Reboilers and evaporators are essential components in industrial heat exchange processes, with reboilers providing the necessary heat to drive vaporization in distillation columns, while evaporators remove solvent through boiling. Understanding the differences in their functions and designs helps optimize energy efficiency and process performance. Explore the rest of this article to learn how these devices impact your industrial operations.
Table of Comparison
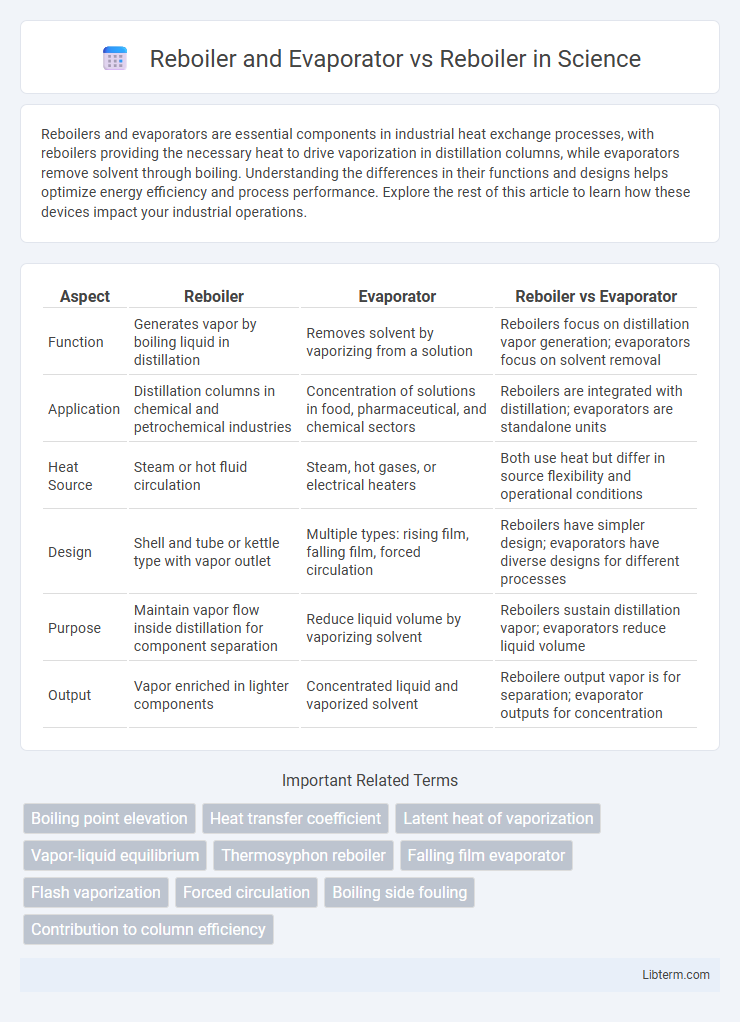
| Aspect | Reboiler | Evaporator | Reboiler vs Evaporator |
|---|---|---|---|
| Function | Generates vapor by boiling liquid in distillation | Removes solvent by vaporizing from a solution | Reboilers focus on distillation vapor generation; evaporators focus on solvent removal |
| Application | Distillation columns in chemical and petrochemical industries | Concentration of solutions in food, pharmaceutical, and chemical sectors | Reboilers are integrated with distillation; evaporators are standalone units |
| Heat Source | Steam or hot fluid circulation | Steam, hot gases, or electrical heaters | Both use heat but differ in source flexibility and operational conditions |
| Design | Shell and tube or kettle type with vapor outlet | Multiple types: rising film, falling film, forced circulation | Reboilers have simpler design; evaporators have diverse designs for different processes |
| Purpose | Maintain vapor flow inside distillation for component separation | Reduce liquid volume by vaporizing solvent | Reboilers sustain distillation vapor; evaporators reduce liquid volume |
| Output | Vapor enriched in lighter components | Concentrated liquid and vaporized solvent | Reboilere output vapor is for separation; evaporator outputs for concentration |
Introduction to Reboilers and Evaporators
Reboilers and evaporators are critical heat transfer equipment used in industrial processes for vaporizing liquids. Reboilers supply the necessary heat to the bottom of distillation columns to generate vapor, facilitating separation, while evaporators concentrate solutions by removing solvents through evaporation. Understanding the functional differences between reboilers and evaporators enables optimized design and operation in chemical, petroleum, and food processing industries.
