Information abundance transforms the way your mind processes data, creating both opportunities and challenges in decision-making. Navigating through vast amounts of information requires effective filtering to avoid overload and focus on valuable insights. Explore the rest of this article to learn strategies for managing information abundance and enhancing your cognitive efficiency.
Table of Comparison
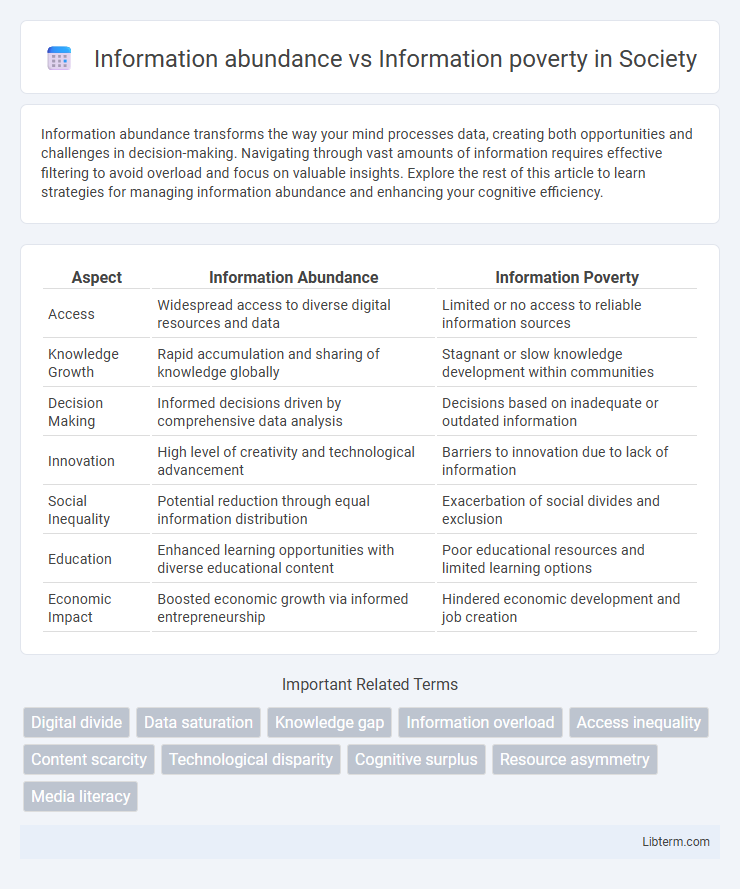
| Aspect | Information Abundance | Information Poverty |
|---|---|---|
| Access | Widespread access to diverse digital resources and data | Limited or no access to reliable information sources |
| Knowledge Growth | Rapid accumulation and sharing of knowledge globally | Stagnant or slow knowledge development within communities |
| Decision Making | Informed decisions driven by comprehensive data analysis | Decisions based on inadequate or outdated information |
| Innovation | High level of creativity and technological advancement | Barriers to innovation due to lack of information |
| Social Inequality | Potential reduction through equal information distribution | Exacerbation of social divides and exclusion |
| Education | Enhanced learning opportunities with diverse educational content | Poor educational resources and limited learning options |
| Economic Impact | Boosted economic growth via informed entrepreneurship | Hindered economic development and job creation |
Understanding Information Abundance and Information Poverty
Information abundance refers to the vast availability of data and knowledge resources accessible through digital platforms, enabling individuals to acquire diverse insights rapidly. Information poverty denotes the lack of access to relevant, reliable, and timely information, which hinders decision-making and perpetuates social and economic disparities. Understanding the dynamics between these two conditions highlights the digital divide and the critical need for equitable information distribution to empower marginalized communities.
The Evolution of the Digital Information Landscape
The evolution of the digital information landscape has amplified the contrast between information abundance and information poverty, with billions of data points accessible through the internet, social media, and digital databases. Advanced search algorithms, cloud storage, and real-time data sharing empower users in developed regions to harness vast knowledge, while digital divides and limited infrastructure perpetuate information poverty in underserved communities. This disparity highlights the critical need for improved digital literacy, equitable internet access, and infrastructure investment to bridge the gap in the global information ecosystem.
Causes and Consequences of Information Abundance
Information abundance is primarily caused by the exponential growth of digital technologies, widespread internet accessibility, and the proliferation of social media platforms, which collectively generate vast amounts of data every second. This overload leads to challenges such as information fatigue, decreased attention spans, and difficulties in discerning credible sources, resulting in potential misinformation and decision paralysis. The consequences extend to economic sectors, where businesses face analysis paralysis, and individuals experience cognitive overload impacting productivity and mental health.
Identifying Roots of Information Poverty
Information poverty stems from limited access to technology, inadequate digital literacy, and socio-economic barriers that restrict individuals' ability to obtain, evaluate, and use information effectively. Geographic disparities and institutional neglect contribute to persistent information gaps, particularly in rural and underdeveloped regions. Tackling these root causes requires targeted infrastructure investment, education programs, and inclusive policies that promote equitable information access.
The Digital Divide: Access and Equity Issues
The digital divide highlights the stark contrast between information abundance and information poverty, where unequal access to technology and internet connectivity creates significant barriers to information equity. Populations in underserved regions or low-income communities face limited access to digital resources, restricting educational, economic, and social opportunities. Ensuring affordable, reliable internet and digital literacy programs is essential to bridge this gap and promote inclusive access to information for all.
Impacts on Education and Lifelong Learning
Information abundance enhances access to diverse educational resources, fostering personalized learning experiences and critical thinking skills development. Conversely, information poverty limits exposure to knowledge, creating barriers to educational attainment and lifelong learning opportunities, often exacerbating social inequalities. Bridging this gap requires equitable access to digital technologies and quality content to support continuous skill acquisition and informed decision-making.
Social, Economic, and Cultural Ramifications
Information abundance fosters social connectivity and economic innovation by providing widespread access to digital resources, leading to enhanced educational opportunities and entrepreneurial growth. In contrast, information poverty exacerbates social inequality, limits economic participation, and stifles cultural expression, as marginalized communities lack access to crucial knowledge and communication technologies. Addressing these disparities requires targeted policies to ensure equitable information infrastructure and digital literacy programs that empower underserved populations.
Strategies to Bridge the Information Gap
Implementing community-based digital literacy programs enhances access to technology and critical evaluation skills, reducing information poverty. Collaborations between governments and NGOs can expand broadband infrastructure in underserved areas, directly addressing connectivity disparities. Furthermore, promoting open-access educational resources empowers individuals to harness available information effectively, bridging the information abundance gap.
The Role of Technology in Shaping Access
Technology significantly influences access to information by bridging gaps between information abundance and information poverty. Digital platforms, high-speed internet, and mobile devices enable vast data dissemination, empowering users in developed regions to access diverse knowledge easily. However, technological disparities and limited infrastructure in low-income areas perpetuate information poverty, restricting opportunities for education, economic growth, and social inclusion.
Building a More Inclusive Information Society
Bridging the gap between information abundance and information poverty is crucial for building a more inclusive information society where equitable access to digital resources empowers underserved communities. Implementing widespread digital literacy programs and affordable internet infrastructure fosters equal participation in the global knowledge economy. Addressing systemic barriers in information access promotes social inclusion and drives sustainable development across marginalized populations.
Information abundance Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com