Differentiation is a fundamental concept in calculus that measures how a function changes as its input changes, allowing you to determine rates of change and slopes of curves. It plays a crucial role in various fields such as physics, engineering, and economics by providing insights into dynamic systems. Explore the rest of this article to master the techniques and applications of differentiation for your mathematical proficiency.
Table of Comparison
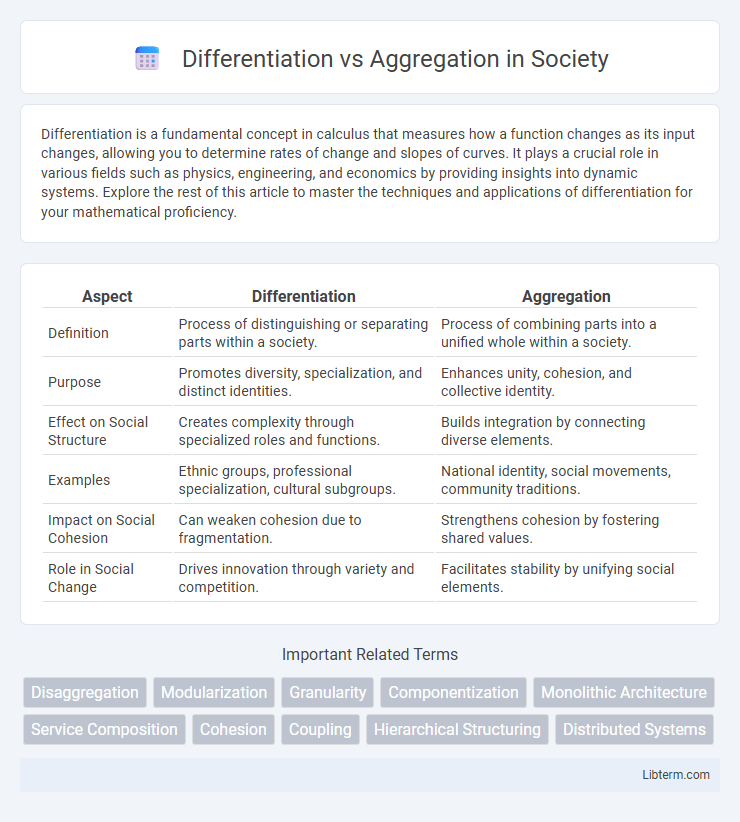
| Aspect | Differentiation | Aggregation |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Process of distinguishing or separating parts within a society. | Process of combining parts into a unified whole within a society. |
| Purpose | Promotes diversity, specialization, and distinct identities. | Enhances unity, cohesion, and collective identity. |
| Effect on Social Structure | Creates complexity through specialized roles and functions. | Builds integration by connecting diverse elements. |
| Examples | Ethnic groups, professional specialization, cultural subgroups. | National identity, social movements, community traditions. |
| Impact on Social Cohesion | Can weaken cohesion due to fragmentation. | Strengthens cohesion by fostering shared values. |
| Role in Social Change | Drives innovation through variety and competition. | Facilitates stability by unifying social elements. |
Understanding Differentiation and Aggregation
Differentiation involves identifying and emphasizing unique features or characteristics within data to highlight distinct values or categories, enabling refined analysis and decision-making. Aggregation, conversely, consolidates data by summarizing or combining multiple data points into a single metric, such as sums, averages, or counts, to present an overarching view or trend. Mastering differentiation and aggregation techniques is critical for effective data analysis, optimizing insights by balancing detailed granularity with comprehensive summaries.
Core Concepts: What is Differentiation?
Differentiation is a core concept in calculus and mathematical analysis that measures how a function changes as its input changes, essentially capturing the rate of change or slope of the function at any given point. It involves calculating the derivative, which quantifies how a small change in the input variable affects the output value. Differentiation is critical for understanding motion, growth rates, optimization problems, and real-world phenomena governed by variable changes.
Defining Aggregation in Modern Contexts
Aggregation in modern contexts refers to the process of combining multiple individual components or data points into a unified whole to enhance functionality, efficiency, or insight. This concept plays a critical role in fields like data science, software engineering, and business analytics by enabling consolidated views, streamlined operations, and improved decision-making. Unlike differentiation, which emphasizes distinct identities and specialized roles, aggregation focuses on integration and collective value creation through interconnected elements.
Key Differences Between Differentiation and Aggregation
Differentiation emphasizes unique, specific features to distinguish products or services, enhancing competitive advantage by targeting niche markets. Aggregation focuses on combining multiple elements or data sets to create a unified whole, improving efficiency and broad application through consolidated information. Key differences include differentiation's goal of distinctiveness versus aggregation's aim of integration and simplification.
Applications of Differentiation Across Industries
Differentiation plays a crucial role in industries such as finance, where it is used to calculate rates of change in asset prices and optimize investment strategies. In manufacturing, differentiation helps analyze stress and strain in materials, improving product durability and performance. The technology sector leverages differentiation in machine learning algorithms to enhance predictive accuracy and drive innovation in artificial intelligence applications.
Aggregation Strategies and Their Impact
Aggregation strategies in data processing involve combining multiple data points or metrics to provide a summarized view, which enhances decision-making efficiency by reducing complexity. Common aggregation methods include sum, average, maximum, minimum, and count functions, each tailored to highlight specific trends or patterns within large datasets. Effective aggregation improves performance in analytics, reporting, and machine learning by simplifying data representation while preserving key insights.
Benefits and Drawbacks of Differentiation
Differentiation enhances a company's competitive advantage by allowing unique product features tailored to specific customer needs, leading to brand loyalty and the ability to charge premium prices. However, the drawbacks include higher production costs, increased complexity in marketing, and the risk of over-customization that may limit scalability. Companies must balance the benefits of distinctive offerings with the challenges of maintaining efficiency and broad market appeal.
Pros and Cons of Aggregation Approaches
Aggregation approaches offer enhanced data summarization and reduced complexity by consolidating information for improved decision-making and performance analysis. However, aggregation can lead to loss of granular details, potentially masking valuable insights and hindering precise anomaly detection. Balancing aggregation levels is essential to maintain meaningful data interpretation while optimizing storage and processing efficiency.
Choosing the Right Strategy: Differentiation vs Aggregation
Choosing the right strategy between differentiation and aggregation depends on target market characteristics and business goals. Differentiation excels in niche markets by offering unique value propositions and personalized experiences, whereas aggregation leverages economies of scale and broad appeal to drive volume and efficiency. Analyzing customer segmentation, competitive landscape, and operational capabilities ensures alignment with long-term growth objectives.
Future Trends in Differentiation and Aggregation
Future trends in differentiation emphasize hyper-personalization through advanced AI algorithms that analyze vast datasets to create unique customer experiences and targeted marketing strategies. Aggregation is evolving with the integration of decentralized platforms and blockchain technology, enhancing data security and transparency in consolidating information from diverse sources. Both approaches increasingly leverage machine learning models to optimize decision-making and predict consumer behavior, driving efficiency and innovation across industries.
Differentiation Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com