Monounsaturated fats are a type of healthy fat found in foods like olive oil, avocados, and nuts, known for promoting heart health and reducing bad cholesterol levels. These fats provide essential nutrients that support cell function and maintain your overall well-being. Discover how incorporating monounsaturated fats into your diet can improve your health by reading the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
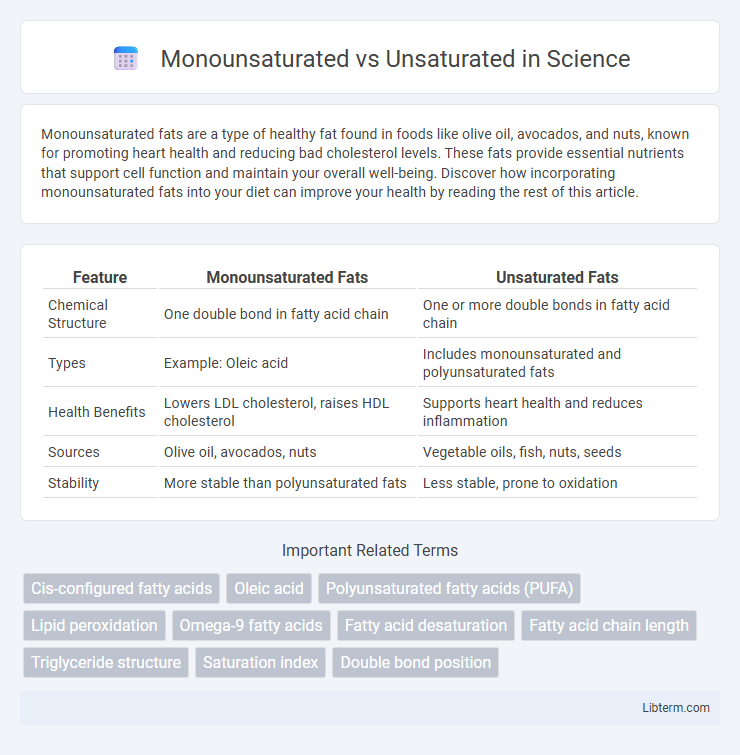
| Feature | Monounsaturated Fats | Unsaturated Fats |
|---|---|---|
| Chemical Structure | One double bond in fatty acid chain | One or more double bonds in fatty acid chain |
| Types | Example: Oleic acid | Includes monounsaturated and polyunsaturated fats |
| Health Benefits | Lowers LDL cholesterol, raises HDL cholesterol | Supports heart health and reduces inflammation |
| Sources | Olive oil, avocados, nuts | Vegetable oils, fish, nuts, seeds |
| Stability | More stable than polyunsaturated fats | Less stable, prone to oxidation |
Introduction to Monounsaturated and Unsaturated Fats
Monounsaturated fats contain one double bond in their fatty acid chains, making them a healthy type of unsaturated fat found in olive oil, avocados, and nuts. Unsaturated fats include both monounsaturated and polyunsaturated fats, characterized by one or more double bonds, and are essential for heart health and reducing bad cholesterol levels. These fats are typically liquid at room temperature and play a crucial role in cell function and inflammation regulation.
Understanding the Structure of Fatty Acids
Monounsaturated fatty acids (MUFAs) contain a single double bond in their hydrocarbon chain, which introduces a kink that affects fluidity and melting point. Unsaturated fatty acids encompass both monounsaturated and polyunsaturated types, distinguished by the number and position of double bonds within their carbon chains. The structural differences impact the physical properties and biological roles of these fats in cell membranes and metabolism.
What Are Monounsaturated Fats?
Monounsaturated fats are a type of unsaturated fat characterized by a single double bond in their fatty acid chain, commonly found in olive oil, avocados, and nuts. These fats help improve heart health by reducing bad LDL cholesterol while maintaining good HDL cholesterol levels. Incorporating monounsaturated fats into a balanced diet supports cardiovascular function and may reduce the risk of chronic diseases.
Types of Unsaturated Fats: Mono vs Polyunsaturated
Monounsaturated fats contain a single double bond in their fatty acid chain, making them more stable than polyunsaturated fats, which have multiple double bonds. Common sources of monounsaturated fats include olive oil, avocados, and nuts, while polyunsaturated fats are abundant in fish, flaxseeds, and walnuts. Both types of unsaturated fats contribute to heart health by improving cholesterol levels and reducing inflammation, but polyunsaturated fats also provide essential omega-3 and omega-6 fatty acids vital for brain function and cell growth.
Food Sources of Monounsaturated Fats
Monounsaturated fats are primarily found in olive oil, avocados, and nuts such as almonds and cashews, which contribute to heart health by improving cholesterol levels. These fats differ from polyunsaturated fats, including omega-3 and omega-6 fatty acids found in fish, flaxseeds, and walnuts, which support brain function and reduce inflammation. Incorporating monounsaturated fat-rich foods into the diet supports cardiovascular health by reducing bad LDL cholesterol without affecting beneficial HDL cholesterol.
Health Benefits of Monounsaturated Fats
Monounsaturated fats, a type of unsaturated fat found in olive oil, avocados, and nuts, support heart health by reducing LDL cholesterol levels while maintaining HDL cholesterol. These fats also help regulate blood sugar levels and may decrease inflammation, contributing to lower risks of cardiovascular disease and type 2 diabetes. Incorporating monounsaturated fats into the diet can improve overall lipid profiles and promote metabolic health.
Dietary Sources of Polyunsaturated Fats
Polyunsaturated fats are primarily found in plant-based oils such as sunflower, safflower, and soybean oils, as well as in fatty fish like salmon, mackerel, and sardines. These fats include essential omega-3 and omega-6 fatty acids, which are crucial for heart health and brain function. Incorporating a variety of nuts, seeds, and leafy green vegetables enhances intake of polyunsaturated fats, supporting overall dietary balance.
Monounsaturated vs Polyunsaturated: Key Differences
Monounsaturated fats contain one double bond in their fatty acid chain, while polyunsaturated fats have two or more double bonds, affecting their chemical structure and stability. Monounsaturated fats, found in olive oil and avocados, are known for improving heart health by reducing LDL cholesterol without lowering HDL cholesterol. Polyunsaturated fats, including omega-3 and omega-6 fatty acids from fish and flaxseeds, play essential roles in brain function and inflammation regulation.
Impact of Unsaturated Fats on Heart Health
Unsaturated fats, including both monounsaturated and polyunsaturated types, play a crucial role in improving heart health by reducing low-density lipoprotein (LDL) cholesterol levels and lowering inflammation. Monounsaturated fats, found in olive oil and avocados, promote arterial flexibility and reduce the risk of cardiovascular disease. Polyunsaturated fats, especially omega-3 fatty acids from fatty fish, further support heart health by decreasing triglycerides and preventing arrhythmias.
Recommendations for Including Healthy Fats in Your Diet
Monounsaturated fats, found in olive oil, avocados, and nuts, are recommended for improving heart health and reducing LDL cholesterol levels. Including a variety of unsaturated fats, both monounsaturated and polyunsaturated, from sources such as fatty fish, flaxseeds, and sunflower oil supports overall cardiovascular function and inflammation control. Experts suggest replacing saturated fats with these healthy fats to optimize lipid profiles and promote long-term wellness.
Monounsaturated Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com