Integrative approaches combine diverse methodologies to create a holistic understanding of complex issues. By bridging different disciplines and perspectives, integrative strategies foster innovation and comprehensive solutions. Explore the rest of the article to discover how integrative techniques can enhance your problem-solving skills.
Table of Comparison
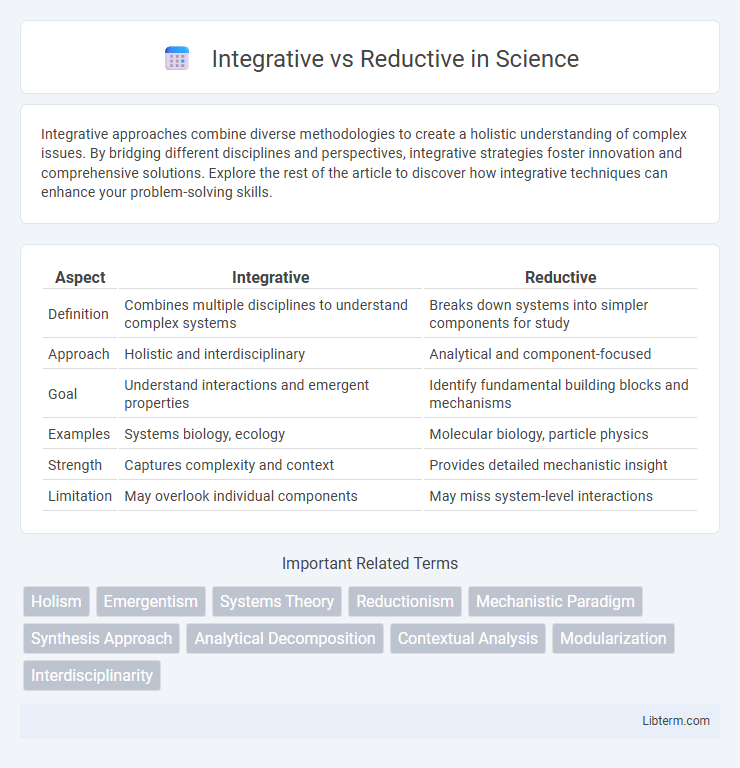
| Aspect | Integrative | Reductive |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Combines multiple disciplines to understand complex systems | Breaks down systems into simpler components for study |
| Approach | Holistic and interdisciplinary | Analytical and component-focused |
| Goal | Understand interactions and emergent properties | Identify fundamental building blocks and mechanisms |
| Examples | Systems biology, ecology | Molecular biology, particle physics |
| Strength | Captures complexity and context | Provides detailed mechanistic insight |
| Limitation | May overlook individual components | May miss system-level interactions |
Understanding Integrative and Reductive Approaches
Integrative approaches focus on combining diverse perspectives and methodologies to create a holistic understanding of complex systems, emphasizing the interconnectedness of components. Reductive approaches break down systems into their simplest parts to analyze individual elements and underlying mechanisms in detail. Understanding these approaches involves recognizing when to apply comprehensive synthesis versus detailed analysis for effective problem-solving in scientific and philosophical contexts.
Historical Context of Integrative vs Reductive Methods
The historical context of integrative versus reductive methods dates back to early scientific paradigms where reductive approaches dominated by breaking complex phenomena into simpler components for analysis. Integrative methods emerged as a response during the 20th century, emphasizing the synthesis of diverse elements to understand systems holistically across disciplines such as biology, psychology, and environmental science. This shift reflects a growing recognition of complexity and interconnectedness in natural and social phenomena, challenging the limitations of purely reductive methodologies.
Core Principles of Integrative Thinking
Integrative thinking centers on synthesizing opposing ideas to create innovative solutions, emphasizing complexity and multiple perspectives rather than simplifying problems. It encourages balancing trade-offs and exploring creative possibilities by holding contradictory elements in tension. Core principles include embracing complexity, generating novel solutions, and pursuing holistic understanding beyond traditional reductive analysis.
Key Features of Reductive Analysis
Reductive analysis breaks down complex systems into simpler components, emphasizing detailed examination of individual parts and their interactions. It enables precise measurement and identification of causal relationships by isolating variables within a system. This approach is essential in fields like molecular biology and classical physics, where understanding fundamental elements drives scientific progress.
Comparative Benefits: Integrative vs Reductive
Integrative approaches synthesize diverse perspectives, enhancing holistic understanding and fostering innovation across complex systems, whereas reductive methods excel in isolating and analyzing individual components for precision and clarity. Integrative strategies improve interdisciplinary collaboration and adaptability, which benefits dynamic problem-solving and real-world applications. Reductive techniques provide robust, detailed insights ideal for experimental validation and developing foundational knowledge.
Applications of Integrative Approaches in Science
Integrative approaches in science combine insights from multiple disciplines to address complex problems, enhancing the accuracy and applicability of research outcomes. These methods are widely applied in fields such as systems biology, environmental science, and neuroscience, where understanding interactions between components is crucial. By synthesizing diverse data and methodologies, integrative science promotes holistic solutions that surpass the limitations of reductive, single-discipline analyses.
Limitations of Reductive Methodologies
Reductive methodologies often face limitations due to their focus on isolated components, which can overlook complex interactions within systems. This approach may fail to capture emergent properties that arise from holistic integration, leading to incomplete or misleading conclusions. The inability to address multifaceted phenomena restricts the applicability of reductive analysis in fields like ecology, psychology, and systems biology.
Case Studies: Integrative vs Reductive Solutions
Case studies comparing integrative and reductive solutions reveal distinct approaches to problem-solving in complex systems. Integrative solutions prioritize holistic understanding by combining diverse data sources and interdisciplinary perspectives, enhancing adaptability and sustainability. Reductive solutions focus on isolating specific variables to simplify analysis, often achieving efficiency but potentially overlooking systemic interactions critical for long-term effectiveness.
Choosing the Right Approach: Factors to Consider
Choosing the right approach between integrative and reductive methods depends on the complexity and scope of the problem, as well as the desired depth of understanding. Integrative approaches are ideal for addressing multifaceted issues by combining diverse perspectives and data, while reductive approaches excel in isolating specific variables for targeted analysis. Key factors to consider include the nature of the subject, available resources, time constraints, and the intended application of the findings.
Future Trends in Integrative and Reductive Thinking
Future trends in integrative thinking emphasize combining diverse perspectives to solve complex problems, leveraging artificial intelligence and data analytics to synthesize information across disciplines. Reductive thinking continues to advance in specialized fields with precision algorithms and micro-level analysis enhancing efficiency and innovation in targeted areas. Emerging hybrid models aim to balance holistic insights with detailed scrutiny, driving adaptive decision-making in dynamic environments.
Integrative Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com