Expanding your social circle enhances personal growth, emotional support, and networking opportunities that enrich both your personal and professional life. Engaging with diverse groups fosters new perspectives, deeper connections, and meaningful relationships that contribute to overall well-being. Discover effective ways to broaden your social circle and strengthen your connections by reading the rest of the article.
Table of Comparison
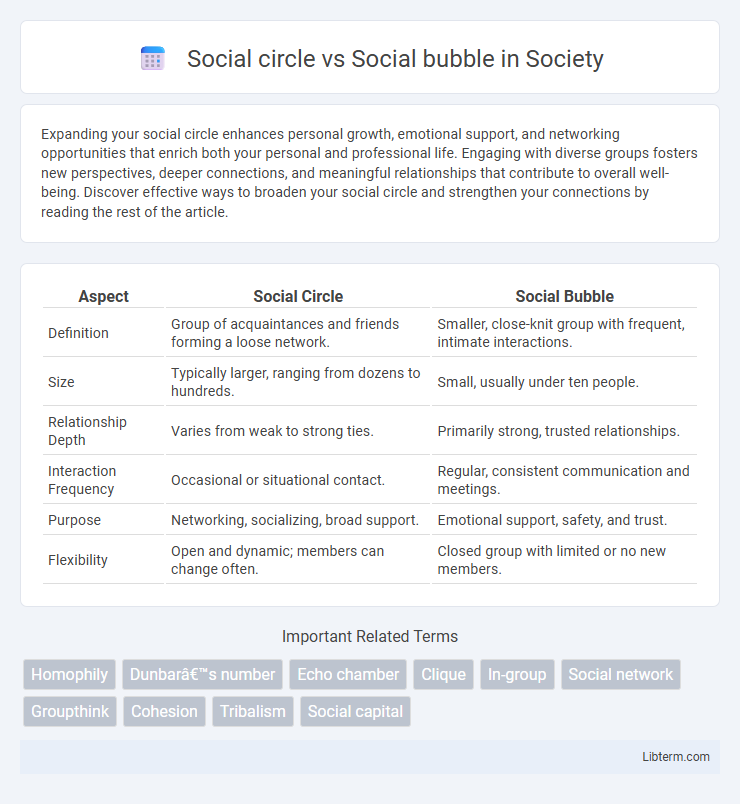
| Aspect | Social Circle | Social Bubble |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Group of acquaintances and friends forming a loose network. | Smaller, close-knit group with frequent, intimate interactions. |
| Size | Typically larger, ranging from dozens to hundreds. | Small, usually under ten people. |
| Relationship Depth | Varies from weak to strong ties. | Primarily strong, trusted relationships. |
| Interaction Frequency | Occasional or situational contact. | Regular, consistent communication and meetings. |
| Purpose | Networking, socializing, broad support. | Emotional support, safety, and trust. |
| Flexibility | Open and dynamic; members can change often. | Closed group with limited or no new members. |
Understanding Social Circles and Social Bubbles
Social circles consist of a broader network of acquaintances, friends, family, and colleagues, offering diverse social interactions and support systems. Social bubbles are smaller, more intimate groups formed to minimize exposure to external contacts, often used during health crises to reduce infection risks. Understanding these distinctions helps manage social needs while maintaining safety and emotional well-being.
Key Differences Between Social Circles and Social Bubbles
Social circles encompass a broad range of relationships, including friends, family, colleagues, and acquaintances, characterized by varying levels of emotional closeness and interaction frequency. Social bubbles are smaller, more exclusive groups formed to limit exposure to external contacts, often for health or safety reasons, emphasizing consistent, close-knit interactions. The key difference lies in the scope and purpose: social circles are natural and expansive networks, while social bubbles are deliberate, controlled groups designed to minimize risk and increase trust.
The Psychology Behind Social Circles
Social circles represent the broader network of acquaintances and friends influencing individual behavior and social identity, while social bubbles are smaller, close-knit groups fostering emotional safety and deeper trust. The psychology behind social circles highlights the importance of belonging, social comparison, and identity formation, where interactions within these groups shape self-perception and emotional well-being. Understanding the distinct roles of social circles and bubbles reveals how human connections drive motivation, conformity, and support systems in daily life.
How Social Bubbles Shape Our Interactions
Social bubbles create a more intimate and controlled network compared to broader social circles, limiting interactions to trusted individuals and reinforcing shared values. This selective engagement enhances emotional security and reduces social anxiety, influencing how people communicate and build relationships. As a result, social bubbles shape behavior by fostering close-knit connections that prioritize quality over quantity in social interactions.
Advantages of Expanding Your Social Circle
Expanding your social circle enhances opportunities for personal and professional growth by exposing you to diverse perspectives and networking possibilities. A larger social circle increases access to resources, support systems, and collaborative ventures, fostering resilience and innovation. Broad social interactions also promote improved communication skills and emotional intelligence, essential for thriving in dynamic social environments.
Benefits and Drawbacks of Social Bubbles
Social bubbles create a close-knit group that enhances trust and emotional support by limiting interactions to a defined set of people, reducing exposure to outside risks such as contagious diseases. However, these bubbles may lead to social isolation, restricted perspectives, and limited networking opportunities compared to broader social circles. Balancing the advantages of intimacy and safety with the drawbacks of potential social monotony is crucial for mental well-being and social development.
Social Circles and Mental Health Impacts
Social circles, comprising close friends, family, and acquaintances, significantly influence mental health by providing emotional support, reducing stress, and fostering a sense of belonging. Research shows that strong social circles can decrease the risk of depression and anxiety, enhancing overall psychological well-being. Maintaining diverse and meaningful social connections is crucial for resilience against mental health challenges.
Navigating Relationships: Circle or Bubble?
Navigating relationships requires understanding the difference between a social circle and a social bubble to maintain meaningful connections while managing social boundaries. A social circle encompasses a broader network of acquaintances and friends, offering diverse interactions and opportunities for social growth. In contrast, a social bubble consists of a smaller, close-knit group focused on trust and emotional safety, promoting deeper, more intimate relationships.
Social Circles, Bubbles, and Building Connections
Social circles are broader networks of acquaintances and friends that provide diverse social interactions, while social bubbles are smaller, more exclusive groups designed for closer, safer connections. Building connections within social circles fosters opportunities for collaboration, support, and community growth, enhancing social capital. Understanding the dynamics of both social circles and bubbles is essential for cultivating meaningful relationships and balancing social exposure.
Choosing the Right Social Dynamics for You
Choosing the right social dynamics involves understanding the difference between a social circle and a social bubble. A social circle consists of diverse connections, including friends, colleagues, and acquaintances, offering broader social engagement and networking opportunities. A social bubble, by contrast, is a smaller, more intimate group of trusted individuals, prioritizing deeper relationships and emotional support within a controlled environment.
Social circle Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com