Crepuscular animals are active primarily during the twilight periods of dawn and dusk, optimizing their behavior to avoid predators and extreme temperatures. This unique adaptation enhances survival and hunting efficiency in low-light environments. Explore the rest of the article to discover which creatures are crepuscular and how this behavior impacts their ecosystem.
Table of Comparison
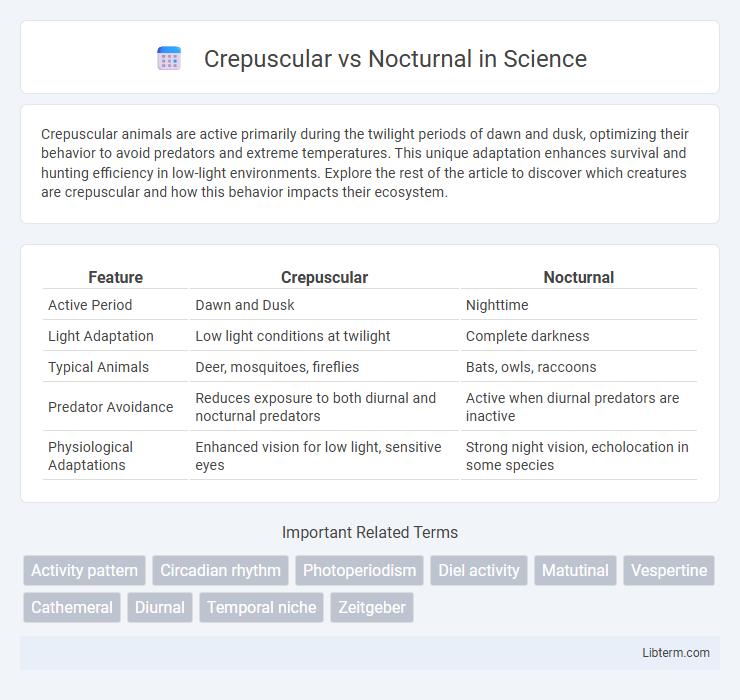
| Feature | Crepuscular | Nocturnal |
|---|---|---|
| Active Period | Dawn and Dusk | Nighttime |
| Light Adaptation | Low light conditions at twilight | Complete darkness |
| Typical Animals | Deer, mosquitoes, fireflies | Bats, owls, raccoons |
| Predator Avoidance | Reduces exposure to both diurnal and nocturnal predators | Active when diurnal predators are inactive |
| Physiological Adaptations | Enhanced vision for low light, sensitive eyes | Strong night vision, echolocation in some species |
Understanding Crepuscular and Nocturnal Behaviors
Crepuscular animals are primarily active during twilight periods--dawn and dusk--capitalizing on low light conditions to forage and avoid predators, whereas nocturnal animals exhibit peak activity during the night when darkness prevails. Understanding crepuscular and nocturnal behaviors involves examining adaptations such as enhanced night vision, heightened sensory perception, and behavioral patterns that optimize survival and resource acquisition in dim or dark environments. Research on these activity cycles reveals crucial insights into ecological dynamics, predator-prey interactions, and habitat utilization in various species.
Key Differences Between Crepuscular and Nocturnal Animals
Crepuscular animals are primarily active during twilight periods--dawn and dusk--while nocturnal animals are active throughout the night. Crepuscular behavior offers advantages like reduced predation risk and cooler temperatures during transitional light conditions, whereas nocturnal animals rely on adaptations such as enhanced night vision and heightened senses to navigate complete darkness. These differing activity patterns influence ecological roles, predator-prey dynamics, and habitat utilization in various species.
Evolutionary Advantages of Crepuscular Activity
Crepuscular animals benefit from evolutionary advantages by avoiding the extreme heat of the day and the high predation risks found during full nighttime, optimizing survival and energy efficiency. Their activity during dawn and dusk reduces competition for resources, as fewer species are active at these transitional times. This temporal niche allows crepuscular species to exploit prey availability while minimizing exposure to predators that are primarily diurnal or nocturnal.
Nocturnal Adaptations and Survival Strategies
Nocturnal animals possess specialized adaptations such as enhanced night vision through a high density of rod cells in their retinas and tapetum lucidum, which reflects light to improve sight in low-light conditions. They also exhibit heightened auditory and olfactory senses to navigate and hunt in the dark, alongside behavioral strategies like reduced movement to avoid detection by predators. These adaptations ensure efficient foraging, predator evasion, and energy conservation during nighttime activity.
Examples of Common Crepuscular Species
Examples of common crepuscular species include white-tailed deer (Odocoileus virginianus), eastern cottontail rabbits (Sylvilagus floridanus), and certain species of bats such as the little brown bat (Myotis lucifugus). These animals are most active during the twilight periods of dawn and dusk, which helps them avoid predators and extreme temperatures. Crepuscular behavior differs from nocturnal habits observed in animals like owls or raccoons, which are primarily active during the night.
Notable Nocturnal Animals Around the World
Notable nocturnal animals around the world include owls, bats, and various species of rodents that have adapted to thrive in low-light environments. These animals possess specialized sensory adaptations such as enhanced night vision, echolocation, and acute hearing to navigate and hunt effectively in darkness. Their nocturnal behavior helps reduce competition and predation while maximizing access to food resources unavailable during daylight hours.
Environmental Factors Influencing Activity Patterns
Crepuscular animals are primarily active during dawn and dusk, adapting to lower light levels and moderate temperatures that reduce predation risk and energy expenditure. Nocturnal species thrive in nighttime conditions, exploiting cooler temperatures and reduced competition for resources while avoiding daytime predators. Environmental factors such as ambient temperature, predator presence, and food availability strongly influence whether a species adopts crepuscular or nocturnal activity patterns.
Impact of Human Activity on Crepuscular and Nocturnal Wildlife
Human activity significantly disrupts crepuscular and nocturnal wildlife by altering natural light cycles and habitats, leading to behavioral changes and reduced survival rates. Artificial lighting, such as streetlights and urban development, interferes with nocturnal animals' navigation, foraging, and reproduction, while crepuscular species experience compressed activity windows. Habitat fragmentation and noise pollution from human presence further exacerbate stress and decrease biodiversity among both crepuscular and nocturnal ecosystems.
How to Observe Crepuscular vs Nocturnal Animals
Observing crepuscular animals is most effective during twilight hours--dawn and dusk--when these species are naturally active in low light conditions. Nocturnal animals are best observed using night-vision equipment or infrared cameras after sunset, as they remain active throughout the night. Selecting the right time and specialized gear enhances visibility and increases chances of spotting these distinct behavioral patterns in wildlife.
Conclusion: The Importance of Diel Activity in Ecosystems
Diel activity patterns, such as crepuscular (active during dawn and dusk) and nocturnal (active at night), play crucial roles in ecosystem dynamics by influencing species interactions, predator-prey relationships, and resource availability. Understanding these activity cycles aids in biodiversity conservation and habitat management by revealing temporal niches that reduce competition and promote ecosystem stability. The balance between crepuscular and nocturnal behaviors is essential for maintaining ecological processes and resilience in diverse habitats.
Crepuscular Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com