Facilitation enhances group collaboration by guiding discussions, resolving conflicts, and ensuring all voices are heard, leading to more effective decision-making. Skilled facilitators use techniques that promote engagement and foster a productive environment without dominating the conversation. Explore the rest of the article to discover practical facilitation strategies that can improve your teamwork and project outcomes.
Table of Comparison
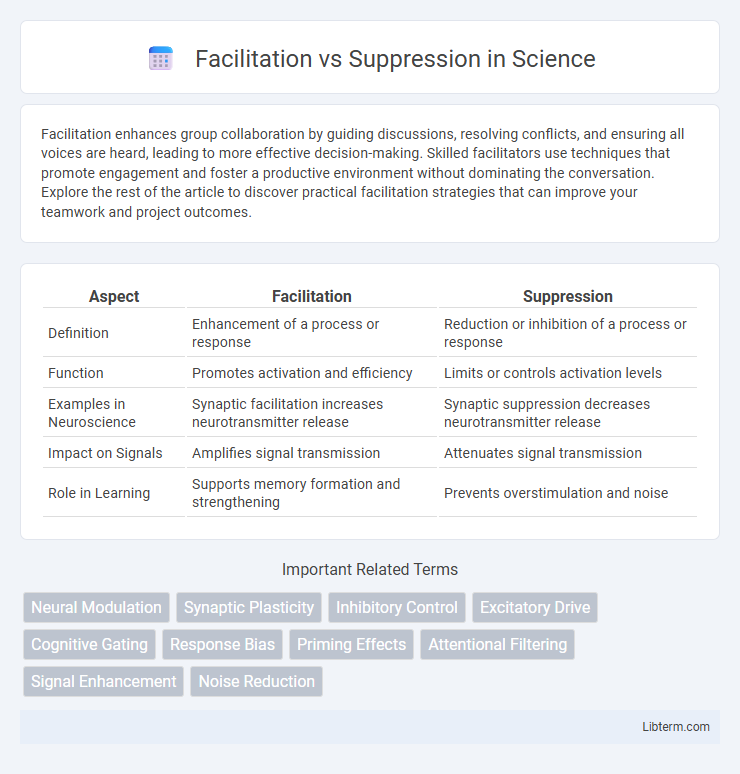
| Aspect | Facilitation | Suppression |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Enhancement of a process or response | Reduction or inhibition of a process or response |
| Function | Promotes activation and efficiency | Limits or controls activation levels |
| Examples in Neuroscience | Synaptic facilitation increases neurotransmitter release | Synaptic suppression decreases neurotransmitter release |
| Impact on Signals | Amplifies signal transmission | Attenuates signal transmission |
| Role in Learning | Supports memory formation and strengthening | Prevents overstimulation and noise |
Defining Facilitation and Suppression
Facilitation refers to the process by which one stimulus enhances the response of a neuron or neural pathway, increasing the likelihood of signal transmission and improving cognitive or motor function. Suppression involves the decrease or inhibition of neural activity in response to specific stimuli, reducing signal transmission and modulating behavioral or sensory outputs. Both mechanisms play crucial roles in neural plasticity, sensory processing, and the regulation of complex brain functions.
Key Differences Between Facilitation and Suppression
Facilitation enhances neural activity by increasing synaptic strength or neuronal responsiveness, while suppression reduces neural activity through inhibitory mechanisms or decreased synaptic efficacy. Facilitation often involves excitatory neurotransmitters like glutamate, whereas suppression typically engages inhibitory neurotransmitters such as GABA. The key differences lie in their roles within neural circuits: facilitation promotes signal transmission and plasticity, whereas suppression controls excessive excitation and maintains neural homeostasis.
The Psychology Behind Facilitation and Suppression
Facilitation in psychology refers to the process where certain neural or cognitive activities are enhanced, increasing the likelihood of a behavior or response, driven by mechanisms such as reinforcement learning and positive feedback loops. Suppression involves inhibiting or reducing neural or behavioral responses, often managed by executive control functions within the prefrontal cortex to regulate emotions and impulses. Understanding facilitation and suppression provides insights into adaptive behaviors, emotional regulation, and cognitive control, highlighting the brain's dynamic balance between excitation and inhibition.
Impacts on Communication and Collaboration
Facilitation enhances communication by encouraging active listening, open dialogue, and mutual understanding, fostering effective collaboration and problem-solving within teams. Suppression impedes communication by limiting expression, creating barriers to trust, and reducing the willingness to share ideas, which undermines collaboration and innovation. The impact on group dynamics shows that facilitation drives positive engagement, whereas suppression leads to conflict, disengagement, and decreased productivity.
Benefits of Embracing Facilitation
Embracing facilitation enhances collaboration by encouraging open communication and idea sharing, leading to more innovative and effective problem-solving. Facilitation fosters a positive team environment that boosts engagement, motivation, and collective ownership of outcomes. In contrast to suppression, facilitation reduces resistance and conflict, promoting smoother project execution and stronger interpersonal relationships.
Risks Associated with Suppression
Suppression in emotional or behavioral contexts often leads to increased psychological distress, including heightened anxiety, depression, and stress-related disorders. Chronic suppression can disrupt natural emotional processing, resulting in impaired cognitive function and reduced overall well-being. Research indicates that reliance on suppression as a coping mechanism elevates the risk of negative health outcomes, emphasizing the importance of facilitation strategies for healthier emotional regulation.
Real-World Examples: Facilitation vs. Suppression
Facilitation in neural processes is exemplified by long-term potentiation (LTP) in the hippocampus, where repeated stimulation strengthens synaptic connections, enhancing memory formation. In contrast, suppression occurs in cases like sensory gating, where inhibitory interneurons reduce neuronal responses to repetitive stimuli, preventing information overload. Real-world applications include cognitive therapies leveraging facilitation mechanisms to improve learning and pharmacological interventions targeting suppression pathways to treat conditions like epilepsy.
When to Facilitate and When to Suppress
Facilitation should be employed when enhancing neural signals or amplifying responses is necessary for improved cognitive, sensory, or motor functions. Suppression is crucial in situations requiring the inhibition of irrelevant or harmful stimuli to maintain focus and prevent overstimulation. Effective balance between facilitation and suppression optimizes brain performance and behavioral outcomes.
Strategies to Promote Facilitation Over Suppression
Promoting facilitation over suppression involves utilizing cognitive-behavioral techniques such as mindfulness and positive reinforcement to enhance emotional regulation and adaptive coping mechanisms. Implementing structured environments that encourage open communication and proactive problem-solving fosters facilitation by reducing stress-induced suppression responses. Neurofeedback and targeted behavioral interventions can also optimize neural pathways associated with facilitation, improving overall mental health and resilience.
Conclusion: Striking the Right Balance
Striking the right balance between facilitation and suppression is essential for effective communication and decision-making processes. Facilitation encourages open dialogue, creativity, and collaboration, while suppression helps maintain focus and prevent disruptions. Achieving equilibrium ensures that ideas flow freely without chaos, fostering productive outcomes and sustainable progress.
Facilitation Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com