Understanding the complexities of law is essential for protecting your rights and making informed decisions in everyday life. From contracts and property to criminal and family law, each area plays a critical role in society's functioning and individual well-being. Explore the full article to gain deeper insights into how legal principles impact you and navigate the legal landscape more effectively.
Table of Comparison
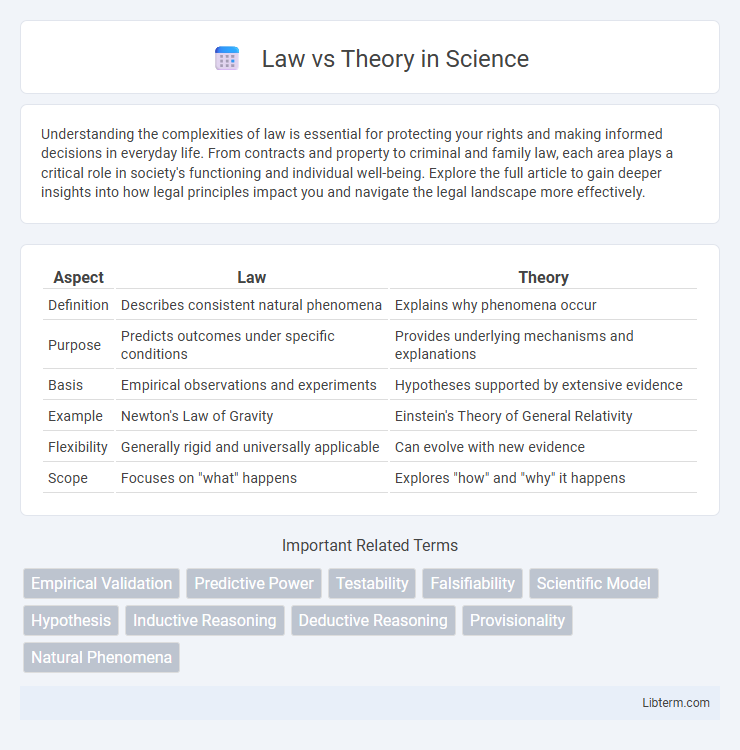
| Aspect | Law | Theory |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Describes consistent natural phenomena | Explains why phenomena occur |
| Purpose | Predicts outcomes under specific conditions | Provides underlying mechanisms and explanations |
| Basis | Empirical observations and experiments | Hypotheses supported by extensive evidence |
| Example | Newton's Law of Gravity | Einstein's Theory of General Relativity |
| Flexibility | Generally rigid and universally applicable | Can evolve with new evidence |
| Scope | Focuses on "what" happens | Explores "how" and "why" it happens |
Understanding the Basics: What is a Law?
A law in science is a concise statement that describes consistent and universal natural phenomena, often expressed mathematically or through precise formulas. It differs from a theory by providing predictable and reproducible outcomes without explaining the underlying mechanisms. Scientific laws, such as Newton's Law of Gravity or the Laws of Thermodynamics, establish fundamental principles that serve as the foundation for scientific study and technological advancements.
Defining a Theory: More Than Just a Guess
A theory represents a well-substantiated explanation of natural phenomena supported by extensive evidence and experimentation, distinguishing it from mere speculation or guesswork. It provides a framework for understanding complex relationships and making testable predictions within scientific disciplines. Unlike laws that describe consistent patterns, theories explain the underlying mechanisms driving those patterns.
Key Differences Between Laws and Theories
Scientific laws describe consistent, universal observations often expressed mathematically, while theories provide comprehensive explanations supported by evidence and experimentation. Laws predict what happens under specific conditions, whereas theories explain why phenomena occur and integrate multiple observations. Both are fundamental to scientific understanding but serve distinct roles in advancing knowledge.
Origins and Development: How Laws and Theories Emerge
Scientific laws originate from consistent, repeatable observations and empirical data that describe natural phenomena with precise, often mathematical, formulations. Theories develop through extensive experimentation and validation, providing comprehensive explanations that unify multiple laws and observations within a broader conceptual framework. Both evolve through rigorous testing, peer review, and refinement, but laws emphasize descriptive accuracy while theories focus on explanatory depth.
Real-World Examples: Laws vs. Theories in Science
Newton's law of universal gravitation describes the precise mathematical relationship governing the attraction between two masses, consistently applied in engineering and space exploration. In contrast, the theory of evolution explains the mechanism of species adaptation and biodiversity, supported by fossil records and genetic evidence but open to refinement as new data emerges. Laws offer definitive, predictable outcomes under specific conditions, while theories provide comprehensive explanations that integrate multiple laws and observations in scientific practice.
Misconceptions About Scientific Laws and Theories
Scientific laws and theories serve different purposes; laws describe consistent natural phenomena, while theories explain the underlying mechanisms. A common misconception is that laws are absolute truths and theories are mere guesses, but theories are rigorously tested explanations supported by extensive evidence. Scientific laws summarize observations, whereas theories provide comprehensive understanding, both essential for scientific progress.
The Role of Evidence in Supporting Laws and Theories
Laws summarize consistent, empirically observed phenomena and rely on robust, repeatable evidence to establish predictable relationships, whereas theories offer comprehensive explanations based on a broader set of evidence and are continually tested and refined. Evidence supporting laws is typically quantitative and demonstrable through experimentation or observation, while theories depend on converging lines of evidence from multiple studies and disciplines to explain underlying mechanisms. Both laws and theories require rigorous validation, but laws describe what happens under specific conditions, and theories explain why it happens.
How Laws and Theories Interact in Scientific Progress
Scientific progress relies on the interaction between laws and theories, where laws describe consistent natural phenomena through concise mathematical relationships, while theories provide explanatory frameworks that interpret and predict those phenomena. Laws serve as foundational truths within specific conditions, and theories integrate these laws into broader contexts, evolving with new evidence. This dynamic interplay advances understanding by refining, challenging, or expanding both laws and theories over time.
The Evolution of Laws and Theories Over Time
Scientific laws and theories evolve as new evidence emerges, reflecting the dynamic nature of knowledge. Laws describe consistent natural phenomena, while theories provide explanatory frameworks that can expand or shift with discoveries in fields like physics and biology. The progression from Newtonian mechanics to Einstein's relativity exemplifies how laws and theories adapt to accommodate deeper understanding and experimental validation.
Why Knowing the Difference Matters in Science
Understanding the difference between law and theory is crucial in science because laws describe consistent, observable phenomena while theories provide explanatory frameworks for those phenomena. Scientific laws summarize patterns found in nature, such as Newton's laws of motion, whereas theories, like the theory of evolution, offer deeper understanding and predictive power. Recognizing this distinction helps prevent misconceptions about the certainty and scope of scientific knowledge, fostering more accurate communication and critical thinking in scientific inquiry.
Law Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com