The underground economy consists of economic activities that are not reported to authorities and thus escape taxation and regulation, including unregistered businesses and informal labor exchanges. This hidden sector can significantly impact a nation's economic health by distorting official statistics and reducing government revenue. Discover how understanding the underground economy can help you recognize its effects and explore strategies to address it in the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
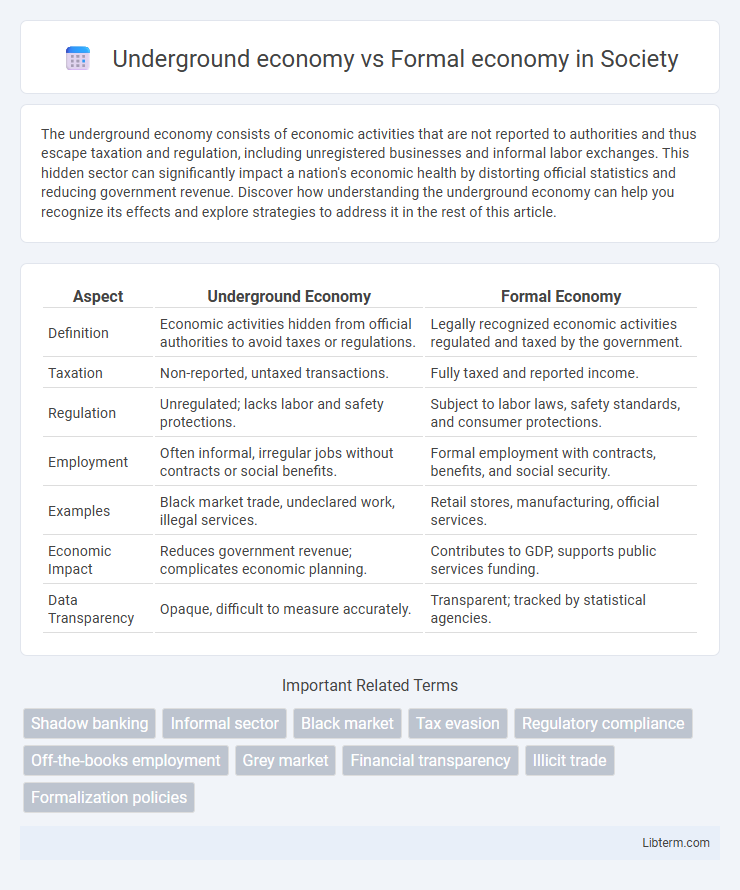
| Aspect | Underground Economy | Formal Economy |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Economic activities hidden from official authorities to avoid taxes or regulations. | Legally recognized economic activities regulated and taxed by the government. |
| Taxation | Non-reported, untaxed transactions. | Fully taxed and reported income. |
| Regulation | Unregulated; lacks labor and safety protections. | Subject to labor laws, safety standards, and consumer protections. |
| Employment | Often informal, irregular jobs without contracts or social benefits. | Formal employment with contracts, benefits, and social security. |
| Examples | Black market trade, undeclared work, illegal services. | Retail stores, manufacturing, official services. |
| Economic Impact | Reduces government revenue; complicates economic planning. | Contributes to GDP, supports public services funding. |
| Data Transparency | Opaque, difficult to measure accurately. | Transparent; tracked by statistical agencies. |
Understanding the Underground Economy
The underground economy comprises unreported income from legal or illegal activities that evade taxes and government regulation, contrasting with the formal economy's transparent and regulated market transactions. Understanding the underground economy involves analyzing factors such as cash-based transactions, informal labor markets, and tax evasion strategies that drive economic activity outside official records. Accurate measurement and assessment of this sector are crucial for policymakers to address revenue losses and ensure equitable resource allocation.
Defining the Formal Economy
The formal economy encompasses all economic activities that are officially recognized, regulated, and taxed by government authorities, including registered businesses, employed labor, and legal trade transactions. It contributes to national GDP measurements, provides social security benefits, and ensures compliance with labor laws and financial reporting standards. The formal sector supports economic growth through transparent operations, access to credit, and formal employment contracts, distinguishing it from the unregulated underground economy.
Key Differences Between Underground and Formal Economies
The underground economy operates outside government regulation, involving unreported income and cash transactions to avoid taxes and legal oversight, while the formal economy is fully regulated, taxed, and recorded by official institutions. Key differences include the underground economy's lack of labor protections, absence of financial transparency, and exclusion from official GDP calculations compared to the formal economy's compliance with labor laws, tax obligations, and integration into economic statistics. The underground economy often thrives in sectors like informal labor and illicit trade, contrasting with the formal economy's structured enterprises and publicly accountable financial practices.
Drivers Behind the Growth of the Underground Economy
The underground economy expands due to high taxation, excessive regulation, and lack of trust in government institutions, pushing individuals and businesses to operate informally to avoid legal constraints. Socioeconomic factors such as unemployment, poverty, and limited access to formal financial services drive participation in unreported economic activities. Technological advancements and cash-based transactions further facilitate the underground economy's growth by enabling anonymity and reducing traceability.
Regulatory Frameworks in Formal Economies
Formal economies operate under comprehensive regulatory frameworks that establish legal standards for taxation, labor rights, and business operations, ensuring transparency and accountability. These regulations facilitate government oversight, promote consumer protection, and enable accurate economic data collection essential for policy-making and economic planning. In contrast, underground economies bypass such regulations, resulting in unreported income, tax evasion, and limited enforcement of labor and safety standards.
Impact on Tax Revenue and Public Services
The underground economy significantly reduces tax revenue by concealing income and transactions from authorities, leading to substantial fiscal deficits. This tax evasion limits government capacity to fund public services such as healthcare, education, and infrastructure, undermining social welfare and economic development. In contrast, the formal economy ensures transparent tax contributions, enhancing funding for public goods and enabling effective governance and public service delivery.
Employment Patterns in Both Economies
Employment patterns in the underground economy are characterized by informal, often unregulated jobs lacking legal protections, social security, or official records. In contrast, the formal economy features regulated employment with standardized contracts, legal safeguards, and access to benefits such as pensions and healthcare. Workers in the underground economy typically engage in temporary, low-wage labor, whereas formal economy jobs offer greater stability, career progression, and compliance with labor laws.
Social and Economic Consequences
The underground economy undermines tax revenues, reducing government capacity to fund public services and social welfare programs, which exacerbates inequality and limits economic development. Informal labor markets lack legal protections, leading to worker exploitation, job insecurity, and absence of social benefits, negatively impacting social stability. Conversely, the formal economy promotes regulatory compliance, transparency, and worker rights, fostering sustainable economic growth and improved social outcomes through stable employment and social security systems.
Strategies to Transition Informal Activities into the Formal Sector
Governments implement targeted policies such as simplifying business registration processes and offering financial incentives to encourage the shift of underground economy activities into the formal economy. Strengthening legal frameworks and enhancing access to credit and social protection promote formalization among informal workers and entrepreneurs. Data-driven approaches leveraging technology improve monitoring and support compliance, facilitating sustainable integration into the formal sector.
Future Trends and Policy Implications
The underground economy, characterized by unreported income and informal labor, is projected to evolve with advancing digital payment systems and increased use of cryptocurrencies, challenging traditional regulatory frameworks. Future trends indicate growing efforts to integrate informal sectors into the formal economy through enhanced digital identification and blockchain technologies, improving transparency and tax compliance. Policymakers must prioritize adaptive regulatory measures and innovative monitoring tools to balance enforcement with incentives for formalization, ensuring sustainable economic growth and social protection.
Underground economy Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com