Core electrons are the innermost electrons in an atom that remain tightly bound to the nucleus, playing a crucial role in shielding the outer electrons from nuclear charge. These electrons influence atomic properties and chemical behavior by affecting the effective nuclear charge experienced by valence electrons. Discover how understanding core electrons can deepen your insight into atomic structure and reactivity in the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
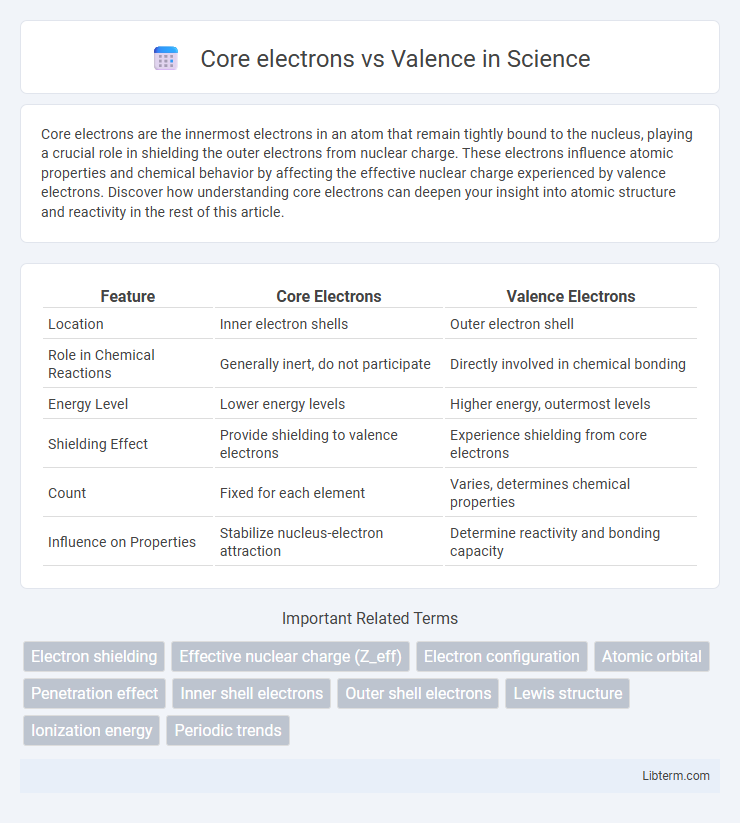
| Feature | Core Electrons | Valence Electrons |
|---|---|---|
| Location | Inner electron shells | Outer electron shell |
| Role in Chemical Reactions | Generally inert, do not participate | Directly involved in chemical bonding |
| Energy Level | Lower energy levels | Higher energy, outermost levels |
| Shielding Effect | Provide shielding to valence electrons | Experience shielding from core electrons |
| Count | Fixed for each element | Varies, determines chemical properties |
| Influence on Properties | Stabilize nucleus-electron attraction | Determine reactivity and bonding capacity |
Introduction to Core and Valence Electrons
Core electrons are tightly bound to the nucleus and occupy the inner shells of an atom, playing a minimal role in chemical reactions. Valence electrons reside in the outermost shell and primarily determine an element's chemical properties and bonding behavior. Understanding the distinction between core and valence electrons is essential for predicting atom reactivity and molecular structure.
Definition of Core Electrons
Core electrons are the electrons found in the inner shells of an atom, residing closer to the nucleus and not involved in chemical bonding. These electrons have lower energy levels compared to valence electrons, which occupy the outermost shell and participate in forming chemical bonds. The distinction between core and valence electrons is essential for understanding an atom's reactivity and its placement in the periodic table.
Definition of Valence Electrons
Valence electrons are the outermost electrons of an atom that participate in chemical bonding and determine the atom's reactivity and chemical properties. Core electrons, in contrast, are the inner electrons that do not typically interact in chemical reactions and primarily serve to shield the valence electrons from the nucleus. The number of valence electrons influences the atom's ability to form covalent or ionic bonds, playing a crucial role in the formation of molecules and compounds.
Location of Core vs Valence Electrons in Atoms
Core electrons are located in the inner shells of an atom, closest to the nucleus, where they experience a strong electrostatic attraction from the positively charged protons. Valence electrons occupy the outermost electron shell and determine the chemical reactivity and bonding behavior of the atom. The distinct locations of core and valence electrons influence atomic size, ionization energy, and electron shielding effects in multi-electron atoms.
Role of Core Electrons in Atomic Structure
Core electrons, located in inner atomic shells, primarily serve to shield the nucleus, reducing the effective nuclear charge experienced by valence electrons and stabilizing the atom's overall structure. These electrons do not typically participate in chemical bonding, allowing valence electrons to determine reactivity and bond formation. The presence of core electrons influences atomic radius and ionization energy by modulating the electrostatic forces within the atom.
Importance of Valence Electrons in Chemical Reactions
Valence electrons, located in the outermost shell of an atom, play a crucial role in chemical reactions by determining an element's reactivity and bonding behavior. These electrons participate directly in forming covalent, ionic, and metallic bonds, influencing molecule formation and compound stability. In contrast, core electrons remain tightly bound to the nucleus and do not typically engage in chemical interactions, making valence electrons essential for predicting reaction outcomes and chemical properties.
Differences in Energy Levels: Core vs Valence
Core electrons reside in the inner energy levels of an atom, possessing significantly lower energy compared to valence electrons found in the outermost shells. Valence electrons occupy higher energy levels, making them more reactive and crucial in chemical bonding and interactions. The energy difference between core and valence electrons influences atomic properties such as ionization energy and electron affinity.
How to Identify Core and Valence Electrons
Core electrons are located in the inner shells of an atom, occupying energy levels closer to the nucleus, while valence electrons reside in the outermost shell and participate in chemical bonding. To identify core and valence electrons, first determine the element's electron configuration and recognize that electrons in completely filled inner shells are core electrons, whereas electrons in the highest principal quantum number shell are valence electrons. For example, in sodium (Na), the electron configuration is 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s1, where the 1s2 2s2 2p6 electrons are core, and the 3s1 electron is a valence electron.
Core and Valence Electrons in the Periodic Table
Core electrons are the inner electrons of an atom that reside in the energy levels below the outermost shell, playing a critical role in shielding valence electrons from the nucleus. Valence electrons are located in the outermost shell and primarily determine an element's chemical reactivity and bonding behavior, as seen across groups in the Periodic Table where elements within the same group have similar valence electron configurations. The distinction between core and valence electrons is essential for understanding periodic trends such as atomic size, ionization energy, and electronegativity.
Summary: Key Differences and Significance
Core electrons occupy inner shells closest to the nucleus, exhibiting low reactivity and shielding valence electrons from nuclear charge. Valence electrons reside in the outermost shell and primarily determine an element's chemical properties and bonding behavior. Understanding the distinction between core and valence electrons is essential for predicting atomic interactions and reactivity trends in chemistry.
Core electrons Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com