Sublimation is the process where a solid changes directly into a gas without passing through the liquid phase, commonly seen in materials like dry ice or mothballs. This phase transition occurs under specific temperature and pressure conditions, making it valuable in industrial applications such as freeze-drying and material purification. Discover how sublimation impacts various fields and enhances your understanding by reading the full article.
Table of Comparison
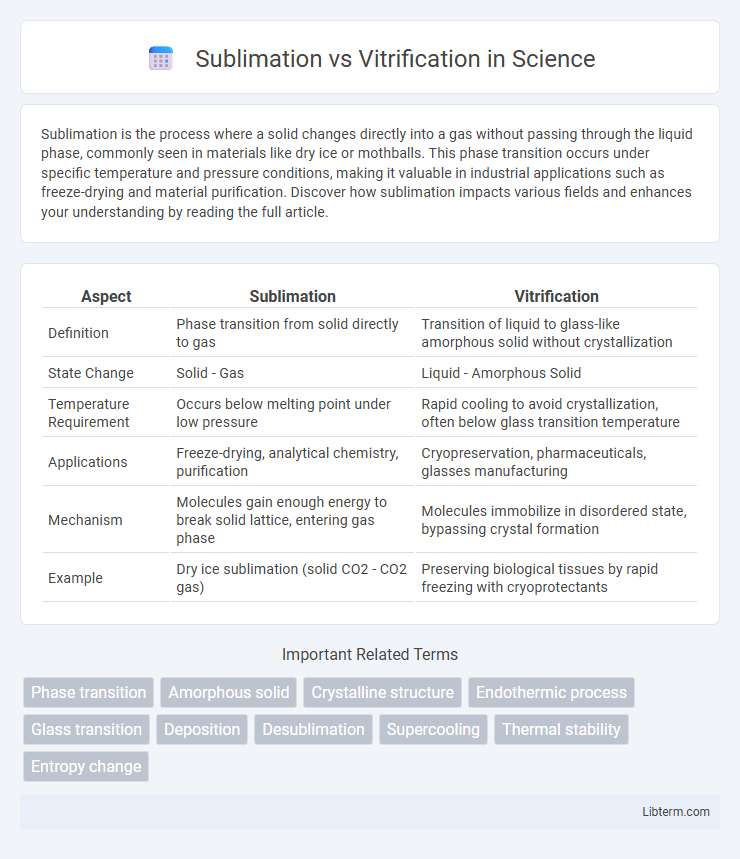
| Aspect | Sublimation | Vitrification |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Phase transition from solid directly to gas | Transition of liquid to glass-like amorphous solid without crystallization |
| State Change | Solid - Gas | Liquid - Amorphous Solid |
| Temperature Requirement | Occurs below melting point under low pressure | Rapid cooling to avoid crystallization, often below glass transition temperature |
| Applications | Freeze-drying, analytical chemistry, purification | Cryopreservation, pharmaceuticals, glasses manufacturing |
| Mechanism | Molecules gain enough energy to break solid lattice, entering gas phase | Molecules immobilize in disordered state, bypassing crystal formation |
| Example | Dry ice sublimation (solid CO2 - CO2 gas) | Preserving biological tissues by rapid freezing with cryoprotectants |
Introduction to Sublimation and Vitrification
Sublimation is the phase transition where a substance changes directly from solid to vapor without passing through the liquid state, commonly utilized in freeze-drying processes to preserve biological samples. Vitrification involves the rapid cooling of a liquid into a glass-like amorphous solid, preventing ice crystal formation and preserving cellular structures in cryopreservation. Both techniques are critical in pharmaceutical, biological, and cryogenic applications for maintaining material integrity during storage and transport.
Defining Sublimation: Process and Principles
Sublimation is the phase transition where a substance changes directly from a solid to a gas without passing through a liquid state, driven by temperature and pressure conditions below its triple point. This endothermic process occurs when molecules gain sufficient kinetic energy to overcome intermolecular forces, bypassing the melting phase. Sublimation is widely utilized in applications such as freeze-drying, purification of solids, and material deposition techniques.
