Antagonistic action occurs when a substance or agent interferes with or opposes the effects of another, often reducing its overall impact. This interaction is common in pharmacology, where one drug inhibits the effectiveness of another, leading to diminished therapeutic outcomes. Explore the rest of the article to understand how antagonistic actions influence treatments and your health.
Table of Comparison
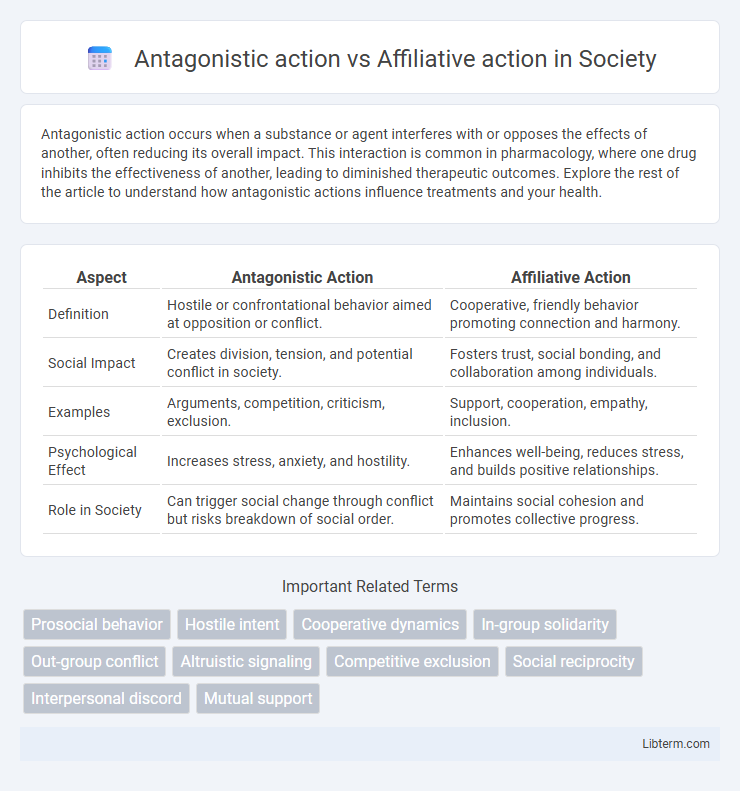
| Aspect | Antagonistic Action | Affiliative Action |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Hostile or confrontational behavior aimed at opposition or conflict. | Cooperative, friendly behavior promoting connection and harmony. |
| Social Impact | Creates division, tension, and potential conflict in society. | Fosters trust, social bonding, and collaboration among individuals. |
| Examples | Arguments, competition, criticism, exclusion. | Support, cooperation, empathy, inclusion. |
| Psychological Effect | Increases stress, anxiety, and hostility. | Enhances well-being, reduces stress, and builds positive relationships. |
| Role in Society | Can trigger social change through conflict but risks breakdown of social order. | Maintains social cohesion and promotes collective progress. |
Introduction to Antagonistic and Affiliative Actions
Antagonistic actions involve behaviors that create conflict, competition, or hostility between individuals or groups, often driven by aggression or defense mechanisms. Affiliative actions, in contrast, promote social bonding, cooperation, and positive interactions that strengthen relationships and group cohesion. Understanding these concepts helps in analyzing social dynamics, animal behavior, and human interactions by highlighting the opposing drives of conflict and connection.
Defining Antagonistic Action
Antagonistic action refers to behaviors intended to oppose, harm, or create conflict between individuals or groups, often characterized by aggression, hostility, or competition. This form of interaction contrasts sharply with affiliative action, which aims to build social bonds, cooperation, and positive relationships. Understanding antagonistic action is crucial in fields like social psychology and conflict resolution, where identifying sources of discord helps develop strategies for managing or mitigating conflict.
Understanding Affiliative Action
Affiliative action involves behaviors that promote social bonding, cooperation, and positive interactions among individuals, often enhancing group cohesion and trust. These actions, such as sharing, comforting, and supporting, activate neural pathways linked to reward and empathy, facilitating stronger interpersonal connections. Understanding affiliative action is essential for comprehending how social structures and relationships are maintained across various species, including humans.
Key Differences between Antagonistic and Affiliative Actions
Antagonistic actions involve behaviors aimed at causing harm, asserting dominance, or creating conflict, often observed in competitive or threatening situations. Affiliative actions promote social bonding, cooperation, and positive interactions, facilitating group cohesion and mutual support. The key differences lie in their purposes: antagonistic actions increase social tension and rivalry, while affiliative actions enhance trust and group harmony.
Psychological Roots of Antagonistic Behavior
Antagonistic behavior stems from underlying psychological mechanisms such as fear, insecurity, and perceived threats to self-esteem or social status, often triggering defensive or aggressive responses. This hostility contrasts affiliative actions that are driven by the innate human need for social bonding, trust, and cooperation critical for emotional well-being. Research identifies factors such as early childhood experiences, attachment styles, and neurobiological imbalances in neurotransmitters like serotonin as pivotal in shaping antagonistic tendencies.
Motivations Behind Affiliative Behavior
Affiliative behavior is primarily motivated by the need for social bonding, emotional support, and cooperation within groups, which enhances survival and well-being. Oxytocin and endorphins play significant roles in reinforcing these positive social interactions, promoting trust and attachment. This behavior contrasts with antagonistic actions, which stem from competition, threat response, and dominance motives aimed at self-preservation and resource control.
Impact on Interpersonal Relationships
Antagonistic actions, characterized by hostility or opposition, often lead to conflict, decreased trust, and deterioration of interpersonal relationships. Affiliative actions promote positive social bonding by encouraging cooperation, empathy, and mutual support, which strengthen relational ties and enhance communication. The balance between these behaviors significantly influences the quality and stability of personal and professional connections.
Antagonistic vs. Affiliative Actions in Team Dynamics
Antagonistic actions in team dynamics involve behaviors such as conflict, competition, and resistance that can hinder collaboration and reduce group cohesion. Affiliative actions promote positive interactions, cooperation, and trust, enhancing communication and collective problem-solving within the team. Effective team performance relies on balancing antagonistic and affiliative behaviors to manage tension while fostering a supportive environment.
Strategies to Foster Affiliative Actions
Effective strategies to foster affiliative actions include promoting empathy through perspective-taking exercises and encouraging collaborative problem-solving to build positive social bonds. Implementing consistent positive reinforcement for prosocial behaviors helps strengthen group cohesion and reduces antagonistic interactions. Creating environments that emphasize mutual respect and open communication further supports affiliative dynamics by mitigating conflict and enhancing social trust.
Conclusion: Balancing Antagonistic and Affiliative Actions
Balancing antagonistic and affiliative actions is essential for effective social dynamics, as antagonistic behaviors can establish boundaries and assert dominance, while affiliative actions promote cooperation and bonding. Optimal interaction involves strategically integrating assertiveness with empathy to maintain group cohesion and resolve conflicts. Understanding the context and individuals involved enables adaptive modulation of these behaviors to foster healthy relationships and social stability.
Antagonistic action Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com