Matutinal activities, those occurring in the early morning, are linked to increased productivity and mental clarity throughout the day. Adopting a matutinal routine can positively influence your sleep cycle and overall health by aligning with natural circadian rhythms. Explore the rest of the article to discover how incorporating matutinal habits can transform your daily life.
Table of Comparison
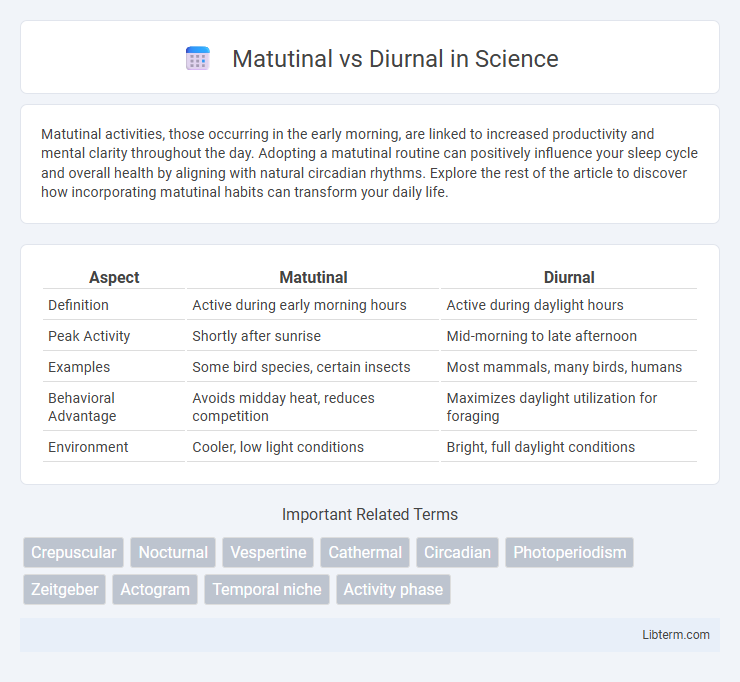
| Aspect | Matutinal | Diurnal |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Active during early morning hours | Active during daylight hours |
| Peak Activity | Shortly after sunrise | Mid-morning to late afternoon |
| Examples | Some bird species, certain insects | Most mammals, many birds, humans |
| Behavioral Advantage | Avoids midday heat, reduces competition | Maximizes daylight utilization for foraging |
| Environment | Cooler, low light conditions | Bright, full daylight conditions |
Understanding Matutinal and Diurnal Behaviors
Matutinal behaviors refer to activities occurring during the early morning, often at dawn, while diurnal behaviors describe actions carried out throughout the daylight hours. Many animals exhibit matutinal patterns to exploit cooler temperatures and reduced predation risk at sunrise, contrasting with diurnal species that remain active during the full spectrum of daylight. Understanding these temporal activity patterns is crucial in ecology for studying species' adaptation, resource use, and predator-prey dynamics.
Definition of Matutinal Activity
Matutinal activity refers to behavior or physiological patterns occurring predominantly in the early morning hours, typically shortly after dawn. This contrasts with diurnal activity, which encompasses behaviors active throughout the daytime period. Matutinal organisms often exploit cooler temperatures and reduced competition found in morning hours for feeding or mating.
What Does Diurnal Mean?
Diurnal describes organisms or behaviors that are active during daylight hours and rest at night, contrasting with nocturnal or matutinal activity patterns. This term is commonly applied in zoology and ecology to classify animal species based on their daily activity cycles. Diurnal animals, such as many bird and primate species, rely on daylight for feeding, mating, and other essential activities.
Key Differences Between Matutinal and Diurnal Animals
Matutinal animals are primarily active during the early morning hours, exhibiting peak activity just before and around dawn, whereas diurnal animals remain active throughout the daylight period. Matutinal species have adapted to cooler temperatures and reduced predation risk during transitional twilight, while diurnal species exploit full daylight for foraging and social interactions. These behavioral patterns influence physiological adaptations such as visual sensitivity, with matutinal animals often possessing heightened low-light vision compared to the broad daylight visual acuity seen in diurnal animals.
Adaptations in Matutinal vs Diurnal Species
Matutinal species exhibit adaptations such as enhanced low-light vision and increased sensitivity to temperature fluctuations, enabling activity during early morning hours when light levels and temperatures are cooler. Diurnal species, conversely, possess adaptations including high visual acuity in bright light, thermoregulation mechanisms to cope with daytime heat, and behaviors optimized for peak daylight activity. These distinct physiological and behavioral traits reflect evolutionary responses to the differing environmental pressures experienced during matutinal and diurnal periods.
Environmental Factors Influencing Activity Patterns
Matutinal organisms exhibit peak activity during early morning hours, often taking advantage of cooler temperatures and reduced predation risk, which are significant environmental factors influencing this behavior. Diurnal species are active throughout daylight hours, optimizing energy use with abundant sunlight for foraging and social interactions. Temperature fluctuations, light intensity, and predator presence critically shape whether species adopt matutinal or diurnal activity patterns.
Advantages of Being Matutinal
Matutinal individuals, who are active early in the morning, benefit from increased productivity and enhanced mental clarity due to fewer distractions and higher cognitive function in the early hours. This advantage often leads to better time management and the ability to tackle complex tasks before the typical daily rush begins. Studies also show that matutinal people tend to experience improved mood and energy levels throughout the day compared to diurnal individuals who are more active during daylight but may face more interruptions.
Benefits of Diurnal Activity
Diurnal activity, characterized by being active during daylight hours, aligns with human circadian rhythms, promoting improved sleep quality and overall well-being. Exposure to natural sunlight during diurnal hours enhances vitamin D synthesis, supporting immune function and mood regulation. This pattern also facilitates social interaction and productivity, as most societal activities and services operate on a diurnal schedule.
Examples of Matutinal and Diurnal Animals
Matutinal animals such as the common nighthawk (Chordeiles minor) and certain species of mosquitoes are most active during the early morning hours at dawn, taking advantage of this niche to avoid predators and extreme heat. Diurnal animals including lions (Panthera leo), parrots (Psittaciformes), and humans (Homo sapiens) exhibit peak activity during daylight, benefiting from visual hunting and social interaction opportunities. Understanding these activity patterns aids in ecological studies and wildlife management strategies.
Evolutionary Significance of Activity Timing
Matutinal species, active during early morning hours, and diurnal species, active throughout daylight, exhibit distinct evolutionary adaptations tied to their activity timing. Matutinal behavior reduces competition and predation risk by exploiting cooler temperatures and lower predator activity at dawn, enhancing survival and energy efficiency. Diurnal activity aligns with optimal foraging opportunities and social interactions, driving evolutionary traits favoring visual acuity and thermoregulation.
Matutinal Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com