Cultural purism emphasizes maintaining the original purity of a culture by resisting external influences and changes. This ideology often leads to efforts in preserving traditional customs, languages, and practices to safeguard cultural identity. Explore the rest of the article to understand how cultural purism shapes societies and affects your perception of heritage.
Table of Comparison
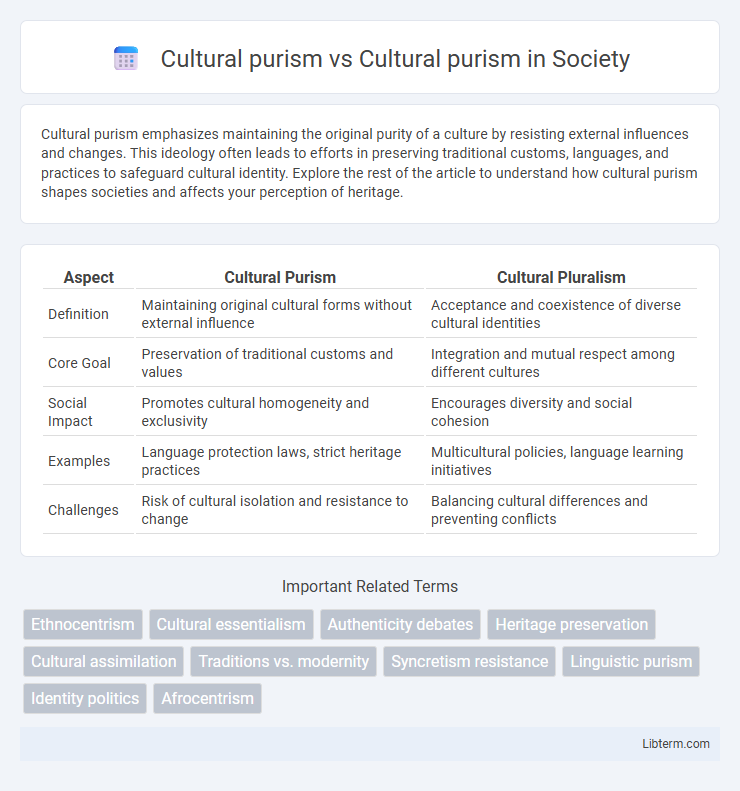
| Aspect | Cultural Purism | Cultural Pluralism |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Maintaining original cultural forms without external influence | Acceptance and coexistence of diverse cultural identities |
| Core Goal | Preservation of traditional customs and values | Integration and mutual respect among different cultures |
| Social Impact | Promotes cultural homogeneity and exclusivity | Encourages diversity and social cohesion |
| Examples | Language protection laws, strict heritage practices | Multicultural policies, language learning initiatives |
| Challenges | Risk of cultural isolation and resistance to change | Balancing cultural differences and preventing conflicts |
Introduction to Cultural Purism
Cultural purism emphasizes preserving the original traditions, languages, and customs of a society while resisting external influences and modernization. This approach seeks to maintain cultural identity by prioritizing authenticity and purity over hybridization or change. Cultural purism often emerges as a response to globalization, colonialism, or perceived cultural dilution, aiming to protect heritage from assimilation and loss.
Defining Cultural Purism: Origins and Evolution
Cultural purism, originating from early 20th-century movements, seeks to preserve a community's traditional customs, language, and values by resisting external influences and globalization. This ideology evolved as a response to rapid modernization, aiming to maintain cultural authenticity and identity amidst social change. The concept often intersects with nationalism and ethnic pride, shaping policies and social attitudes toward cultural preservation and integration.
The Ideals Behind Cultural Purism
Cultural purism champions the preservation of a society's original customs, language, and values to maintain cultural integrity and resist external influences perceived as diluting traditional identity. Advocates argue that safeguarding these ideals fosters social cohesion and protects heritage from globalization's homogenizing effects. Critics, however, warn that rigid cultural purism can stifle diversity and hinder cultural evolution in increasingly interconnected societies.
Internal Contradictions Within Cultural Purism
Cultural purism often involves preserving perceived authentic traditions while simultaneously resisting external influences, yet this stance contains internal contradictions as cultures are inherently dynamic and continuously influenced by interaction and adaptation. The rigid emphasis on unchanging heritage can lead to selective memory or idealization, distorting cultural realities and ignoring historical evolutions. This tension undermines the coherence of cultural purism by highlighting how cultural identity is both constructed and fluid, challenging the very notion of purity it seeks to uphold.
Cultural Purism in Different Societies
Cultural purism manifests uniquely across societies, emphasizing the preservation of traditional customs and languages to maintain national identity and resist globalization's influence. In societies like Japan, cultural purism promotes the protection of indigenous arts and language, while in some indigenous communities, it serves to safeguard ancestral heritage against external cultural assimilation. The tension between cultural purism and cultural adaptation illustrates diverse societal responses to globalization and cultural exchange pressures.
Arguments For and Against Cultural Purism
Cultural purism advocates maintaining traditional cultural elements to preserve identity and resist external influences perceived as diluting authenticity. Critics argue that it can lead to exclusionary practices, stifle cultural evolution, and foster xenophobia by rejecting multicultural integration. Proponents emphasize the importance of safeguarding heritage, while opponents highlight the dynamic nature of culture and the value of intercultural exchange.
Case Studies: When Cultural Purism Meets Reality
Examining case studies reveals that cultural purism often clashes with the dynamic, hybrid nature of contemporary societies, where globalization and migration introduce diverse influences that challenge rigid preservationist ideals. In indigenous communities, efforts to maintain linguistic purity face practical adaptations as younger generations incorporate external elements into traditional practices, illustrating cultural evolution rather than static preservation. Urban multicultural settings demonstrate how strict cultural purism can hinder social cohesion, while flexible approaches enable inclusive identities that reflect lived realities and intercultural exchanges.
Cultural Purism and Globalization
Cultural purism emphasizes preserving traditional customs, languages, and identities against external influences, often resisting globalization's homogenizing effects. This approach prioritizes safeguarding indigenous practices to maintain cultural integrity amid the global spread of dominant cultures and technologies. It highlights tensions between local cultural preservation and the dynamic exchange inherent in globalization processes.
The Impact of Cultural Purism on Identity
Cultural purism enforces strict adherence to traditional customs and norms, often resisting external influences to preserve a singular identity. This rigid preservation can lead to a homogenized community identity, limiting diversity and innovation within cultural expressions. Such purism sometimes results in exclusionary practices, reinforcing boundaries that can impact social cohesion and intercultural dialogue.
Future Perspectives on Cultural Purism
Future perspectives on cultural purism emphasize dynamic cultural exchange influenced by globalization, digital communication, and migration patterns. Increasing cultural hybridity challenges strict preservation, promoting adaptive identities that integrate diverse elements without erasing origins. Technological advancements and cross-cultural dialogues foster inclusive narratives, redefining cultural purism to balance heritage conservation with innovation and intercultural collaboration.
Cultural purism Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com