Tribalism influences social behavior by creating strong group identities that prioritize loyalty and shared values over individual interests. This phenomenon can lead to both positive community bonds and negative conflicts when group divisions intensify. Explore the rest of the article to understand how tribalism shapes your interactions and society at large.
Table of Comparison
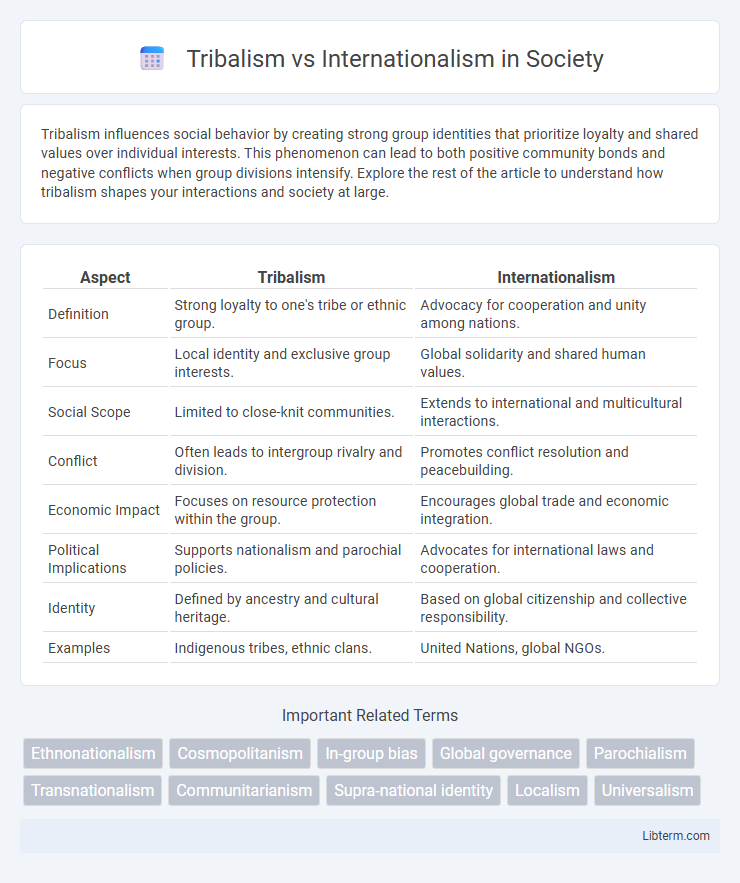
| Aspect | Tribalism | Internationalism |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Strong loyalty to one's tribe or ethnic group. | Advocacy for cooperation and unity among nations. |
| Focus | Local identity and exclusive group interests. | Global solidarity and shared human values. |
| Social Scope | Limited to close-knit communities. | Extends to international and multicultural interactions. |
| Conflict | Often leads to intergroup rivalry and division. | Promotes conflict resolution and peacebuilding. |
| Economic Impact | Focuses on resource protection within the group. | Encourages global trade and economic integration. |
| Political Implications | Supports nationalism and parochial policies. | Advocates for international laws and cooperation. |
| Identity | Defined by ancestry and cultural heritage. | Based on global citizenship and collective responsibility. |
| Examples | Indigenous tribes, ethnic clans. | United Nations, global NGOs. |
Understanding Tribalism and Internationalism
Tribalism emphasizes loyalty and identity within a specific group, often fostering strong in-group cohesion and exclusion of outsiders, which can lead to social fragmentation and conflict. Internationalism advocates for cooperation and solidarity beyond national or ethnic boundaries, promoting global unity, shared values, and collective problem-solving. Understanding the dynamics of tribalism and internationalism is crucial for addressing issues related to nationalism, cultural identity, and global governance.
