Inclusion fosters diverse perspectives and creates equitable environments where everyone feels valued and empowered. Embracing inclusion enhances collaboration, innovation, and organizational success by recognizing individual strengths and addressing barriers. Discover how your commitment to inclusion can transform communities and workplaces in the rest of the article.
Table of Comparison
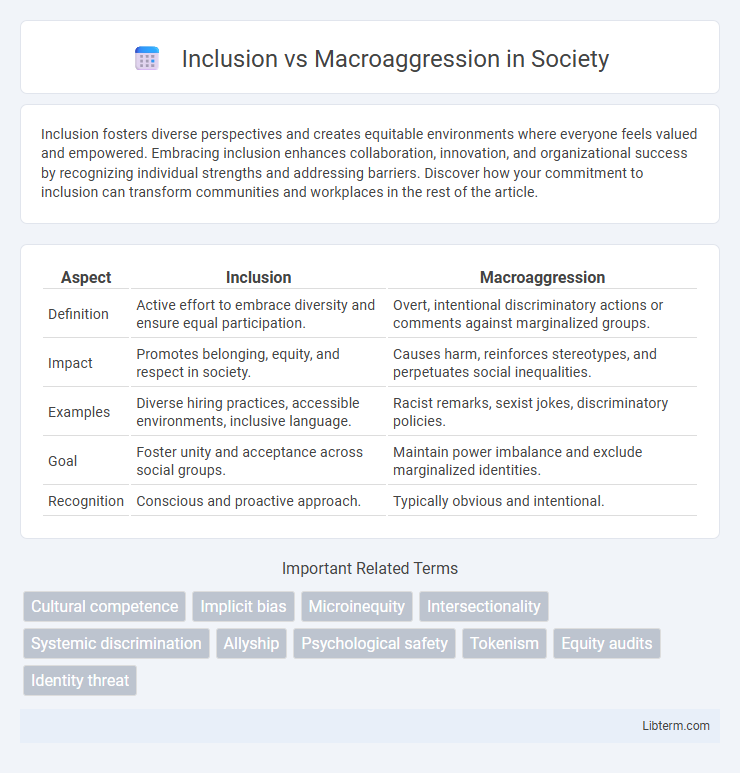
| Aspect | Inclusion | Macroaggression |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Active effort to embrace diversity and ensure equal participation. | Overt, intentional discriminatory actions or comments against marginalized groups. |
| Impact | Promotes belonging, equity, and respect in society. | Causes harm, reinforces stereotypes, and perpetuates social inequalities. |
| Examples | Diverse hiring practices, accessible environments, inclusive language. | Racist remarks, sexist jokes, discriminatory policies. |
| Goal | Foster unity and acceptance across social groups. | Maintain power imbalance and exclude marginalized identities. |
| Recognition | Conscious and proactive approach. | Typically obvious and intentional. |
Understanding Inclusion: Definition and Importance
Inclusion refers to creating environments where individuals of diverse backgrounds feel valued, respected, and have equal access to opportunities. It is essential for fostering innovation, enhancing collaboration, and improving employee engagement within organizations. Understanding inclusion helps to prevent macroaggressions, which are subtle or overt expressions of bias that undermine these efforts.
What is Macroaggression? Key Concepts Explained
Macroaggression refers to overt, intentional acts of discrimination or hostility directed at marginalized groups, often manifesting through harmful words, behaviors, or policies. Key concepts include explicit bias, power imbalance, and the reinforcement of systemic inequality, distinguishing macroaggressions from subtle or unintentional microaggressions. Understanding macroaggression is essential for creating inclusive environments that actively reject blatant discrimination and promote equity.
The Impact of Inclusion on Workplace Culture
Inclusion fosters a positive workplace culture by promoting diversity, equity, and belonging, which enhances employee engagement and productivity. It actively reduces instances of macroaggressions--subtle, often unintentional discriminatory comments or behaviors--by encouraging awareness and respect among colleagues. Cultivating an inclusive environment leads to improved collaboration, innovation, and overall organizational success.
Recognizing Macroaggressions: Common Examples
Recognizing macroaggressions involves identifying subtle, often unintentional comments or actions that invalidate or marginalize individuals based on their identity, such as microinvalidations, microinsults, and microassaults. Common examples include assuming someone's abilities based on stereotypes, making insensitive jokes about race or gender, or dismissing experiences of discrimination as exaggerated. Awareness of these behaviors is crucial for fostering genuine inclusion and creating respectful environments.
Psychological Effects: Inclusion vs Macroaggression
Inclusion fosters psychological safety, enhancing self-esteem, belonging, and motivation among diverse individuals by validating their identities and experiences. Macroaggressions trigger stress responses, anxiety, and diminished mental health, contributing to feelings of exclusion, invisibility, and marginalization. Research demonstrates that inclusive environments reduce the incidence of psychological distress and improve overall well-being compared to settings where macroaggressions are prevalent.
Building Inclusive Environments: Strategies that Work
Building inclusive environments involves recognizing and addressing macroaggressions--subtle, often unintentional acts of exclusion or discrimination that undermine diversity efforts. Effective strategies include implementing bias training, fostering open dialogues, and promoting diverse representation in leadership roles to create a culture of belonging. Regular assessment through feedback mechanisms ensures continuous improvement and reinforces inclusive practices.
How Macroaggressions Undermine Diversity Efforts
Macroaggressions, subtle or overt discriminatory comments and actions, significantly undermine diversity efforts by creating hostile environments that deter marginalized individuals from fully participating. These micro-invalidations disrupt trust and psychological safety, impairing team cohesion and innovation critical to inclusive workplaces. Persistent macroaggressions increase turnover rates among underrepresented groups, thereby weakening organizational commitment to authentic diversity and inclusion.
Addressing Macroaggressions: Practical Interventions
Addressing macroaggressions requires implementing targeted interventions such as diversity training that emphasizes recognition and response to subtle biases. Creating safe spaces for open dialogue encourages individuals to share experiences and fosters empathy within organizations. Establishing clear policies and reporting mechanisms ensures accountability while promoting inclusive environments that actively counteract micro- and macroaggressions.
The Role of Leadership in Fostering Inclusion
Leadership plays a critical role in fostering inclusion by setting clear expectations regarding respect and equity within the organization. Inclusive leaders actively identify and address macroaggressions, promoting a culture of psychological safety where diverse perspectives are valued. Implementing bias training, establishing accountability mechanisms, and encouraging open dialogue are essential strategies leaders use to reduce exclusionary behaviors and enhance organizational inclusivity.
Measuring Progress: Inclusion Metrics and Macroaggression Reduction
Inclusion metrics quantify workforce diversity, equity, and belonging by tracking representation, engagement, and retention rates across demographic groups to assess organizational progress. Macroaggression reduction is measured through employee surveys, reported incident rates, and qualitative feedback to identify overt discriminatory behaviors and their decline over time. Combining these metrics enables organizations to evaluate the effectiveness of diversity initiatives and drive data-informed strategies for creating an inclusive workplace culture.
Inclusion Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com