Egalitarianism advocates for equal rights and opportunities, emphasizing the elimination of social hierarchies and discrimination. It promotes fairness in wealth distribution, education, and political power to create a just society where everyone can thrive. Explore this article to understand how egalitarianism shapes modern social and political thought.
Table of Comparison
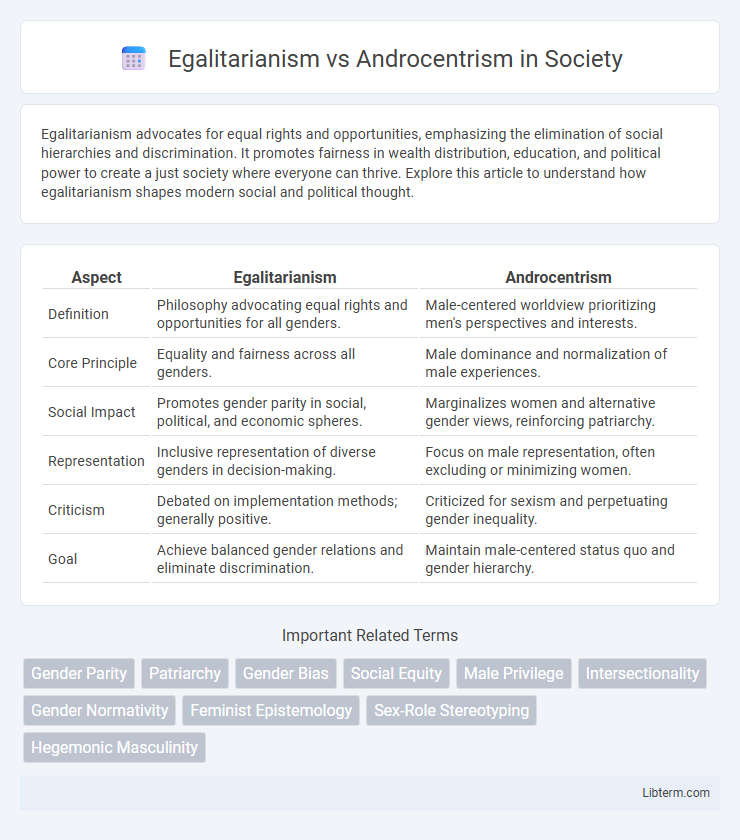
| Aspect | Egalitarianism | Androcentrism |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Philosophy advocating equal rights and opportunities for all genders. | Male-centered worldview prioritizing men's perspectives and interests. |
| Core Principle | Equality and fairness across all genders. | Male dominance and normalization of male experiences. |
| Social Impact | Promotes gender parity in social, political, and economic spheres. | Marginalizes women and alternative gender views, reinforcing patriarchy. |
| Representation | Inclusive representation of diverse genders in decision-making. | Focus on male representation, often excluding or minimizing women. |
| Criticism | Debated on implementation methods; generally positive. | Criticized for sexism and perpetuating gender inequality. |
| Goal | Achieve balanced gender relations and eliminate discrimination. | Maintain male-centered status quo and gender hierarchy. |
Understanding Egalitarianism: Core Principles
Egalitarianism is founded on the principle of equal rights and opportunities for all individuals regardless of gender, race, or social status, challenging androcentrism's male-centered worldview that often marginalizes women and non-male perspectives. Core principles include the belief in intrinsic human equality and the rejection of systemic biases that privilege one group over others, promoting fairness in social, political, and economic spheres. This framework encourages policies and cultural shifts aimed at dismantling patriarchal structures and ensuring inclusive representation and participation across all levels of society.
Defining Androcentrism in Society
Androcentrism in society refers to the practice of centering men and male perspectives as the default or norm, often marginalizing women and non-binary individuals in cultural, political, and social contexts. This bias influences language, media representation, workplace dynamics, and legal frameworks, perpetuating gender inequalities by privileging masculine experiences. Egalitarianism challenges androcentrism by advocating for equal rights, opportunities, and representation regardless of gender, promoting a balanced and inclusive societal structure.
Historical Roots of Egalitarianism
Egalitarianism traces its roots to ancient philosophical traditions, notably in Socratic dialogues advocating for equality in moral and political realms. The Enlightenment period further cemented egalitarian ideals through thinkers like Rousseau and Locke, emphasizing natural rights and social contracts that challenge hierarchical structures. Contrastingly, androcentrism, often institutionalized in patriarchal societies, marginalizes women's experiences by centering male perspectives throughout history.
The Rise and Impact of Androcentrism
The rise of androcentrism, the practice of centering male perspectives and experiences as the norm, has profoundly shaped social structures, cultural narratives, and academic discourses, often marginalizing women's voices and contributions. This male-centric worldview underpins systemic gender inequalities by prioritizing male values, behaviors, and goals in politics, media, and workplace environments. In contrast, egalitarianism advocates for equal rights and opportunities regardless of gender, challenging androcentric biases and promoting inclusivity and gender parity across societal institutions.
Key Differences: Egalitarianism vs Androcentrism
Egalitarianism advocates for equal rights, opportunities, and treatment regardless of gender, promoting fairness and inclusivity across all social and political domains. Androcentrism centers male perspectives and experiences as the default, often marginalizing or excluding women's values and contributions in societal norms, language, and institutional structures. The key difference lies in egalitarianism's focus on gender equality versus androcentrism's inherent male bias and dominance in cultural and social frameworks.
Cultural Representations and Media Influence
Cultural representations in media often reflect androcentrism by prioritizing male perspectives and marginalizing female experiences, reinforcing gender hierarchies and limiting diverse narratives. Egalitarianism challenges these portrayals by advocating for balanced and inclusive depictions that promote gender equality and empower underrepresented groups. Media influence plays a crucial role in shaping societal norms, making the push for egalitarian content essential to dismantling androcentric biases and fostering equitable cultural perceptions.
Effects on Gender Roles and Social Structures
Egalitarianism promotes equal rights and opportunities across genders, reshaping social structures to support gender-neutral roles and reduce discrimination. Androcentrism centers male perspectives and experiences, reinforcing traditional gender roles that prioritize masculinity and often marginalize women and non-binary individuals. The tension between these paradigms influences policies, workplace dynamics, and cultural norms, impacting gender equity and social hierarchy.
Policy Approaches: Promoting Equality
Policy approaches promoting equality under egalitarianism emphasize creating and enforcing laws that guarantee equal rights and opportunities regardless of gender, supporting measures such as pay equity and anti-discrimination legislation. In contrast, androcentrism often results in policies that prioritize male perspectives and interests, leading to systemic biases and unequal resource distribution. Effective equality promotion requires dismantling androcentric norms embedded in institutions to ensure inclusive policy frameworks that represent all genders fairly.
Challenges in Overcoming Androcentric Norms
Overcoming androcentric norms faces significant challenges due to deeply ingrained gender biases embedded in cultural, social, and institutional structures. Persistent male-centered perspectives shape language, policies, and media representation, reinforcing stereotypes that marginalize women and non-binary individuals. Efforts to promote egalitarianism require comprehensive reforms in education, workplace practices, and legislative frameworks to dismantle systemic androcentrism.
Future Directions: Towards a More Egalitarian Society
Future directions towards a more egalitarian society emphasize dismantling androcentrism by promoting gender-neutral policies and inclusive language in education, media, and workplace practices. Advancements in technology and social platforms are leveraged to amplify marginalized voices, fostering equal representation and challenging male-centered narratives. Increasing interdisciplinary research on gender dynamics supports evidence-based reforms that advance gender equality and cultural shifts.
Egalitarianism Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com