Underpronation, also known as supination, occurs when your foot rolls outward excessively during walking or running, causing added strain on the outer edges of your feet. This biomechanical imbalance can lead to foot pain, ankle instability, and increased risk of injury. Discover effective tips and solutions to manage underpronation and improve your overall foot health in the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
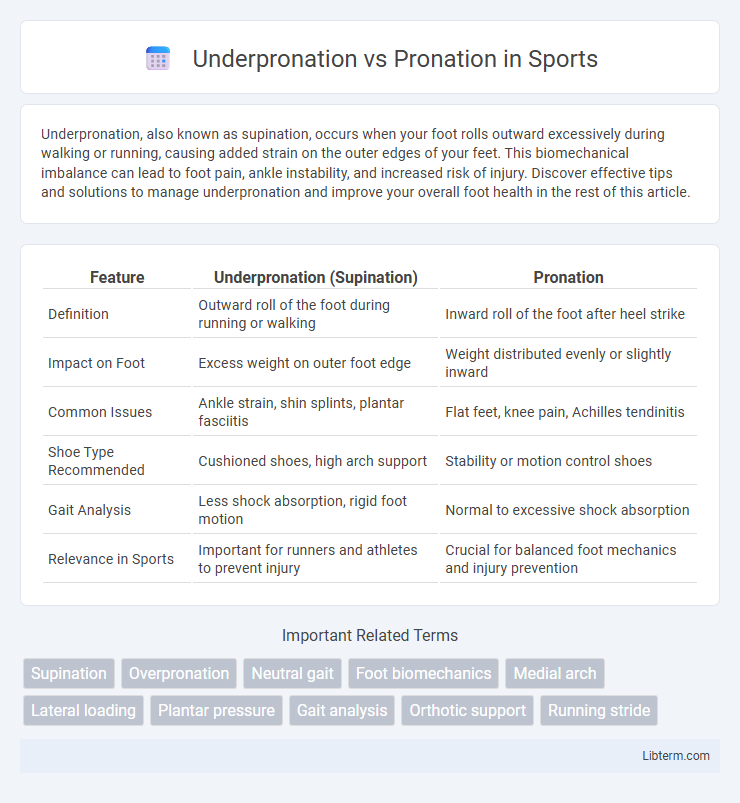
| Feature | Underpronation (Supination) | Pronation |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Outward roll of the foot during running or walking | Inward roll of the foot after heel strike |
| Impact on Foot | Excess weight on outer foot edge | Weight distributed evenly or slightly inward |
| Common Issues | Ankle strain, shin splints, plantar fasciitis | Flat feet, knee pain, Achilles tendinitis |
| Shoe Type Recommended | Cushioned shoes, high arch support | Stability or motion control shoes |
| Gait Analysis | Less shock absorption, rigid foot motion | Normal to excessive shock absorption |
| Relevance in Sports | Important for runners and athletes to prevent injury | Crucial for balanced foot mechanics and injury prevention |
Understanding Foot Pronation Explained
Foot pronation refers to the natural inward roll of the foot during walking or running, aiding in shock absorption and weight distribution. Underpronation, or supination, occurs when the foot rolls outward excessively, reducing the foot's ability to properly absorb impact and often leading to stress on the outer edges of the foot. Understanding pronation patterns is essential for selecting appropriate footwear, preventing injuries, and improving overall gait mechanics.
What is Underpronation (Supination)?
Underpronation, also known as supination, occurs when the foot rolls outward during the gait cycle, placing excessive weight on the outer edges of the feet. This biomechanical pattern can lead to reduced shock absorption and increased risk of injuries such as ankle sprains, plantar fasciitis, and stress fractures. Proper footwear with enhanced cushioning and support for the arch is essential to correct underpronation and improve walking or running efficiency.
Defining Pronation: The Basics
Pronation refers to the natural inward rolling motion of the foot during walking or running, which helps absorb shock and distribute body weight evenly. Underpronation, also known as supination, occurs when the foot rolls outward excessively, reducing the foot's ability to absorb impact efficiently. Understanding the basics of pronation is crucial for selecting proper footwear and preventing injuries linked to abnormal foot mechanics.
Key Differences: Underpronation vs Pronation
Underpronation, also known as supination, occurs when the foot rolls outward during the gait cycle, placing excess pressure on the outer edges of the feet, whereas pronation involves the inward roll of the foot, distributing weight more evenly across the foot. Key differences include the impact on foot mechanics, with underpronation often linked to high arches and reduced shock absorption, while pronation is typically associated with flat feet and increased stress on the inner foot. These contrasting foot movements influence injury risk and shoe selection, making it essential to identify the specific gait pattern for optimal support and comfort.
Common Causes of Underpronation and Pronation
Underpronation, also known as supination, commonly results from high arches that limit foot flexibility and cause the foot to roll outward during gait. Pronation occurs due to flat feet or weakened muscles and ligaments, leading to excessive inward rolling of the foot. Both conditions are influenced by factors such as improper footwear, repetitive stress, and biomechanical imbalances.
Signs and Symptoms to Look For
Underpronation, also known as supination, often presents with signs such as excessive wear on the outer edges of shoes, foot pain, and ankle instability. Pronation is characterized by inward rolling of the foot, leading to flat feet, arch pain, and shoe wear patterns that show more wear on the inner soles. Both conditions can cause knee, hip, or lower back pain due to improper foot alignment and gait mechanics.
Impact on Running and Walking Gait
Underpronation, characterized by insufficient inward foot roll during foot strike, results in increased pressure on the outer edge of the foot, leading to higher risk of ankle sprains and inefficient shock absorption during running and walking gait. Pronation involves a natural inward roll of the foot, aiding in shock absorption and weight distribution, but excessive pronation can cause overuse injuries such as plantar fasciitis and shin splints due to uneven stress on muscles and joints. Proper footwear and gait analysis are crucial in addressing these biomechanical variations to optimize running performance and reduce injury risk.
Associated Injuries and Risks
Underpronation, characterized by insufficient inward foot roll, commonly leads to ankle sprains, plantar fasciitis, and stress fractures due to reduced shock absorption. Pronation, the excessive inward roll, increases risks of knee pain, shin splints, and Achilles tendonitis by causing improper alignment and added strain on muscles and joints. Understanding these biomechanical differences is crucial for preventing injury and selecting appropriate footwear or orthotics.
Choosing the Right Footwear for Your Pronation Type
Choosing the right footwear for underpronation or pronation is essential to enhance comfort and prevent injuries. For underpronators, shoes with extra cushioning and flexibility support the foot's natural shock absorption, while overpronators benefit from motion control shoes that provide stability and prevent excessive inward foot roll. Understanding your pronation type through gait analysis ensures optimal shoe selection, improving overall foot health and performance.
Tips for Prevention and Proper Foot Care
Underpronation and pronation impact foot mechanics, requiring targeted prevention strategies to avoid injuries. Using supportive footwear with adequate cushioning and arch support helps maintain proper alignment and reduces strain on the feet. Regular foot exercises, such as toe stretches and calf raises, alongside orthotic inserts tailored to your pronation type, promote optimal foot health and prevent overuse injuries.
Underpronation Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com