Unsistematic approaches often lead to inconsistent results and hinder efficient progress in any project. Without a clear structure or plan, important details can be overlooked, causing confusion and delays. Discover how adopting systematic methods can transform your workflow by reading the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
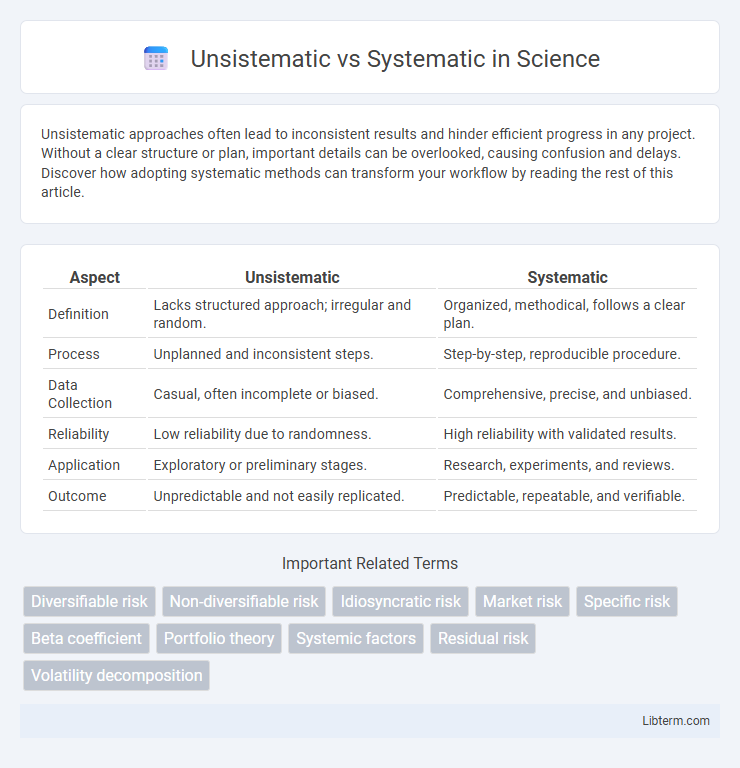
| Aspect | Unsistematic | Systematic |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Lacks structured approach; irregular and random. | Organized, methodical, follows a clear plan. |
| Process | Unplanned and inconsistent steps. | Step-by-step, reproducible procedure. |
| Data Collection | Casual, often incomplete or biased. | Comprehensive, precise, and unbiased. |
| Reliability | Low reliability due to randomness. | High reliability with validated results. |
| Application | Exploratory or preliminary stages. | Research, experiments, and reviews. |
| Outcome | Unpredictable and not easily replicated. | Predictable, repeatable, and verifiable. |
Introduction: Defining Unsistematic and Systematic
Unsystematic risk refers to the type of risk that affects a specific company or industry, arising from factors such as management decisions, competitive pressures, or product recalls. Systematic risk, also known as market risk, impacts the entire market or economy and stems from macroeconomic factors like interest rate changes, inflation, or geopolitical events. Understanding the distinction between unsystematic and systematic risk is essential for effective portfolio diversification and risk management strategies.
Key Differences Between Unsistematic and Systematic
Unsystematic risk refers to company-specific or industry-specific risks that can be mitigated through diversification, while systematic risk impacts the entire market or economy and cannot be diversified away. Unsistematic risk includes factors like management decisions, product recalls, or labor strikes, whereas systematic risk involves macroeconomic elements such as inflation, interest rates, and geopolitical events. Understanding these key differences is essential for effective portfolio management and risk assessment strategies.
Real-World Examples of Unsistematic and Systematic Approaches
Systematic approaches in project management, like Six Sigma at General Electric, utilize structured methodologies and data-driven analysis to improve processes and achieve consistent results. Unsistematic approaches often appear in startups where rapid, intuitive decision-making is necessary, allowing flexibility but increasing the risk of errors due to lack of formal processes. The contrast is evident in industries such as manufacturing, where systematic quality control ensures product reliability, versus creative industries where unsystematic experimentation fosters innovation.
Advantages of a Systematic Approach
A systematic approach ensures consistency, accuracy, and efficient use of resources by following structured procedures and methodologies. It enables better decision-making through comprehensive data analysis and reduces errors compared to unsystematic methods. This approach enhances predictability and accountability, making project outcomes more reliable and scalable.
Drawbacks of Unsistematic Methods
Unsystematic methods in research often suffer from inconsistency and lack of reproducibility, resulting in unreliable and biased data outcomes. These approaches typically lack structured protocols, making it difficult to validate findings or compare results across studies. The absence of standardized procedures leads to inefficiencies and increases the risk of overlooking critical variables essential for accurate and comprehensive analysis.
When Is an Unsistematic Approach Beneficial?
An unsystematic approach is beneficial when flexibility and rapid decision-making are critical, such as in highly dynamic or unpredictable environments where structured methods may hinder adaptability. This approach allows for creative problem-solving and quick responses without the constraints of rigid protocols, making it ideal for innovation-driven fields or early-stage exploration. However, it is most effective when paired with experienced judgment to balance spontaneity with informed intuition.
Impact on Decision-Making: Systematic vs Unsistematic
Systematic decision-making relies on structured processes, data analysis, and consistent evaluation criteria, leading to more predictable and reliable outcomes. Unsystematic decision-making is often influenced by intuition, emotions, or incomplete information, increasing the risk of bias and errors. Systematic approaches minimize uncertainty and improve strategic planning by reducing randomness and enhancing data-driven insights.
Applications in Business and Management
Unsystematic risk refers to company-specific or industry-specific uncertainties that can be mitigated through diversification, whereas systematic risk affects the entire market and cannot be eliminated through diversification. In business and management, understanding these risks informs strategic decision-making, such as portfolio management, where managers assess unsystematic risk to optimize asset allocation while monitoring systematic risk for macroeconomic trends impacting financial stability. Tools like risk assessment models and scenario analysis are employed to quantify and manage these risks, enhancing overall organizational resilience and performance.
Tips for Shifting from Unsistematic to Systematic
Transitioning from unsystematic to systematic requires implementing structured routines, such as setting clear goals, prioritizing tasks, and using tools like planners or digital apps to track progress. Consistently reviewing and refining workflows enhances efficiency and reduces overlooked details. Adopting habits like time blocking and standardized procedures fosters discipline and predictability in achieving objectives.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Approach
Choosing between unsystematic and systematic approaches depends on the project scope, objectives, and desired outcomes. Systematic methods provide structured, replicable results ideal for complex problems requiring consistency, while unsystematic approaches offer flexibility and creativity suitable for exploratory or preliminary stages. Evaluating resource availability, time constraints, and accuracy needs ensures optimal decision-making for selecting the appropriate strategy.
Unsistematic Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com