Apprenticeship offers hands-on experience that bridges the gap between education and the professional world, equipping you with practical skills and industry knowledge. This approach enhances employability by providing mentorship and real-world problem-solving opportunities in a specific trade or profession. Explore the rest of the article to discover how apprenticeships can transform your career path and open doors to new opportunities.
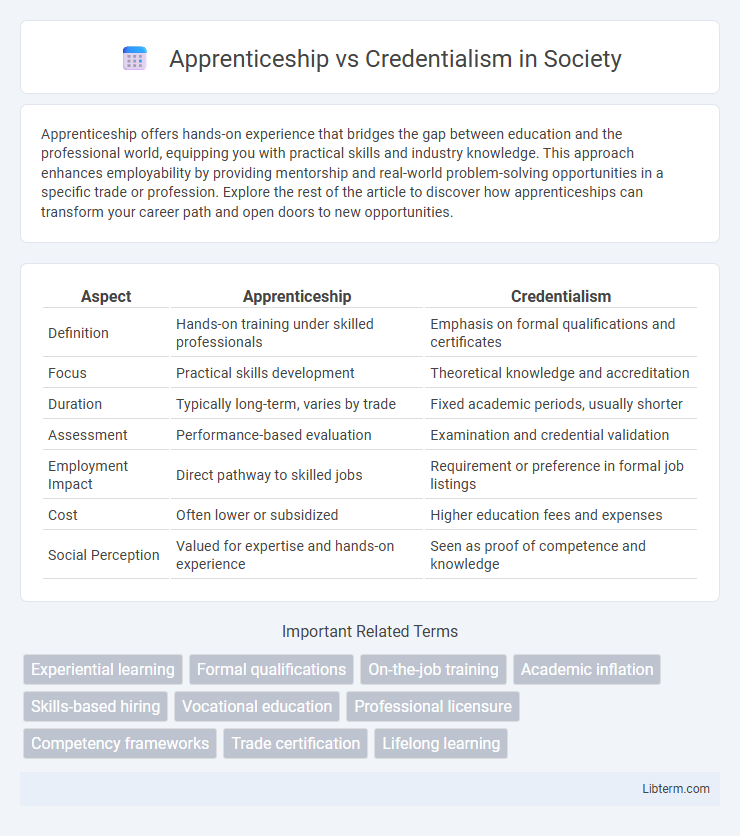
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Apprenticeship | Credentialism |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Hands-on training under skilled professionals | Emphasis on formal qualifications and certificates |
| Focus | Practical skills development | Theoretical knowledge and accreditation |
| Duration | Typically long-term, varies by trade | Fixed academic periods, usually shorter |
| Assessment | Performance-based evaluation | Examination and credential validation |
| Employment Impact | Direct pathway to skilled jobs | Requirement or preference in formal job listings |
| Cost | Often lower or subsidized | Higher education fees and expenses |
| Social Perception | Valued for expertise and hands-on experience | Seen as proof of competence and knowledge |
Understanding Apprenticeships: A Practical Approach
Apprenticeships provide hands-on training that combines on-the-job experience with classroom instruction, making them a practical pathway to skill mastery in various trades and professions. This approach emphasizes real-world application and mentorship, fostering competency and employability without the need for extensive formal education credentials. Understanding apprenticeships highlights their role in bridging skill gaps and promoting workforce development through experiential learning.
What is Credentialism? Defining the Concept
Credentialism refers to the overemphasis on formal educational qualifications and certificates as a measure of a person's skills or competence, often overshadowing practical experience and abilities. It prioritizes diplomas and degrees as essential proof of capability, impacting hiring decisions and social status. This concept challenges the value of hands-on learning methods like apprenticeships by favoring standardized credentials over demonstrated expertise.
Historical Evolution of Skills Training
The historical evolution of skills training reveals a shift from traditional apprenticeships, where hands-on learning under master craftsmen ensured practical expertise, toward credentialism that emphasizes formal certifications and academic qualifications. Apprenticeships dominated pre-industrial societies, embedding skills through direct experience, while the rise of industrialization and expanded educational systems propelled credentialism as a means to standardize and verify competencies. This transition reflects broader social and economic changes, including increased specialization and the demand for measurable qualifications in the modern labor market.
Comparing Learning Outcomes: Hands-On vs. Academic
Apprenticeships provide hands-on learning experiences that develop practical skills and job-specific competencies through real-world application, enhancing workplace readiness and technical proficiency. In contrast, credentialism emphasizes academic achievements and formal qualifications, often prioritizing theoretical knowledge and standardized testing over experiential learning. Studies show that apprentices gain deeper skill retention and adaptability, while credentialed individuals may excel in analytical thinking and foundational theory relevant to broader career advancement.
Employability: Which Path Yields Better Job Prospects?
Apprenticeships provide hands-on experience and industry-specific skills, often leading to higher employability and faster job placement due to direct employer engagement. Credentialism emphasizes formal qualifications, which can enhance job opportunities but may not guarantee practical competence or immediate access to roles requiring technical expertise. Studies show apprenticeship graduates typically have lower unemployment rates and higher income potential in skilled trades compared to those relying solely on academic credentials.
Economic Impacts of Apprenticeships and Credentialism
Apprenticeships significantly enhance workforce skills through hands-on experience, leading to higher employment rates and increased earnings for participants, thereby strengthening local economies. In contrast, credentialism often results in degree inflation, causing job market saturation and underemployment, which can slow economic growth and reduce efficiency in labor allocation. Investing in apprenticeship programs reduces skill gaps and improves productivity more effectively than overreliance on formal credentials alone.
Industry Preferences: What Employers Really Want
Employers increasingly prioritize practical skills and hands-on experience gained through apprenticeships over formal credentials, emphasizing job readiness and productivity. Industry leaders report higher retention rates and immediate contributions from apprenticeship graduates compared to those with traditional academic credentials. Hiring decisions often favor candidates who demonstrate proven competency and adaptability, reflecting a shift toward competency-based evaluation in workforce development.
Cost and Accessibility: Barriers to Entry
Apprenticeships often offer lower cost barriers because they combine paid on-the-job training with classroom instruction, making them more accessible to individuals without significant financial resources. Credentialism, by contrast, typically requires expensive tuition fees and lengthy academic commitments, which can limit access for underrepresented or economically disadvantaged populations. These financial and structural barriers in credential-based education systems contribute to unequal workforce participation and skills development opportunities.
Future Trends: Will Apprenticeship Replace Credentialism?
Future trends indicate a growing emphasis on apprenticeships as industries seek practical skills and hands-on experience, challenging the traditional dominance of credentialism. Employers increasingly value competency-based training and real-world expertise over formal degrees, especially in tech, manufacturing, and trade sectors. While credentialism remains prevalent in professions requiring licensure, the shift toward apprenticeship programs signals a hybrid future blending credentials with experiential learning.
Choosing the Right Path: Key Considerations for Learners
Choosing the right path between apprenticeship and credentialism depends on individual career goals, learning preferences, and industry demands. Apprenticeships offer practical, hands-on experience that can lead to immediate employment, while credentialism emphasizes formal qualifications often required for professional advancement. Learners should evaluate job market trends, employer expectations, and personal skill development needs to determine the most effective route for long-term success.
Apprenticeship Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com