Social reform transforms societies by addressing inequalities and promoting justice through policy changes and community action. It empowers individuals and groups to advocate for better education, healthcare, and civil rights, fostering a more inclusive and equitable environment. Discover how social reform can impact your life and drive positive change by reading the full article.
Table of Comparison
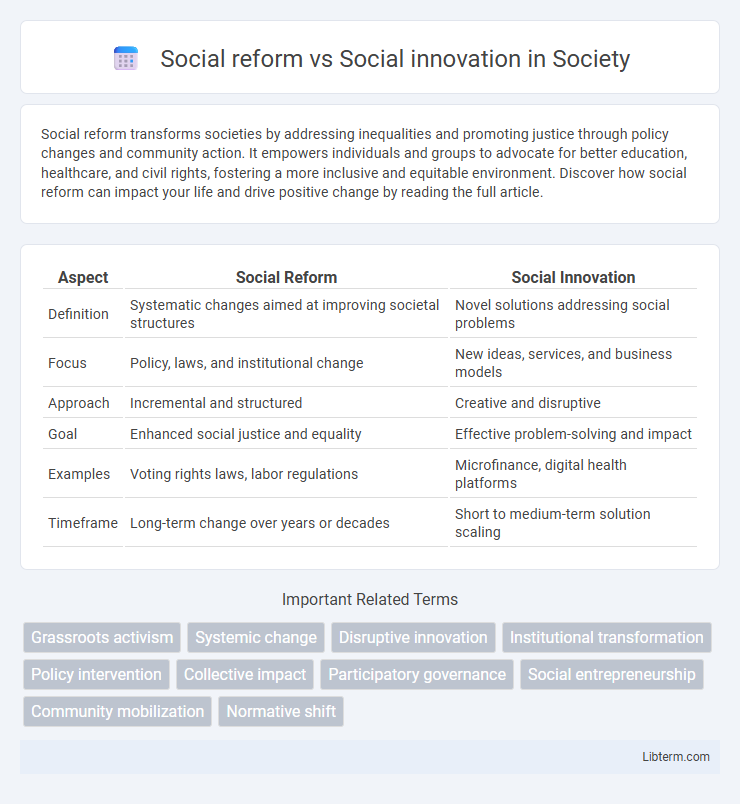
| Aspect | Social Reform | Social Innovation |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Systematic changes aimed at improving societal structures | Novel solutions addressing social problems |
| Focus | Policy, laws, and institutional change | New ideas, services, and business models |
| Approach | Incremental and structured | Creative and disruptive |
| Goal | Enhanced social justice and equality | Effective problem-solving and impact |
| Examples | Voting rights laws, labor regulations | Microfinance, digital health platforms |
| Timeframe | Long-term change over years or decades | Short to medium-term solution scaling |
Defining Social Reform and Social Innovation
Social reform involves systematic efforts to improve societal structures, laws, and policies to address social injustices and promote equity. Social innovation refers to the development and implementation of novel solutions, products, or strategies that effectively meet social needs and create positive community impact. Both concepts aim to improve social conditions but differ in approach: reform modifies existing systems, while innovation introduces new mechanisms or practices.
Historical Context of Social Reform
Social reform movements emerged prominently during the 19th and early 20th centuries, driven by industrialization's impact on labor, urbanization, and social inequalities. Key historical examples include the abolition of slavery, women's suffrage, and labor rights campaigns, which aimed to address systemic injustices through policy changes and legal frameworks. These reforms laid the groundwork for modern social welfare systems and influenced later approaches to social innovation by highlighting the need for structural change.
The Evolution of Social Innovation
The evolution of social innovation reflects a shift from traditional social reform efforts toward more dynamic, technology-driven solutions addressing complex societal challenges. Social innovation emphasizes collaborative systems and adaptive strategies that generate sustainable impact through novel approaches in fields like education, healthcare, and environmental sustainability. This progression demonstrates increased reliance on cross-sector partnerships and digital platforms to scale transformative ideas beyond conventional reform models.
Key Differences Between Reform and Innovation
Social reform involves systematic changes aimed at improving existing social structures and policies to address inequalities and injustices, emphasizing gradual and legislative approaches. Social innovation introduces novel solutions and creative methods to tackle social challenges, often focusing on new practices, technologies, or models that disrupt traditional systems. The key difference lies in social reform's emphasis on modifying established frameworks, while social innovation prioritizes pioneering and experimental approaches to achieve societal progress.
Drivers and Motivations Behind Change
Social reform is driven primarily by the urgent need to address existing societal inequalities and injustices through legislative or policy changes, often motivated by social movements and public advocacy. Social innovation, on the other hand, is motivated by the desire to develop new and effective solutions to complex social problems, leveraging technology, entrepreneurship, and cross-sector collaboration. Both approaches aim to improve social welfare but differ in their methods, with reform focusing on systemic change and innovation emphasizing novel practices and scalable impact.
Impact on Policy and Society
Social reform primarily focuses on changing existing policies and institutions to address social issues through legislative and regulatory measures, resulting in incremental improvements within established frameworks. Social innovation introduces novel solutions and approaches that transform societal challenges by creating new norms, practices, or systems, often influencing policy indirectly through grassroots adoption and empirical evidence. Both approaches shape society and governance; social reform optimizes current legal structures, whereas social innovation drives systemic change by fostering adaptive, community-driven policies.
Case Studies: Successful Social Reforms
Social reform focuses on systemic change through policy and legislation, exemplified by the Civil Rights Movement in the United States, which led to landmark laws like the Civil Rights Act of 1964 that dismantled institutional racial segregation. In contrast, social innovation introduces novel solutions to social problems, as seen in the Grameen Bank's microfinance model improving financial inclusion in Bangladesh. Successful social reforms often result from sustained advocacy and legal frameworks, while social innovations thrive on creative, scalable approaches addressing immediate community needs.
Case Studies: Groundbreaking Social Innovations
Groundbreaking social innovations such as the Grameen Bank's microfinance model and the Aravind Eye Care System demonstrate how social innovation addresses systemic challenges through novel approaches, contrasting with traditional social reforms that often focus on policy changes. The Grameen Bank revolutionized financial inclusion by providing microloans to impoverished populations, enabling economic empowerment without relying solely on government interventions. Aravind Eye Care's innovative efficiency in delivering affordable eye care services showcases how organizational innovation can create scalable, sustainable social impact beyond conventional reform frameworks.
Challenges and Barriers to Implementation
Social reform faces challenges such as entrenched institutional resistance, limited political will, and societal inertia that impede policy changes and systemic improvements. Social innovation encounters barriers like scarce funding, difficulties in scaling pilot projects, and the complexity of integrating novel solutions within existing social structures. Both approaches struggle with measuring impact accurately and overcoming skepticism from stakeholders resistant to change.
Future Directions and Integration of Both Approaches
Future directions in social reform emphasize policy adaptation and systemic change to address inequality, while social innovation focuses on creating scalable solutions through technology and community engagement. Integrating both approaches enables the development of sustainable strategies that combine institutional support with grassroots innovation, enhancing social impact. Collaboration between governments, nonprofits, and startups facilitates alignment of resources and expertise, driving inclusive growth and resilient societies.
Social reform Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com