A social plateau refers to a period in social development or relationships where progress seems to stagnate, and emotional or communicative growth slows down. This phase can impact your interactions and connection with others, causing frustration or a sense of inertia. Explore the full article to understand how to recognize and overcome social plateaus effectively.
Table of Comparison
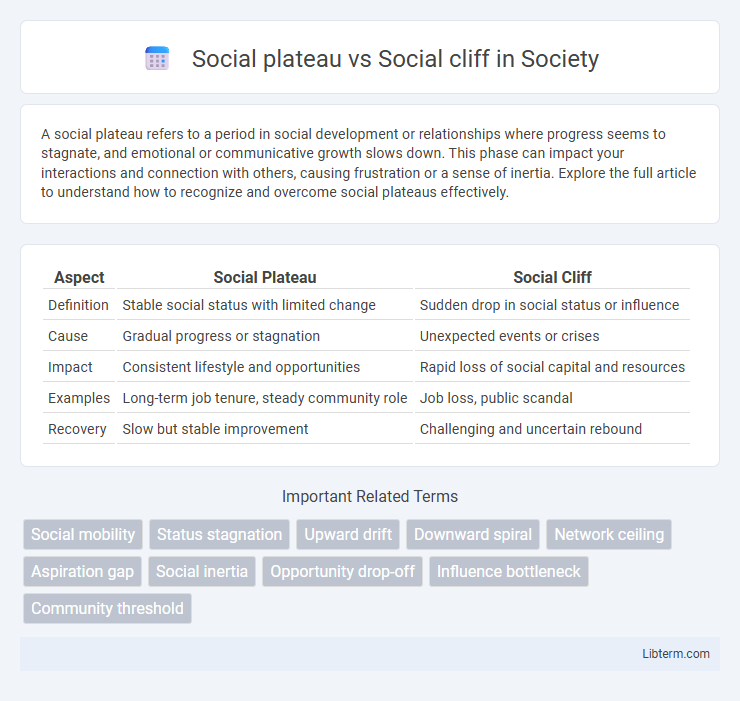
| Aspect | Social Plateau | Social Cliff |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Stable social status with limited change | Sudden drop in social status or influence |
| Cause | Gradual progress or stagnation | Unexpected events or crises |
| Impact | Consistent lifestyle and opportunities | Rapid loss of social capital and resources |
| Examples | Long-term job tenure, steady community role | Job loss, public scandal |
| Recovery | Slow but stable improvement | Challenging and uncertain rebound |
Understanding the Social Plateau and Social Cliff
The social plateau refers to a phase in social development where growth in social skills or relationships stabilizes, resulting in limited progress despite continued effort. In contrast, the social cliff describes a sudden and significant decline in social interaction or support, often triggered by changes such as life transitions or mental health challenges. Recognizing the differences between a social plateau and social cliff is crucial for identifying appropriate interventions to maintain or improve social well-being.
Key Differences Between Social Plateau and Social Cliff
Social plateau refers to a period of stagnation in social progress where growth or improvement slows without significant decline, often seen in personal development or career networking. Social cliff denotes a sudden and steep drop in social status or relationships, causing rapid isolation or loss of influence. Key differences include the gradual stagnation of the social plateau versus the abrupt, severe decline characteristic of the social cliff.
Signs You’re Experiencing a Social Plateau
A social plateau is characterized by stagnant growth in social interactions, evident through repeated conversations, lack of meaningful connections, and diminishing invitations to social events. Signs you're experiencing a social plateau include feeling disconnected despite frequent socializing, a decline in new friendships, and a sense of monotony in your social life. Recognizing these indicators can help initiate strategies to break free from routine social patterns and foster genuine engagement.
Warning Indicators of a Social Cliff
Warning indicators of a social cliff include a sudden and drastic decrease in social interactions, significant withdrawal from previously meaningful relationships, and sharp declines in emotional support networks. These signs often precede social isolation, increased loneliness, and potential mental health challenges such as depression or anxiety. Monitoring changes in communication frequency, social engagement activities, and peer group dynamics is crucial to identify and address the onset of a social cliff.
Causes Behind Social Stagnation and Sudden Drops
Social plateau occurs when individuals or groups experience prolonged periods of minimal social growth due to factors like limited networking opportunities, institutional biases, or stagnant economic environments. Social cliff refers to abrupt declines in social status often triggered by crises such as job loss, public scandals, or systemic discrimination. Both phenomena are deeply influenced by structural inequalities and disruption in social capital, affecting long-term social mobility.
The Psychological Impact of Social Plateaus
Experiencing a social plateau can lead to feelings of stagnation and frustration as individuals perceive a halt in social growth or connectivity, impacting self-esteem and motivation. Unlike the abrupt isolation of a social cliff, social plateaus often cause prolonged psychological stress due to persistent unmet social expectations and reduced social rewards. This gradual decline in social engagement can contribute to anxiety, depression, and a diminished sense of belonging, highlighting the importance of proactive social strategies and mental health support.
Navigating the Risks of a Social Cliff
A social cliff represents a sudden and severe drop in social status or connections, often triggered by events like job loss, relocation, or public scandal, posing significant risks to mental health and community belonging. In contrast, a social plateau indicates a stable but stagnant state with limited social growth, which may feel less alarming but can lead to long-term dissatisfaction. Navigating the risks of a social cliff requires proactive networking, seeking support systems, and maintaining resilience to mitigate isolation and rebuild social capital effectively.
Strategies to Overcome a Social Plateau
Overcoming a social plateau involves diversifying social interactions by engaging in new group activities and expanding networks beyond current circles. Implementing targeted communication skills training enhances interpersonal effectiveness, breaking stagnation in social growth. Regular feedback loops and self-reflection practices enable identification of behavioral patterns, promoting continuous social development.
Preventing and Recovering From a Social Cliff
Preventing a social cliff involves maintaining consistent social interactions and gradually expanding networks to avoid sudden isolation. Recovery from a social cliff requires proactive re-engagement through community involvement, supportive relationships, and mental health resources to rebuild social connections. Prioritizing regular social activities and seeking professional guidance can help sustain social well-being and prevent abrupt declines in social integration.
Long-Term Solutions for Sustainable Social Growth
Social plateau represents a phase of stagnation in social growth, where progress halts despite ongoing efforts, while a social cliff indicates a rapid decline in social well-being or cohesion. Long-term solutions for sustainable social growth focus on systemic reforms including equitable resource distribution, inclusive policymaking, and continuous investment in education and healthcare. Emphasizing resilience-building and community empowerment creates adaptive social structures that prevent both plateaus and cliffs, ensuring enduring societal advancement.
Social plateau Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com