Role conflict arises when competing demands from different social roles create stress and hinder effective decision-making. Balancing multiple responsibilities at work and home can lead to emotional exhaustion and reduced productivity. Explore the rest of this article to understand strategies for managing role conflict and improving your well-being.
Table of Comparison
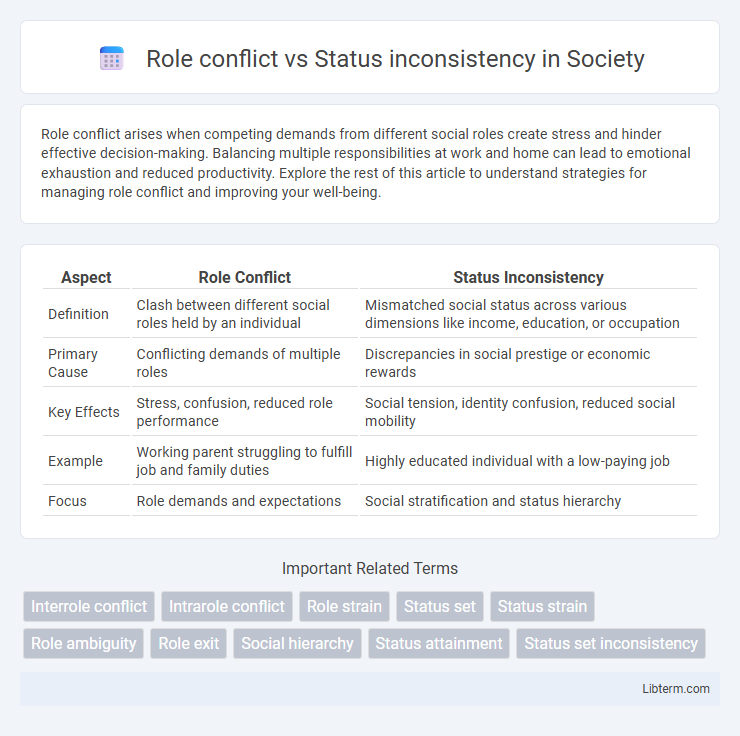
| Aspect | Role Conflict | Status Inconsistency |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Clash between different social roles held by an individual | Mismatched social status across various dimensions like income, education, or occupation |
| Primary Cause | Conflicting demands of multiple roles | Discrepancies in social prestige or economic rewards |
| Key Effects | Stress, confusion, reduced role performance | Social tension, identity confusion, reduced social mobility |
| Example | Working parent struggling to fulfill job and family duties | Highly educated individual with a low-paying job |
| Focus | Role demands and expectations | Social stratification and status hierarchy |
Introduction to Role Conflict and Status Inconsistency
Role conflict occurs when an individual faces incompatible demands from different social roles simultaneously, leading to stress and difficulty in fulfilling responsibilities. Status inconsistency arises when a person's social positions hold conflicting levels of prestige or rank, creating tension between expectations tied to each status. Understanding these sociological concepts helps clarify how individuals navigate complex social structures and the challenges related to identity and social expectations.
Defining Role Conflict: Meaning and Examples
Role conflict occurs when an individual faces incompatible demands from different social roles simultaneously, causing stress and difficulty in fulfilling expectations. For example, a working parent may experience role conflict when job responsibilities clash with family obligations, such as attending a critical meeting while needing to care for a sick child. Understanding role conflict highlights the challenges in balancing multiple social positions that impose contradictory pressures on behavior.
Understanding Status Inconsistency: Concepts and Cases
Status inconsistency occurs when an individual's social positions have conflicting rankings across different status dimensions, such as education, occupation, or income, leading to confusion in social roles and expectations. This phenomenon contrasts with role conflict, which involves incompatible demands within a single status or role. Case studies reveal that individuals experiencing status inconsistency often face psychological stress and social tension due to contradictory societal evaluations of their status attributes.
Key Differences Between Role Conflict and Status Inconsistency
Role conflict occurs when an individual faces incompatible demands from multiple roles simultaneously, creating tension and stress, while status inconsistency arises when a person's social positions hold conflicting levels of prestige or power across different status dimensions, such as occupation, education, or income. Role conflict centers on the challenges of fulfilling diverse behavioral expectations associated with different social roles, whereas status inconsistency highlights disparities in social ranking that influence an individual's access to resources and social respect. The key difference lies in role conflict involving contradictory role expectations creating behavioral dilemmas, compared to status inconsistency involving hierarchical mismatches impacting social standing and identity.
Causes of Role Conflict in Modern Societies
Role conflict in modern societies often stems from competing demands between work and family responsibilities, heightened by rapid social change and evolving gender roles. Technological advancements and globalization increase expectations for multitasking and availability, intensifying pressure on individuals to fulfill contradictory roles simultaneously. Status inconsistency occurs when an individual's social positions hold conflicting levels of prestige, which can exacerbate stress but differs from role conflict, where the clash arises specifically from incompatible role demands.
Factors Leading to Status Inconsistency
Status inconsistency arises when an individual's social positions across factors such as occupation, education, and income do not align, creating conflicting social expectations. Key factors leading to status inconsistency include disparities between educational attainment and occupational prestige, significant income variations despite similar job roles, and differences in social recognition across community or cultural contexts. These discrepancies generate tension as individuals navigate contradictory social roles tied to their mismatched status indicators.
Social Impacts of Role Conflict vs Status Inconsistency
Role conflict arises when an individual faces incompatible demands from multiple social roles, leading to stress, reduced productivity, and strained relationships. Status inconsistency occurs when a person's social positions have conflicting levels of prestige or power, causing social tension, identity confusion, and challenges in social acceptance. Both phenomena disrupt social cohesion by undermining individuals' ability to navigate social expectations effectively.
Role Theory Perspective on Conflict and Inconsistency
Role conflict arises when incompatible expectations are associated with a single social position, leading to tension in fulfilling role demands, whereas status inconsistency occurs when an individual's social positions vary in rank or prestige, creating discord between statuses. From a Role Theory perspective, conflict emerges due to competing role obligations that challenge behavioral coherence, while inconsistency highlights disparities between social roles that affect identity and social interactions. Understanding these concepts is crucial for analyzing how conflicting role expectations and mismatched social statuses contribute to social stress and individual behavior in complex social structures.
Strategies for Managing Role Conflict and Status Inconsistency
Effective strategies for managing role conflict include clear communication, priority setting, and seeking social support to balance competing demands associated with multiple roles. Addressing status inconsistency involves enhancing role integration through adaptive identity management and aligning social expectations to reduce psychological tension. Employing these approaches fosters greater personal coherence and social harmony amid complex status and role dynamics.
Conclusion: Navigating Complex Social Roles and Status
Navigating complex social roles and status requires understanding the distinct dynamics of role conflict and status inconsistency; role conflict arises when a person faces incompatible demands from multiple roles, while status inconsistency occurs when an individual's social positions have conflicting levels of prestige or power. Effective management of these challenges involves recognizing the sources of tension and employing adaptive strategies to maintain social equilibrium. Awareness of these social phenomena supports better interpersonal relationships and organizational functioning by clarifying expectations and reducing stress.
Role conflict Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com