Inheritance allows the seamless transfer of assets and wealth from one generation to the next, ensuring your family's financial security and legacy. Understanding the legal frameworks and tax implications involved helps minimize disputes and maximize the value passed on. Explore the rest of the article to learn how to effectively manage and protect your inheritance.
Table of Comparison
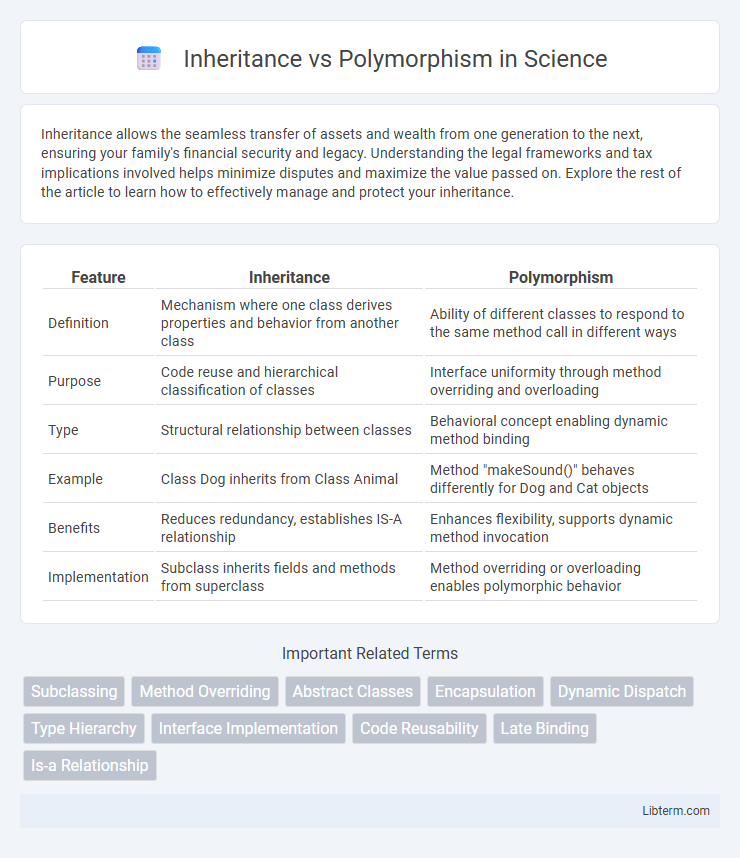
| Feature | Inheritance | Polymorphism |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Mechanism where one class derives properties and behavior from another class | Ability of different classes to respond to the same method call in different ways |
| Purpose | Code reuse and hierarchical classification of classes | Interface uniformity through method overriding and overloading |
| Type | Structural relationship between classes | Behavioral concept enabling dynamic method binding |
| Example | Class Dog inherits from Class Animal | Method "makeSound()" behaves differently for Dog and Cat objects |
| Benefits | Reduces redundancy, establishes IS-A relationship | Enhances flexibility, supports dynamic method invocation |
| Implementation | Subclass inherits fields and methods from superclass | Method overriding or overloading enables polymorphic behavior |
Understanding Inheritance in Object-Oriented Programming
Inheritance in object-oriented programming enables classes to derive properties and behaviors from a parent class, promoting code reuse and hierarchical relationships. It allows a subclass to inherit methods and fields, facilitating the creation of specialized objects while maintaining a shared structure. This mechanism supports extensibility and reduces redundancy by leveraging existing class definitions.
The Basics of Polymorphism Explained
Polymorphism in object-oriented programming allows objects of different classes to be treated as instances of a common superclass, enabling methods to perform different functions based on the object's actual class. It leverages method overriding, where a subclass provides a specific implementation of a method declared in its superclass, enhancing code flexibility and reuse. Unlike inheritance, which defines a hierarchical relationship between classes, polymorphism focuses on the ability to invoke the same method on different objects, resulting in behavior tailored to each object's class.
Key Differences Between Inheritance and Polymorphism
Inheritance enables a class to acquire properties and behaviors from a parent class, promoting code reuse and hierarchical relationships. Polymorphism allows objects of different classes to be treated as instances of a common superclass, enabling methods to perform different tasks based on the object's actual type at runtime. The key difference lies in inheritance establishing an "is-a" relationship for structure reuse, while polymorphism focuses on dynamic method invocation for flexible and extensible behavior.
Advantages of Using Inheritance in Code Design
Inheritance enhances code reusability by allowing new classes to adopt properties and methods from existing ones, reducing redundancy. It promotes logical organization and hierarchical classification, making the codebase easier to maintain and understand. Inheritance also supports method overriding, enabling customized behavior while preserving a consistent interface across related classes.
Benefits of Polymorphism for Code Flexibility
Polymorphism enhances code flexibility by allowing methods to process objects of different classes through a common interface, enabling seamless method overriding and dynamic method binding. This capability reduces code redundancy and increases maintainability by supporting interchangeable object behaviors without altering existing code structures. Unlike inheritance, which establishes a static class hierarchy, polymorphism facilitates runtime decision-making, promoting extensible and adaptable software design.
Common Use Cases for Inheritance
Inheritance is commonly used to establish hierarchical relationships in object-oriented programming, enabling code reuse and logical classification of related classes such as animals in a zoo management system or employee types in a payroll application. It simplifies maintenance by allowing base class modifications to propagate across derived classes while supporting method overriding for specialized behavior. Common use cases include implementing abstract base classes, modeling "is-a" relationships, and promoting extensibility in software design.
Practical Applications of Polymorphism
Polymorphism enables objects of different classes to be treated as instances of a common superclass, streamlining code maintenance and scalability in software development. It allows methods to process objects differently based on their actual class, facilitating dynamic method binding and runtime flexibility in applications such as GUI frameworks, game development, and API integrations. Practical applications include implementing design patterns like Strategy and Observer, where polymorphism supports interchangeable behaviors and dynamic event handling, enhancing modularity and reusability.
Potential Drawbacks of Inheritance
Inheritance can lead to tightly coupled code, making changes in a parent class potentially disruptive to all derived subclasses. Overuse of inheritance may cause fragile base class problems, where modifications introduce bugs or unexpected behavior in child classes. Polymorphism offers more flexible design by allowing objects to be treated as instances of their parent class while maintaining independent implementations.
Limitations and Challenges of Polymorphism
Polymorphism in object-oriented programming faces limitations such as increased complexity in code maintenance and debugging due to dynamic method binding, which can obscure the flow of control. Performance overhead is another challenge, as runtime polymorphism requires additional processing to resolve method calls dynamically compared to compile-time inheritance. Furthermore, excessive use of polymorphism can lead to design difficulties, including creating tightly coupled systems and making it harder to enforce type safety and predict program behavior.
Choosing Between Inheritance and Polymorphism: Best Practices
Choosing between inheritance and polymorphism depends on the design goals and flexibility requirements of your software architecture. Favor inheritance when establishing clear hierarchical relationships to promote code reuse and maintainability, while polymorphism excels in enabling dynamic method behavior through interfaces or abstract classes, supporting extensibility and reducing tight coupling. Best practices suggest using polymorphism for scalable systems requiring interchangeable components and reserving inheritance for situations where subclass behaviors are extensions of a base class.
Inheritance Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com