Valence electrons determine an atom's chemical properties and reactivity by occupying its outermost electron shell. Understanding how these electrons interact during bonding helps explain why certain elements form specific compounds and how molecules achieve stability. Discover how mastering valence electrons can enhance your grasp of chemistry in the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
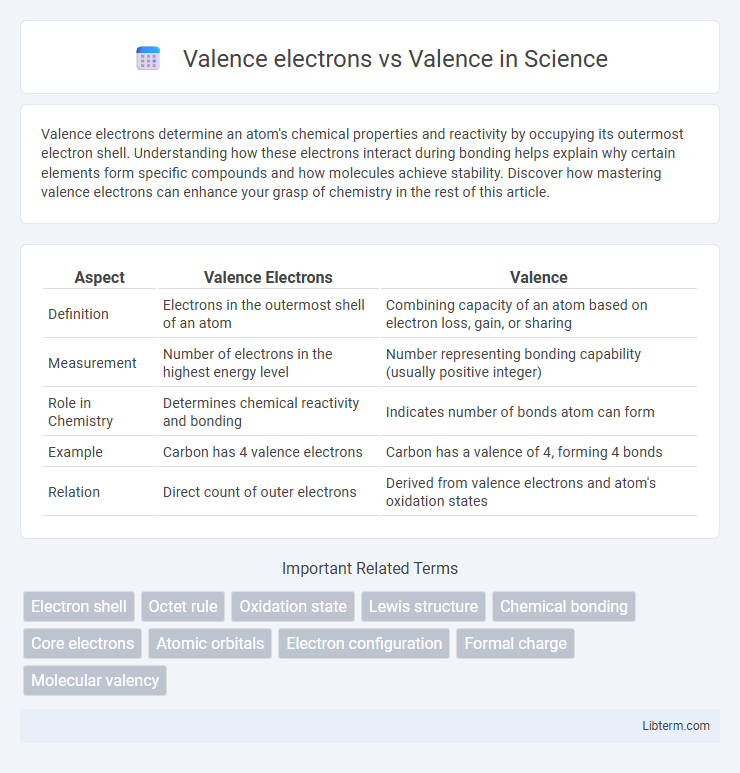
| Aspect | Valence Electrons | Valence |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Electrons in the outermost shell of an atom | Combining capacity of an atom based on electron loss, gain, or sharing |
| Measurement | Number of electrons in the highest energy level | Number representing bonding capability (usually positive integer) |
| Role in Chemistry | Determines chemical reactivity and bonding | Indicates number of bonds atom can form |
| Example | Carbon has 4 valence electrons | Carbon has a valence of 4, forming 4 bonds |
| Relation | Direct count of outer electrons | Derived from valence electrons and atom's oxidation states |
Introduction to Valence and Valence Electrons
Valence refers to the combining capacity of an atom, indicating how many chemical bonds it can form, which is determined by the number of electrons in its outermost shell. Valence electrons are the electrons located in the outermost electron shell that participate directly in chemical bonding and reactions. Understanding both valence and valence electrons is essential for predicting an element's chemical behavior and bonding patterns.
Defining Valence Electrons
Valence electrons are the outermost electrons of an atom that participate in chemical bonding, determining an element's reactivity and bonding behavior. Valence refers to the combining capacity of an atom, often related to the number of valence electrons available for forming bonds. Understanding valence electrons is crucial for predicting molecular structure and chemical properties.
What is Chemical Valence?
Chemical valence refers to the ability of an atom to bond with other atoms, determined by the number of electrons an atom can gain, lose, or share to achieve a stable electron configuration. Valence electrons are the outermost electrons of an atom that participate directly in chemical bonding. Understanding valence helps predict molecular structure, reactivity, and the formation of compounds based on electron interactions.
Origin and Historical Development of Both Concepts
Valence electrons, the electrons in the outermost shell of an atom responsible for chemical bonding, were first conceptualized in the early 20th century as quantum theory developed to explain atomic structure. The term "valence," originating in the 19th century from Avogadro's work, initially described the combining capacity of elements without specific reference to electrons. The historical development of valence evolved from empirical observations of bonding patterns to a more precise understanding with the discovery of valence electrons, linking chemical reactivity directly to electronic configuration.
Key Differences Between Valence and Valence Electrons
Valence refers to the combining capacity of an atom, often indicated by the number of chemical bonds it can form, while valence electrons are the specific electrons located in the outermost shell of an atom responsible for chemical bonding. Valence quantifies the atom's bonding potential, whereas valence electrons explain the electron configuration that determines that potential. Understanding this distinction is crucial in predicting molecular structure, reactivity, and chemical properties in elements and compounds.
Role of Valence Electrons in Chemical Bonding
Valence electrons, the outermost electrons in an atom, directly influence chemical bonding by determining an element's ability to form stable bonds through electron sharing or transfer. The valence, which refers to the combining capacity of an atom, is inherently defined by the number of valence electrons available for bond formation. These electrons facilitate covalent, ionic, and metallic bonds, playing a crucial role in molecule stability and reactivity.
Determining an Element’s Valence
Valence electrons are the outermost electrons of an atom that participate in chemical bonding, directly influencing an element's valence, which is its ability to combine with other atoms. Determining an element's valence involves counting these valence electrons to understand how many bonds it can form, typically guided by the octet rule for main-group elements. Transition metals often exhibit variable valences due to their d-electrons, making their valence determination more complex than that of s- and p-block elements.
Importance in Predicting Reactivity
Valence electrons determine an atom's ability to form chemical bonds by occupying the outermost electron shell, directly influencing its reactivity and bonding behavior. The concept of valence refers to the combining capacity of an element, often predicted by counting valence electrons, which helps in understanding molecule formation and predicting reaction outcomes. Accurate knowledge of valence electrons enables chemists to forecast an element's chemical properties and its likelihood to participate in specific reactions, making it essential in fields like inorganic chemistry and materials science.
Applications in Modern Chemistry
Valence electrons determine an atom's ability to form chemical bonds, influencing molecular structure and reactivity in modern chemistry applications such as catalysis and material design. Valence, referring to the combining capacity of an element, is critical in predicting reaction outcomes in organic synthesis and coordination chemistry. Understanding both concepts enables chemists to engineer compounds with specific properties for pharmaceuticals, nanotechnology, and energy storage systems.
Summary and Comparative Table
Valence electrons are the outermost electrons available for chemical bonding, determining an atom's reactivity and bonding behavior, while valence refers to the combining capacity of an element, often represented by the number of bonds it can form. In a comparative summary, valence electrons quantify the actual count of electrons in the outer shell, whereas valence represents the effective bonding ability, which can be inferred from electron configuration but also influenced by oxidation states. A concise comparison table highlights valence electrons as an electron count metric, valence as a chemical bonding potential, with valence electrons measured per atom and valence commonly expressed as an integer reflecting bonding capacity.
Valence electrons Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com