Ambilineal descent systems allow individuals to trace their ancestry through either the maternal or paternal line based on personal or cultural choice, offering flexibility in family affiliations. This system contrasts with strictly patrilineal or matrilineal societies by enabling varied inheritance and social identity patterns. Discover how ambilineal descent impacts social structures and your understanding of lineage by exploring the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
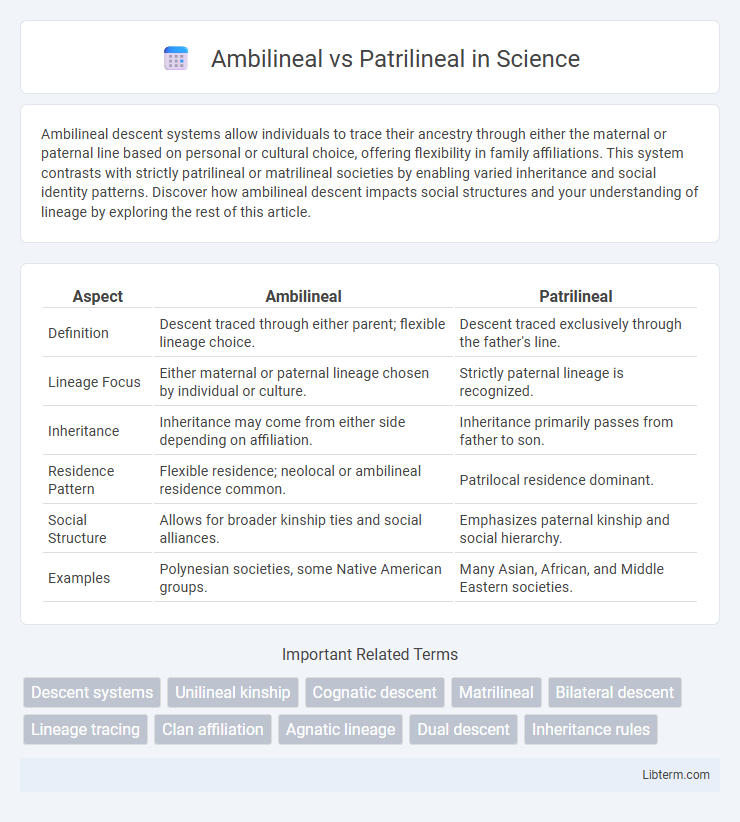
| Aspect | Ambilineal | Patrilineal |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Descent traced through either parent; flexible lineage choice. | Descent traced exclusively through the father's line. |
| Lineage Focus | Either maternal or paternal lineage chosen by individual or culture. | Strictly paternal lineage is recognized. |
| Inheritance | Inheritance may come from either side depending on affiliation. | Inheritance primarily passes from father to son. |
| Residence Pattern | Flexible residence; neolocal or ambilineal residence common. | Patrilocal residence dominant. |
| Social Structure | Allows for broader kinship ties and social alliances. | Emphasizes paternal kinship and social hierarchy. |
| Examples | Polynesian societies, some Native American groups. | Many Asian, African, and Middle Eastern societies. |
Understanding Lineal Descent Systems
Ambilineal descent systems allow individuals to trace their lineage through both maternal and paternal lines, offering flexible kinship affiliations based on choice or social context. Patrilineal descent systems strictly follow the male line, determining inheritance, clan membership, and social identity through the father's lineage. Understanding these lineal descent systems is crucial for analyzing kinship patterns, inheritance rights, and social organization in different cultures worldwide.
What Is Ambilineal Descent?
Ambilineal descent is a kinship system allowing individuals to trace their lineage through either the mother's or father's ancestry, depending on personal or social choice, rather than being strictly patrilineal or matrilineal. This flexible descent system contrasts with patrilineal descent, where lineage and inheritance follow the father's line exclusively. Ambilineal societies often emphasize bilateral family ties, enabling more diverse inheritance patterns and social affiliations.
Defining Patrilineal Descent
Patrilineal descent is a kinship system where lineage, inheritance, and social identity are traced through the male line, emphasizing the importance of paternal ancestry in determining family ties. This system contrasts with ambilineal descent, which allows individuals to affiliate with either their mother's or father's lineage, providing more flexibility in tracing descent. Patrilineal societies often prioritize male inheritance and succession, reinforcing male authority and lineage continuity across generations.
Key Differences Between Ambilineal and Patrilineal
Ambilineal descent systems allow individuals to choose affiliation with either the mother's or father's lineage, providing flexibility in inheritance and clan membership, whereas patrilineal systems strictly trace descent and inheritance through the male line only. Ambilineal societies often exhibit more fluid social structures and property rights distributed based on selected lineage, contrasting with patrilineal societies where male heirs typically inherit land, titles, and family name. Key differences include the method of lineage determination, inheritance patterns, and the social roles assigned within each system.
Cultural Examples of Ambilineal Societies
Ambilineal descent systems, found in cultures like the Hawaiian and certain Polynesian societies, allow individuals to trace lineage through either the mother or father, offering flexibility in inheritance and social identity. In contrast to strictly patrilineal societies, where descent and inheritance follow the male line exclusively, ambilineal systems emphasize bilateral kinship ties and often incorporate both maternal and paternal relatives in social obligations and property rights. Examples include the Kanak people of New Caledonia, whose ambilineal descent shapes clan membership and resource distribution, highlighting diverse cultural approaches to family and lineage organization.
Societies Practicing Patrilineal Descent
Societies practicing patrilineal descent trace lineage and inheritance through the male line, commonly observed in agrarian and patriarchal cultures across Asia, Africa, and parts of the Middle East. This system emphasizes male authority in family structure, land ownership, and succession, often affecting social roles and kinship obligations. Patrilineal descent contrasts with ambilineal systems by restricting descent recognition to one gendered lineage, reinforcing patriarchal norms and inheritance patterns.
Inheritance Patterns: Ambilineal vs Patrilineal
Ambilineal inheritance allows individuals to choose affiliation with either the mother's or father's lineage, granting flexibility in property and status transmission across generations. Patrilineal inheritance strictly follows the male line, where property, names, and titles pass exclusively from fathers to sons, reinforcing male dominance in lineage continuity. These contrasting patterns influence family structure, resource control, and social identity within different cultural systems.
Social Implications and Family Structure
Ambilineal descent systems allow individuals to trace ancestry through either the maternal or paternal line, promoting flexible family structures and accommodating diverse social roles within kinship networks. Patrilineal systems emphasize lineage through the male line, often resulting in patriarchal family dynamics where inheritance, social status, and residence patterns revolve around male descendants. The social implications of ambilineal descent include greater individual autonomy and bilateral alliances, whereas patrilineal descent tends to reinforce male authority and lineage continuity within specific clans or tribes.
Modern Adaptations and Challenges
Modern adaptations of ambilineal and patrilineal kinship systems reveal significant shifts due to urbanization, globalization, and changing gender roles. Ambilineal descent, allowing individuals to choose affiliation with either parental line, increasingly suits diverse family structures and promotes gender equality. Patrilineal systems face challenges adapting to contemporary values, often pressured to accommodate women's inheritance rights and evolving social dynamics.
Conclusion: Choosing Descent Systems
Choosing between ambilineal and patrilineal descent systems depends on cultural priorities, social structure, and inheritance patterns. Ambilineal descent offers flexibility by recognizing lineage through either maternal or paternal lines, promoting broader kinship networks. Patrilineal descent emphasizes male lineage continuity, reinforcing male authority and inheritance within a defined paternal framework.
Ambilineal Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com