achieve. The ability to customize mosaics with diverse materials enhances artistic expression and adds cultural and historical value to architectural and decorative projects.
Choosing the Right Method: Composite or Mosaic
Choosing between composite and mosaic methods depends on the specific goals and data characteristics of your project. Composite techniques blend multiple images to create a single, seamless output, ideal for enhancing visual coherence in satellite imagery or medical imaging. Mosaic approaches stitch together adjacent images to cover larger areas with minimal overlap, suitable for mapping extensive geographic regions or assembling large-scale aerial photographs.
Composite Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com