Integrative approaches combine multiple disciplines or methods to create a comprehensive understanding or solution that addresses complex problems more effectively. This strategy enhances collaboration, innovation, and adaptability across various fields by merging diverse perspectives and expertise. Explore the rest of this article to discover how integrative techniques can transform your approach and yield better results.
Table of Comparison
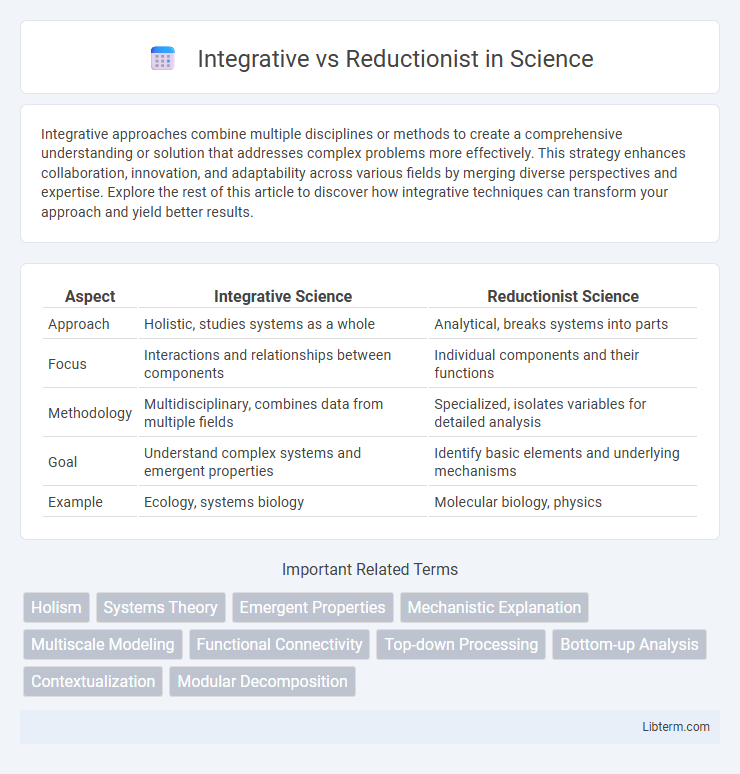
| Aspect | Integrative Science | Reductionist Science |
|---|---|---|
| Approach | Holistic, studies systems as a whole | Analytical, breaks systems into parts |
| Focus | Interactions and relationships between components | Individual components and their functions |
| Methodology | Multidisciplinary, combines data from multiple fields | Specialized, isolates variables for detailed analysis |
| Goal | Understand complex systems and emergent properties | Identify basic elements and underlying mechanisms |
| Example | Ecology, systems biology | Molecular biology, physics |
Understanding Integrative and Reductionist Approaches
Integrative approaches emphasize the holistic understanding of complex systems by examining the interactions between components, whereas reductionist approaches analyze systems by breaking them down into their smallest parts for detailed study. Integrative methods facilitate connections across disciplines, leading to comprehensive insights, while reductionist methods provide precise, mechanistic knowledge about individual elements. Understanding both approaches allows researchers to balance detailed analysis with broad contextual awareness, enhancing problem-solving and innovation across scientific fields.
Historical Perspective: Origins of Both Paradigms
Integrative and reductionist paradigms originated during the scientific revolution, with reductionism rooted in the works of Rene Descartes, emphasizing the analysis of complex systems by breaking them into simpler parts. The integrative approach emerged later as a response to reductionism's limitations, promoting holistic understanding by considering systems as interconnected wholes. Both paradigms have shaped modern science but differ fundamentally in methodology and perspective.
Key Principles of Reductionism
Reductionism emphasizes understanding complex systems by breaking them down into their simplest components, such as molecules, cells, or individual behaviors, to analyze underlying mechanisms. Key principles of reductionism include focusing on specific parts rather than the whole, assuming that the properties of the whole can be fully explained by the properties of its parts, and employing linear cause-and-effect relationships for scientific explanations. This approach is foundational in disciplines like molecular biology and neuroscience, where studying elements in isolation helps reveal fundamental biological processes.
Foundational Concepts of Integrative Thinking
Integrative thinking emphasizes synthesizing diverse perspectives to create innovative solutions, contrasting with reductionist approaches that break problems into isolated parts. Foundational concepts include embracing complexity, balancing opposing ideas, and generating novel solutions that transcend traditional binaries. This approach fosters holistic understanding and adaptive decision-making in complex, dynamic environments.
Strengths and Limitations of Reductionist Methods
Reductionist methods excel in isolating specific variables, enabling precise control and detailed analysis of individual components within complex systems. Their limitation lies in overlooking emergent properties and interactions present in holistic contexts, which integrative approaches capture by considering the system as a whole. This narrow focus can lead to incomplete understanding, particularly in fields like biology or social sciences where interconnectedness is crucial.
Advantages and Challenges of Integrative Approaches
Integrative approaches in science and medicine offer the advantage of addressing complex systems holistically, enabling a comprehensive understanding of interactions within biological, environmental, or social domains. These methods enhance problem-solving by combining multidisciplinary insights, leading to innovative treatments and solutions that reductionist approaches, focused on isolated components, may overlook. Challenges include the difficulty of synthesizing diverse data types, managing increased complexity, and requiring collaboration across specialized fields to achieve meaningful integration.
Application in Science: Integrative vs Reductionist Models
Integrative models in science emphasize the holistic study of complex systems by combining multiple disciplines and levels of analysis to understand interactions and emergent properties. Reductionist models focus on breaking down systems into their basic components to analyze underlying mechanisms and cause-effect relationships at a micro level. The application of integrative approaches is prominent in fields like systems biology and ecology, while reductionist methods are foundational in molecular biology and physics.
Influence on Healthcare and Medicine
Integrative approaches in healthcare emphasize holistic patient care by combining conventional treatments with alternative therapies, enhancing personalized medicine and improving patient outcomes through comprehensive assessments. Reductionist methods focus on isolating specific biological mechanisms and disease causes, driving advancements in targeted drug development and precision diagnostics. The influence of integrative medicine fosters a broader understanding of health beyond symptoms, while reductionist strategies enable the creation of highly specialized interventions critical for complex diseases like cancer and autoimmune disorders.
Interdisciplinary Insights: Bridging the Gap
Integrative approaches synthesize knowledge from multiple disciplines to create comprehensive solutions, while reductionist methods break down complex systems into simpler components for detailed analysis. Interdisciplinary insights bridge the gap by combining holistic understanding with specialized expertise, fostering innovation in fields like systems biology, cognitive science, and environmental studies. This fusion enhances problem-solving capabilities and drives advances in technology, healthcare, and sustainability.
Future Trends: Toward Holistic Understanding
Future trends in science emphasize a shift from reductionist approaches, which isolate components, toward integrative methods that examine complex systems holistically. Advances in artificial intelligence, big data analytics, and systems biology facilitate this transition by enabling multi-dimensional data synthesis and real-time interaction analysis. This trend promises more comprehensive insights into biological, environmental, and social phenomena, fostering breakthroughs in personalized medicine, ecosystem management, and interdisciplinary research.
Integrative Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com