Vitrification Explained: A Comprehensive Overview
Vitrification is a cryopreservation technique that rapidly freezes biological samples, such as embryos or tissues, by transforming them into a glass-like solid without ice crystal formation, preserving cellular integrity. This method involves the use of high concentrations of cryoprotectants and ultra-rapid cooling rates, which prevents damage commonly caused by ice crystals during traditional freezing methods. Vitrification is widely used in reproductive medicine and biobanking due to its effectiveness in maintaining viability and functionality of biological specimens during long-term storage.
Key Differences Between Sublimation and Vitrification
Sublimation involves the direct phase transition of a substance from solid to gas without passing through the liquid phase, commonly used in freeze-drying to preserve biological samples. Vitrification refers to the rapid cooling of a liquid into a glass-like, non-crystalline solid state, preventing ice crystal formation critical in cryopreservation. Key differences include the phase transition process, with sublimation bypassing the liquid phase, while vitrification involves preventing crystallization by solidifying into an amorphous glass.
Applications of Sublimation in Industry and Science
Sublimation is widely used in industry for freeze-drying pharmaceuticals, preserving biological samples, and purifying heat-sensitive materials by directly converting solids to gas without passing through the liquid phase. In scientific research, sublimation facilitates the preparation of high-purity compounds and enables the deposition of thin films in semiconductor manufacturing through physical vapor deposition techniques. This process supports applications such as forensic analysis, where sublimation aids in revealing latent fingerprints using dye sublimation methods.
Vitrification Uses in Medicine and Research
Vitrification employs ultra-rapid cooling to transform biological samples into a glass-like, ice-free state, preventing ice crystal formation that can damage cellular structures. This technique is widely used in cryopreservation of oocytes, embryos, and stem cells, enhancing survival rates and viability in assisted reproductive technology and regenerative medicine. Researchers utilize vitrification for preserving complex tissues and organ samples, supporting advancements in transplantation and biomedical studies.
Advantages and Limitations of Sublimation
Sublimation offers advantages such as preserving the structural integrity of thermally sensitive materials by bypassing the liquid phase, which reduces the risk of contamination and distortion during drying. It enables rapid dehydration with minimal shrinkage, making it ideal for pharmaceuticals, food preservation, and biological samples. However, limitations include high energy consumption, longer processing times, and the need for specialized equipment to maintain controlled temperature and pressure conditions.
Pros and Cons of Vitrification Techniques
Vitrification techniques offer rapid cooling rates that prevent ice crystal formation, preserving the structural integrity and viability of biological samples such as embryos and oocytes. This method minimizes cryodamage and enhances post-thaw survival rates compared to traditional slow freezing methods. However, vitrification requires high concentrations of cryoprotectants, which can introduce cytotoxicity risks, and demands precise handling to avoid thermal stress during the process.
Technological Advances in Sublimation and Vitrification
Technological advances in sublimation have enhanced freeze-drying processes through improved temperature and pressure controls, enabling faster dehydration of heat-sensitive materials like pharmaceuticals and food products while preserving structural integrity. Vitrification techniques have progressed with optimized cryoprotectant formulations and rapid cooling methods that prevent ice crystal formation, ensuring higher viability in biological samples such as embryos and tissues. Innovations in both methods leverage automation and real-time monitoring systems, increasing consistency, efficiency, and scalability in industrial and biomedical applications.
Choosing Between Sublimation and Vitrification: Which Is Best?
Choosing between sublimation and vitrification depends on the specific preservation needs and material properties. Sublimation is ideal for drying materials without passing through the liquid phase, preserving structural integrity in heat-sensitive substances like biological samples or freeze-dried food. Vitrification excels in cryopreservation by preventing ice crystal formation, making it the best choice for delicate tissues and cells requiring rapid cooling and long-term storage.
Sublimation Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com