Conformism involves adopting behaviors, attitudes, or beliefs to align with a group's norms, often driven by social pressure and the desire for acceptance. Understanding how conformism influences your decision-making can help you maintain individuality while navigating social dynamics. Explore the rest of the article to learn strategies for balancing conformity and personal authenticity.
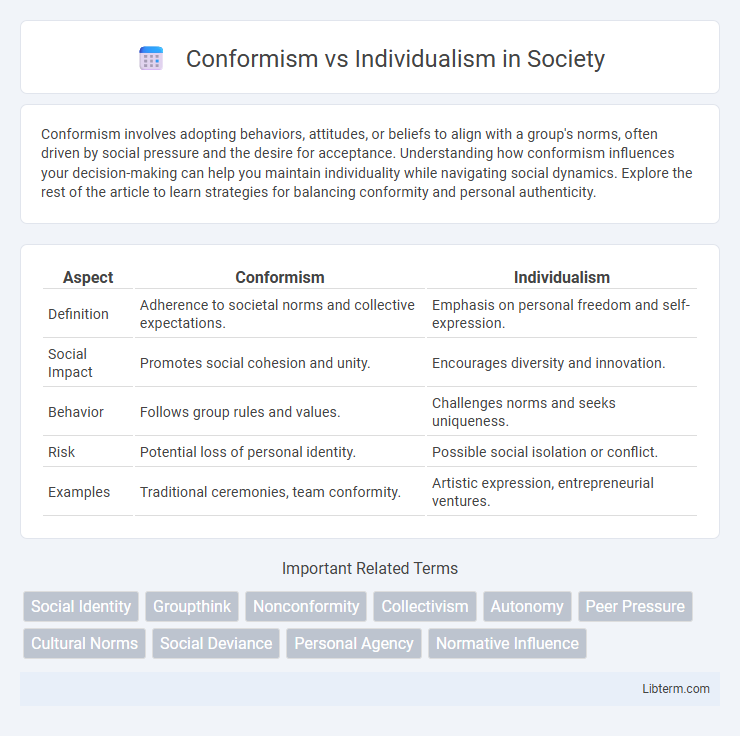
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Conformism | Individualism |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Adherence to societal norms and collective expectations. | Emphasis on personal freedom and self-expression. |
| Social Impact | Promotes social cohesion and unity. | Encourages diversity and innovation. |
| Behavior | Follows group rules and values. | Challenges norms and seeks uniqueness. |
| Risk | Potential loss of personal identity. | Possible social isolation or conflict. |
| Examples | Traditional ceremonies, team conformity. | Artistic expression, entrepreneurial ventures. |
Understanding Conformism: Definition and Origins
Conformism refers to the act of matching attitudes, beliefs, and behaviors to group norms, driven by the desire for social acceptance or fear of rejection. Its origins trace back to social psychology theories such as Solomon Asch's conformity experiments, which demonstrated how individuals often align with majority opinions despite personal doubts. Understanding conformism involves recognizing its evolutionary role in fostering group cohesion and its influence on cultural and societal structures.
The Essence of Individualism: Key Principles
The essence of individualism centers on personal autonomy, emphasizing self-reliance and the unique expression of one's identity. Key principles include the belief in individual rights, freedom of thought, and the pursuit of personal goals independent of societal pressures. This philosophy prioritizes innovation, creativity, and moral responsibility as foundations for personal and social development.
Historical Perspectives: Conformism vs Individualism
Historical perspectives reveal that conformism often dominated social structures in traditional societies, reinforcing collective norms and stability. Individualism gained prominence during the Enlightenment and Industrial Revolution, emphasizing personal freedom, self-expression, and innovation. The tension between these ideologies shaped cultural, political, and economic developments from feudalism to modern democracy.
Societal Impacts: How Conformism Shapes Communities
Conformism fosters social cohesion by aligning individual behavior with shared norms, promoting order and predictability within communities. It often leads to collective identity and mutual support, yet can suppress creativity and discourage diversity of thought. Societies emphasizing conformism may experience stability but risk stagnation due to the diminished presence of innovation and critical thinking.
The Power of Individualism in Personal Growth
Individualism fosters personal growth by encouraging self-expression and authentic decision-making, which enhances creativity and resilience. Embracing individualism allows individuals to challenge societal norms and cultivate unique talents, leading to greater self-awareness and fulfillment. This empowerment through distinct identity drives innovation and contributes significantly to personal development.
Psychological Drivers: Why Do People Conform?
Social conformity is driven by psychological needs such as the desire for acceptance, fear of rejection, and the motivation to reduce uncertainty in ambiguous situations. People conform to group norms due to normative influence, seeking approval and avoiding social punishment, as well as informational influence, relying on others' behaviors as cues for correct actions. Cognitive dissonance theory also explains conformity, where individuals adjust their beliefs or behaviors to align with group consensus and minimize internal conflict.
Conformism in Modern Culture and Media
Conformism in modern culture and media manifests through pervasive social norms that shape consumer behavior, fashion trends, and online interaction patterns, often promoting homogenized ideals for acceptance and success. Media outlets and advertising campaigns leverage psychological triggers to reinforce conformity, encouraging audiences to adopt standardized lifestyles and values. The proliferation of social media algorithms further amplifies conformity by curating content that echoes prevailing cultural narratives, limiting exposure to diverse perspectives and fostering collective identity over individual expression.
The Role of Individualism in Innovation and Creativity
Individualism fosters innovation and creativity by encouraging unique perspectives and personal expression, which drive novel ideas and solutions. Emphasizing autonomy and self-reliance, individualism creates an environment where experimentation and risk-taking thrive, essential components for breakthroughs in technology and art. Cultures and organizations that prioritize individualism often see higher rates of entrepreneurship and creative problem-solving, fueling economic growth and cultural development.
Balancing Act: Navigating Between Conformity and Self-Expression
Balancing the tension between conformism and individualism requires cultivating self-awareness while respecting social norms, enabling personal authenticity without alienating others. Successful navigation involves adaptive decision-making that honors core values yet remains open to collective influence, fostering harmonious social integration. This equilibrium supports psychological well-being by reducing inner conflict and enhancing a sense of belonging balanced with unique self-expression.
Future Trends: The Evolving Debate Between Conformism and Individualism
Future trends in the evolving debate between conformism and individualism reveal a shifting balance fueled by advances in technology, cultural globalization, and increasing emphasis on personal identity. Digital platforms enable greater individual expression while simultaneously exposing users to collective pressures and algorithm-driven homogenization. The interplay between these forces suggests future societies will navigate new forms of social cohesion that blend conformity with individual autonomy.
Conformism Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com