Social identity shapes how individuals perceive themselves based on group memberships, influencing behaviors and interactions within society. Understanding your social identity can enhance self-awareness and foster better communication across diverse communities. Explore the article to discover how social identity impacts your daily life and relationships.
Table of Comparison
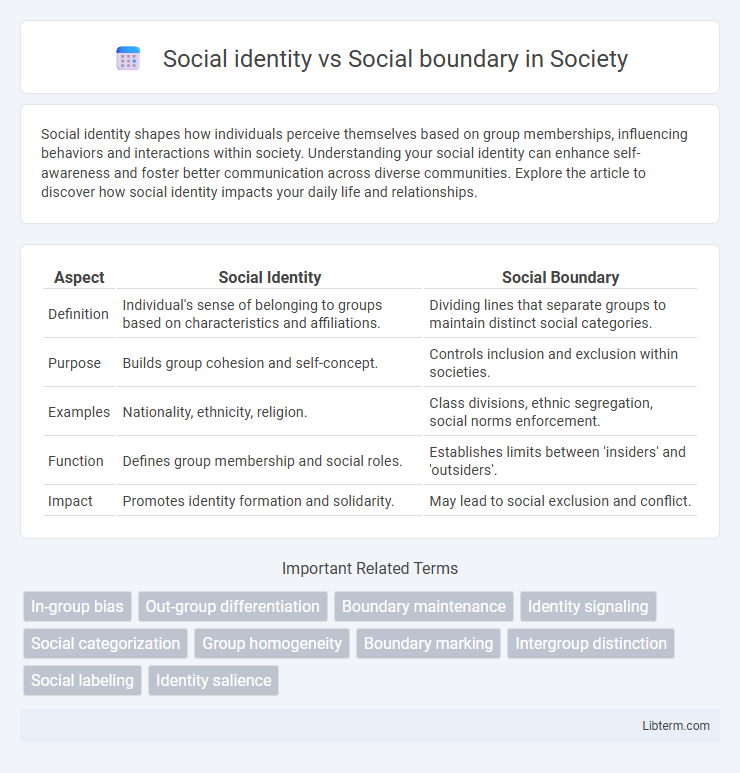
| Aspect | Social Identity | Social Boundary |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Individual's sense of belonging to groups based on characteristics and affiliations. | Dividing lines that separate groups to maintain distinct social categories. |
| Purpose | Builds group cohesion and self-concept. | Controls inclusion and exclusion within societies. |
| Examples | Nationality, ethnicity, religion. | Class divisions, ethnic segregation, social norms enforcement. |
| Function | Defines group membership and social roles. | Establishes limits between 'insiders' and 'outsiders'. |
| Impact | Promotes identity formation and solidarity. | May lead to social exclusion and conflict. |
Understanding Social Identity: Definition and Importance
Social identity refers to an individual's sense of belonging to a particular group based on characteristics such as culture, ethnicity, or social roles, which shapes self-perception and behavior. Understanding social identity is crucial for recognizing how individuals categorize themselves and others, influencing group dynamics, social cohesion, and intergroup relations. Social boundaries emerge from these identifications, delineating 'in-groups' and 'out-groups' that affect inclusion, exclusion, and social interaction patterns.
Defining Social Boundaries: Meaning and Scope
Social boundaries define the invisible lines that separate distinct social groups, establishing norms and roles that govern interaction within and between communities. These boundaries encompass geographic, cultural, linguistic, and economic dimensions, shaping identity and group cohesion. Understanding social boundaries is essential for analyzing how social identity is maintained, reinforced, or challenged in diverse societies.
Key Differences Between Social Identity and Social Boundary
Social identity refers to an individual's sense of belonging to a particular social group based on characteristics such as ethnicity, nationality, or religion, whereas social boundary defines the invisible or explicit lines that separate or distinguish one group from another. Social identity emphasizes shared attributes and group membership, while social boundary highlights the criteria and mechanisms that maintain group distinctiveness and limit interactions across groups. Understanding these key differences helps analyze how social cohesion is formed and how exclusion or inclusion processes operate within societies.
The Formation of Social Identities in Society
Social identity forms through shared characteristics, cultural norms, and group memberships that individuals internalize to define themselves within society. Social boundaries emerge as explicit or implicit limits set between groups to distinguish "us" from "them," reinforcing group cohesion and identity salience. The formation of social identities depends on these boundaries to create recognition, belonging, and differentiation among individuals in complex social structures.
How Social Boundaries Emerge and Are Maintained
Social boundaries emerge through processes of inclusion and exclusion based on shared characteristics such as culture, ethnicity, language, or values, creating distinct social groups. These boundaries are maintained by social norms, ritual practices, and institutional enforcement that reinforce group cohesion and differentiate insiders from outsiders. Mechanisms like stereotyping, group rituals, and symbolic markers help preserve social boundaries by continuously validating group identity and excluding those who do not conform.
The Role of Culture in Shaping Identity and Boundaries
Culture plays a pivotal role in shaping social identity by providing shared symbols, values, and norms that foster group cohesion and distinguish members from others. Social boundaries emerge as cultural practices and beliefs delineate who belongs to a group and who is excluded, reinforcing collective identity through inclusion and exclusion mechanisms. These cultural frameworks influence how individuals perceive themselves and others, creating dynamic interactions between identity formation and boundary maintenance.
Intersectionality: Overlapping Identities and Fluid Boundaries
Social identity theory examines how individuals define themselves based on group memberships, while social boundaries delineate the limits between these groups, often reinforcing inclusion or exclusion. Intersectionality highlights the overlapping and interconnected nature of social identities such as race, gender, class, and sexuality, revealing how fluid boundaries continuously shape experiences of privilege and marginalization. Understanding these fluid boundaries and intersecting identities is critical for analyzing complex social dynamics and fostering inclusive environments.
Social Identity and Group Inclusion/Exclusion
Social identity refers to an individual's sense of belonging to a particular social group, which shapes their self-concept and influences behavior within group dynamics. Group inclusion strengthens social identity by fostering a shared sense of purpose, cultural norms, and mutual support, enhancing cohesion and collective self-esteem. Conversely, social boundaries define limits between groups, often leading to exclusion mechanisms that reinforce in-group loyalty while marginalizing outsiders based on perceived differences.
Breaking Down Social Boundaries: Pathways to Inclusion
Breaking down social boundaries involves dismantling exclusionary practices and stereotypes that maintain group divisions, creating pathways to inclusion by fostering empathy and understanding. Social identity shapes individuals' sense of belonging, but rigid boundaries limit cross-group interaction and reinforce social hierarchies. Promoting diverse social identities within shared spaces encourages inclusion and reduces prejudice, enabling more cohesive and equitable communities.
The Impact of Social Identity and Boundaries on Social Dynamics
Social identity shapes group affiliation by defining shared characteristics and values, while social boundaries establish distinctions that separate groups and influence inclusion or exclusion. These boundaries impact social dynamics by reinforcing in-group cohesion and creating intergroup conflicts or cooperation depending on boundary permeability. Understanding the interplay between social identity and boundaries is crucial for analyzing phenomena like social integration, prejudice, and collective behavior.
Social identity Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com