A knowledge society thrives on the creation, sharing, and utilization of information to foster innovation and economic growth. It empowers individuals and organizations to make informed decisions, enhancing productivity and quality of life. Explore the rest of this article to discover how your engagement in a knowledge society can shape a better future.
Table of Comparison
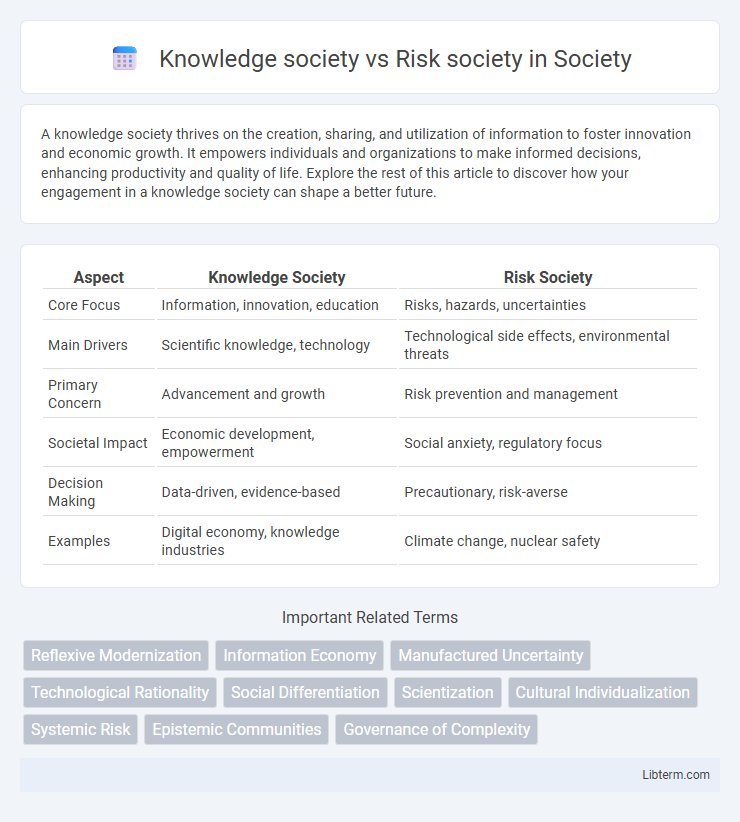
| Aspect | Knowledge Society | Risk Society |
|---|---|---|
| Core Focus | Information, innovation, education | Risks, hazards, uncertainties |
| Main Drivers | Scientific knowledge, technology | Technological side effects, environmental threats |
| Primary Concern | Advancement and growth | Risk prevention and management |
| Societal Impact | Economic development, empowerment | Social anxiety, regulatory focus |
| Decision Making | Data-driven, evidence-based | Precautionary, risk-averse |
| Examples | Digital economy, knowledge industries | Climate change, nuclear safety |
Defining the Knowledge Society
The Knowledge Society is defined by its reliance on information, technology, and innovation as primary drivers of economic growth and social development. It emphasizes the creation, distribution, and utilization of knowledge to enhance productivity, education, and decision-making processes across all sectors. Key components include digital literacy, research institutions, and knowledge-intensive industries that foster continuous learning and adaptation.
Understanding the Risk Society
Understanding the Risk Society involves recognizing how modern societies prioritize managing and mitigating diverse global risks such as environmental hazards, technological failures, and economic uncertainties. Unlike the Knowledge Society, which centers on the production and dissemination of information, the Risk Society emphasizes the societal impact and governance of potential threats arising from scientific and technological advancements. This concept highlights the shift towards a precautionary approach in policy-making and public awareness to address the complex, often invisible risks of contemporary life.
Historical Roots and Development
The concept of the Knowledge Society emerged from the rise of information technology and globalization in the late 20th century, emphasizing the centrality of knowledge production and management for economic and social progress. In contrast, the Risk Society theory, developed by Ulrich Beck in the 1980s, analyzes how modern industrial societies increasingly focus on managing and mitigating risks created by technological advancements and environmental challenges. Both frameworks trace their historical roots to the transformation of industrial societies but diverge in focus, with the Knowledge Society highlighting innovation and digital connectivity, while the Risk Society underscores uncertainties and unintended consequences of modernization.
Key Characteristics of Each Society
Knowledge society is characterized by the widespread creation, dissemination, and utilization of information and expertise, emphasizing innovation, education, and digital technologies as primary drivers of economic and social development. Risk society, on the other hand, focuses on the pervasive presence of manufactured risks stemming from technological advancements, environmental hazards, and social uncertainties that challenge traditional institutions and governance. The key distinction lies in knowledge society's pursuit of progress through information empowerment, whereas risk society revolves around managing and mitigating the unintended consequences of modernization.
The Role of Technology and Information
Technology and information drive the dynamics between knowledge society and risk society, where the knowledge society thrives on the creation, dissemination, and application of digital innovations to enhance education, economy, and governance. In contrast, the risk society emphasizes the unintended hazards and uncertainties introduced by technological advancements, such as cybersecurity threats, data privacy issues, and environmental impacts. The interplay of these factors highlights the dual role of technology as both a catalyst for progress and a source of new societal challenges.
Managing Uncertainty and Risk
Knowledge society emphasizes managing uncertainty through the advancement of information, expertise, and technological innovation, enabling proactive decision-making processes. Risk society highlights the increased awareness of global and environmental risks resulting from modernization, demanding robust frameworks for risk assessment and mitigation. Effective governance in both societies relies on transparency, adaptive policies, and the integration of scientific knowledge to balance progress with safety.
Social Structures and Power Dynamics
Knowledge society centers on the production and dissemination of information, empowering individuals and institutions through access to education and technology, which reshapes social structures by promoting meritocracy and innovation-driven hierarchies. Risk society highlights how modern societies organize around managing uncertainties and hazards generated by technological and industrial advancements, intensifying power struggles as institutions and elites control risk distribution and regulatory frameworks. Both frameworks reveal evolving power dynamics: knowledge society fosters empowerment through information control, while risk society underscores the concentration of power in entities that govern exposure and responses to systemic risks.
Impacts on Policy and Governance
Knowledge society emphasizes data-driven policy-making that fosters innovation, education, and digital inclusion, shaping governance through transparency and participatory decision-making. Risk society prioritizes managing uncertainties and potential hazards, influencing policies to focus on precaution, regulation, and crisis management. Governance in a risk society demands adaptive frameworks capable of responding to complex technological, environmental, and social threats.
Education and Lifelong Learning Implications
In a knowledge society, education emphasizes the continuous acquisition of skills and advanced expertise, supporting lifelong learning to adapt to rapidly evolving technologies and information landscapes. Conversely, a risk society prioritizes education that fosters critical thinking, risk assessment, and resilience to manage uncertainties such as environmental hazards or technological failures. Lifelong learning strategies must therefore balance innovation-driven skill development with the cultivation of adaptive capacities to mitigate complex societal risks.
Challenges and Future Trajectories
The knowledge society faces challenges related to information overload, digital divides, and the ethical management of data, while the risk society grapples with uncertainties stemming from technological hazards, environmental crises, and global systemic risks. Future trajectories indicate an increasing need for adaptive governance, resilient infrastructures, and inclusive policies that balance innovation with precaution. Integrating interdisciplinary approaches and fostering public awareness will be crucial to navigating complexities inherent in both societal models.
Knowledge society Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com