Historical Roots of Tribalism
Tribalism stems from early human societies where survival relied heavily on kinship bonds, shared customs, and collective identity within small, tightly-knit groups. These historical roots trace back to prehistoric clans and tribes, which prioritized loyalty to their immediate community for protection, resource sharing, and social cohesion. The persistence of tribalism is evident in modern ethnonationalism and identity politics, reflecting humanity's deep evolutionary inclination toward in-group favoritism.
The Evolution of Internationalism
The evolution of internationalism reflects a gradual shift from tribalism's emphasis on loyalty to kinship groups toward a broader commitment to global cooperation and shared values. Key milestones include the establishment of the League of Nations after World War I and the United Nations post-World War II, which institutionalized internationalism through diplomacy and collective security. Contemporary internationalism increasingly incorporates global issues like climate change, human rights, and economic interdependence, emphasizing multicultural integration beyond traditional tribal affiliations.
Core Values and Beliefs: A Comparative Overview
Tribalism centers on loyalty to a specific group, emphasizing shared heritage, customs, and collective identity to maintain social cohesion. Internationalism promotes global cooperation, prioritizing universal values such as human rights, equality, and mutual respect across diverse cultures. The core beliefs of tribalism prioritize in-group solidarity, while internationalism advocates for transcending national boundaries to achieve worldwide unity.
Tribalism’s Influence on Modern Society
Tribalism significantly shapes modern society by influencing social identity, group loyalty, and political polarization, often leading to in-group favoritism and out-group bias. This phenomenon affects social cohesion and policy-making, as individuals prioritize group allegiance over broader societal interests. Understanding tribalism's psychological and cultural roots is crucial for addressing conflicts and promoting inclusive international cooperation.
The Impact of Internationalism on Global Relations
Internationalism fosters cooperation among nations by promoting shared goals such as peace, economic development, and human rights, thereby reducing conflicts rooted in tribalism. Organizations like the United Nations and treaties such as the Paris Agreement exemplify internationalism's role in addressing global challenges collectively. This collaborative approach enhances diplomatic relations, encourages cultural exchange, and supports multilateral problem-solving essential for global stability.
Challenges of Balancing Tribalism and Internationalism
Balancing tribalism and internationalism presents challenges such as conflicting loyalties between local community interests and global cooperation goals, which can hinder policy-making and diplomatic relations. The rise of tribalism often fuels nationalism, leading to exclusionary practices that oppose the inclusive values of internationalism. Effective governance requires navigating these tensions to promote both cultural identity preservation and global collaboration on issues like climate change and human rights.
Case Studies: Tribalism vs Internationalism in Action
Tribalism in case studies such as the Balkans conflict reveals how ethnic and national loyalties fuel division and violence, whereas internationalism in the European Union demonstrates cooperation transcending national borders to ensure peace and economic growth. The Rwandan Genocide exemplifies the catastrophic consequences of tribalism-driven violence, contrasting with the international community's coordinated response to the crisis in East Timor, showcasing effective multinational intervention. These examples highlight the divergent outcomes of tribal allegiance versus global collaboration in resolving conflicts and fostering development.
The Role of Technology in Bridging or Deepening Divides
Technology serves as a double-edged sword in the dynamic between tribalism and internationalism, enabling global connectivity through platforms like social media and international broadcasting while also creating echo chambers that entrench tribal identities. Algorithms tailored to user preferences often intensify divisions by promoting homogeneous content, reinforcing in-group biases, and complicating cross-cultural understanding. Conversely, innovations such as real-time translation and virtual collaboration tools facilitate intercultural dialogue and cooperation, highlighting technology's pivotal role in either bridging or deepening societal divides.
Future Prospects: Toward Unity or Fragmentation?
Tribalism, rooted in strong group identities and localized loyalties, risks fostering fragmentation as digital connectivity amplifies echo chambers and cultural divides. Internationalism promotes cooperation through global institutions and shared goals, driving prospects for unity against challenges like climate change and pandemics. Emerging technologies and transnational movements may either bridge divides or deepen conflicts, shaping a future contingent on governance models and societal willingness to embrace diversity.
Tribalism Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com