Definition and Function of Reboilers
Reboilers are heat exchangers used to provide the necessary heat to the bottom of distillation columns, facilitating the vaporization of the liquid mixture to enable separation. Unlike evaporators, which primarily remove moisture by turning liquid into vapor on a surface, reboilers supply continuous heat to sustain vapor-liquid equilibrium in the column's bottom section. Their function is critical to maintaining the desired separation efficiency by generating vapor that rises through the column, driving the distillation process.
Overview of Evaporators in Industrial Processes
Evaporators are essential in industrial processes for concentrating solutions by vaporizing solvents, primarily water, under controlled heat application, which enhances process efficiency and product quality. Unlike reboilers that primarily supply heat to distillation columns for vapor generation, evaporators are standalone units crucial in industries like food processing, pharmaceuticals, and chemical manufacturing where precise vapor-liquid separation is needed. Advanced evaporator designs, such as falling film and forced circulation types, optimize heat transfer rates and minimize fouling, leading to reduced downtime and operational costs in large-scale production environments.
Key Differences Between Reboilers and Evaporators
Reboilers provide the necessary heat to a distillation column by boiling the liquid at the bottom, facilitating vaporization and separation of components. Evaporators, on the other hand, remove solvents from solutions through evaporation, typically concentrating the solute without phase separation involved in distillation processes. The key difference lies in the reboiler's role in vapor-liquid equilibrium within distillation columns, whereas evaporators primarily focus on concentration or drying by phase change from liquid to vapor.
Types of Reboilers: Designs and Applications
Types of reboilers include kettle, thermosyphon, and forced circulation designs, each optimized for specific applications such as distillation, absorption, and evaporation processes. Kettle reboilers are widely used for their reliability in large-scale distillation, while thermosyphon reboilers offer efficient natural circulation heating ideal for moderate duty applications. Forced circulation reboilers provide precise temperature control suitable for viscous or fouling fluids, enhancing operational flexibility compared to conventional evaporators used primarily for phase change and concentration tasks.
Reboiler vs. Reboiler: Comparing Various Reboiler Designs
Reboilers play a critical role in vapor-liquid separation processes by providing necessary heat to generate vapor from the liquid mixture. Comparing various reboiler designs, such as kettle-type, thermosyphon, and fired reboilers, reveals differences in heat transfer efficiency, operational reliability, and suitability for specific process conditions. Selecting the optimal reboiler design depends on factors like fluid properties, fouling tendencies, and process temperature requirements, ensuring efficient energy utilization and stable distillation performance.
Operational Principles of Reboilers and Evaporators
Reboilers transfer heat to a liquid mixture to generate vapor, typically utilizing steam or hot fluids to boil the bottom liquid in distillation columns. Evaporators remove solvent from solutions by vaporizing the solvent at reduced pressure or elevated temperatures to concentrate the remaining liquid. Operationally, reboilers maintain consistent vapor production to sustain separation efficiency, while evaporators focus on controlled solvent removal to achieve product concentration.
Efficiency Factors: Reboilers vs. Evaporators
Reboilers and evaporators both play critical roles in heat transfer processes, yet their efficiency hinges on distinct factors: reboiler efficiency largely depends on heat transfer area, fluid flow rates, and temperature gradients, while evaporator efficiency is influenced by vapor-liquid separation efficiency, concentration polarization, and fouling resistance. Reboilers optimize energy use by recovering latent heat to vaporize the liquid, minimizing energy loss, whereas evaporators focus on maximizing surface area contact and minimizing scaling to improve evaporation rates. Understanding the thermodynamic properties and maintenance of heat exchanger surfaces is vital for enhancing overall system efficiency in both equipment types.
Common Challenges and Maintenance Issues
Reboilers and evaporators often face scaling, corrosion, and fouling due to high heat transfer rates and exposure to process fluids, leading to decreased efficiency and increased downtime. Common challenges include maintaining optimal thermal performance and preventing tube leaks, which require regular inspection and cleaning using chemical or mechanical methods. Preventive maintenance strategies like monitoring temperature differentials, pressure drops, and chemical composition help extend equipment life and reduce unplanned shutdowns.
Application Suitability: When to Choose Each System
Reboilers are primarily suited for applications requiring precise heat transfer to vaporize liquid mixtures in distillation columns, especially in chemical and petrochemical industries. Evaporator-reboiler systems excel in processes that need simultaneous evaporation and recycling of heat, making them ideal for waste treatment, desalination, and food processing. Choosing between these systems depends on factors like thermal efficiency, fluid properties, and operational complexity, with reboilers favored for simplicity and evaporator-reboiler setups for higher energy recovery.
Reboiler and Evaporator Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com