Valency refers to the number of chemical bonds an atom can form with other atoms, defining its combining capacity in molecules. Understanding valency is crucial for predicting molecular structures and chemical reactions. Explore the rest of the article to deepen your knowledge of valency and its role in chemistry.
Table of Comparison
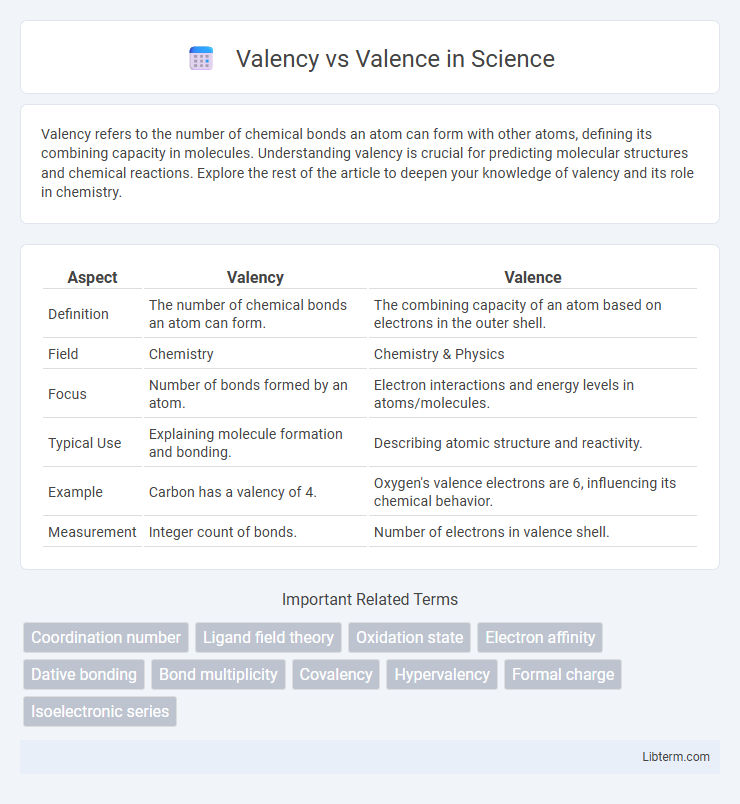
| Aspect | Valency | Valence |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | The number of chemical bonds an atom can form. | The combining capacity of an atom based on electrons in the outer shell. |
| Field | Chemistry | Chemistry & Physics |
| Focus | Number of bonds formed by an atom. | Electron interactions and energy levels in atoms/molecules. |
| Typical Use | Explaining molecule formation and bonding. | Describing atomic structure and reactivity. |
| Example | Carbon has a valency of 4. | Oxygen's valence electrons are 6, influencing its chemical behavior. |
| Measurement | Integer count of bonds. | Number of electrons in valence shell. |
Introduction to Valency and Valence
Valency refers to the capacity of an atom to combine with other atoms, defined by the number of chemical bonds it can form, which is crucial in understanding molecular structures and reactivity. Valence, often used interchangeably with valency, specifically addresses the electron configuration in the outer shell of an atom that participates in bonding. Both concepts are fundamental in chemistry for predicting how atoms interact to form compounds, influencing molecular geometry and stability.
Definitions: Valency and Valence Explained
Valency refers to the combining capacity of an element, indicating how many chemical bonds it can form with other atoms based on its available electrons. Valence, on the other hand, specifically denotes the number of electrons in the outermost shell that participate in bonding, influencing an element's reactivity and bonding behavior. Understanding valency and valence is essential for predicting molecule formation and chemical compound stability.
Historical Perspectives
The terms "valency" and "valence" originated from early 19th-century chemistry, where "valency" described the combining capacity of atoms based on their bonding power. Over time, "valence" emerged primarily in American English to denote similar concepts, influenced by developments in quantum theory and molecular chemistry. Historical texts reveal that "valency" was the preferred term in British scientific literature, while "valence" gained prominence with modern chemical bonding theories and electronic structure studies.
Key Differences Between Valency and Valence
Valency refers to the combining capacity of an atom, specifically the number of hydrogen atoms it can combine with or displace in a compound. Valence, on the other hand, pertains to the number of electrons an atom uses in bonding, often associated with the atom's outer shell electron count. Key differences include valency being a measure of bonding capacity while valence emphasizes electron involvement and how atoms share or transfer electrons in chemical reactions.
Chemical Contexts of Valency
Valency in chemical contexts refers to the combining capacity of an element, indicating the number of chemical bonds an atom can form based on its available valence electrons. Valence typically denotes the number of electrons in the outermost shell of an atom that participate in bond formation or chemical reactions. Understanding valency is essential for predicting molecular structures and bonding patterns, while valence provides insight into the atom's reactive properties and electron configuration.
Linguistic Applications of Valence
Valence in linguistics refers to the number of arguments a verb can have, such as subjects, objects, or complements, playing a crucial role in sentence structure analysis and syntactic parsing. Valency, often used interchangeably with valence, emphasizes the combinatory potential of verbs, helping linguists understand argument realization and predicate-argument structures in various languages. This concept informs computational linguistics and natural language processing algorithms by improving semantic role labeling and enhancing machine translation accuracy.
Examples in Chemistry
Valency refers to the number of chemical bonds an atom can form, such as carbon with a valency of 4 forming four covalent bonds, exemplified by methane (CH4). Valence describes the electrons present in the outermost shell, for example, oxygen has six valence electrons and typically forms two bonds, as seen in water (H2O). The distinction is crucial in chemistry for predicting molecular structure and reactivity in compounds.
Examples in Linguistics
Valency in linguistics refers to the number of arguments a verb can have, such as "give" with three arguments (subject, direct object, indirect object). Valence, often used interchangeably, can also describe the semantic relationship between a verb and its arguments, highlighting roles like agent, patient, or experiencer. For example, in the sentence "She gave him a book," valency is three due to the three arguments, while valence emphasizes the thematic roles assigned to each argument.
Common Misconceptions
Valency and valence are often confused but represent distinct concepts in chemistry; valency refers to the number of chemical bonds an atom can form, while valence relates to the number of electrons in the outermost shell that are involved in bonding. A common misconception is treating valency as a fixed value for an element, whereas it can vary depending on the chemical context and bonding environment. Another frequent error is assuming valence electrons directly correspond to valency, ignoring the role of electron orbitals and molecular structure in determining bonding capacity.
Conclusion: Valency vs Valence
Valency and valence both describe chemical bonding but differ in usage and scope; valency refers to the number of bonds an atom can form based on available electrons, while valence encompasses the atom's total bonding capacity, including electron configuration and oxidation states. Understanding the distinction clarifies chemical behavior in molecular structures, aiding in predicting reactivity and compound formation. Valency is a simpler, more traditional concept, whereas valence offers a comprehensive, modern perspective crucial for advanced chemistry analysis.
Valency Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com